In today’s rapidly evolving world, bridging the gap between non-medical professionals and essential medical knowledge has become increasingly important. With the growing availability of resources such as online courses, understanding concepts in fields like cardiology can empower students, even those without a medical background, to make informed decisions about personal and public health. This article examines how K12 education can integrate a cross-disciplinary medicine curriculum to foster health literacy, scientific thinking, and a well-rounded approach to lifelong learning.
The Need for Health Literacy in K12 Education
Health literacy—the ability to access, understand, and apply health-related information—is a vital skill for navigating modern life. For example, understanding basic concepts like the causes and prevention of heart disease (cardiology) can significantly impact long-term well-being. Unfortunately, traditional educational systems often overlook this area, leaving students ill-equipped to deal with challenges related to personal health and public healthcare systems.
Introducing medical knowledge into K12 education is not about turning students into doctors. Instead, it’s about equipping them with practical knowledge to make better decisions. For example, a course module on cardiology might explain how lifestyle choices influence heart health, covering topics such as diet, exercise, and early warning signs of heart disease.
Designing a Cross-disciplinary Medicine Curriculum
Developing an effective curriculum requires careful planning to ensure that medical knowledge is accessible and engaging for young learners. Here are several key elements to consider:
- Age-appropriate Content: Tailor topics to match the cognitive and emotional maturity of different grade levels. For younger students, focus on basic anatomy and healthy habits; for older students, delve into specialized fields like cardiology or nutrition.
- Interactive Learning Tools: Utilize online courses with multimedia features (videos, quizzes, and simulations) to enhance engagement.
- Real-world Applications: Include case studies and practical exercises that relate medical concepts to daily life. For instance, a cardiology lesson might include monitoring heart rates during physical activity.
- Cross-disciplinary Integration: Combine medical topics with other subjects, such as biology, physical education, and even mathematics, to create a more holistic learning experience.
By incorporating these elements, educators can create a curriculum that not only teaches medical knowledge but also encourages critical thinking and problem-solving.
Leveraging Online Resources for Non-medical Professionals
Online courses are a valuable tool for introducing medical knowledge to K12 students. Platforms like Khan Academy, Coursera, and specialized health education websites offer free or affordable resources tailored to non-medical audiences. These resources often include interactive modules, making complex topics like cardiology more accessible.
For example, an online cardiology course might start with the basics of heart anatomy before addressing common conditions such as arrhythmias, hypertension, and preventive measures. This approach ensures that students gain foundational knowledge without feeling overwhelmed.
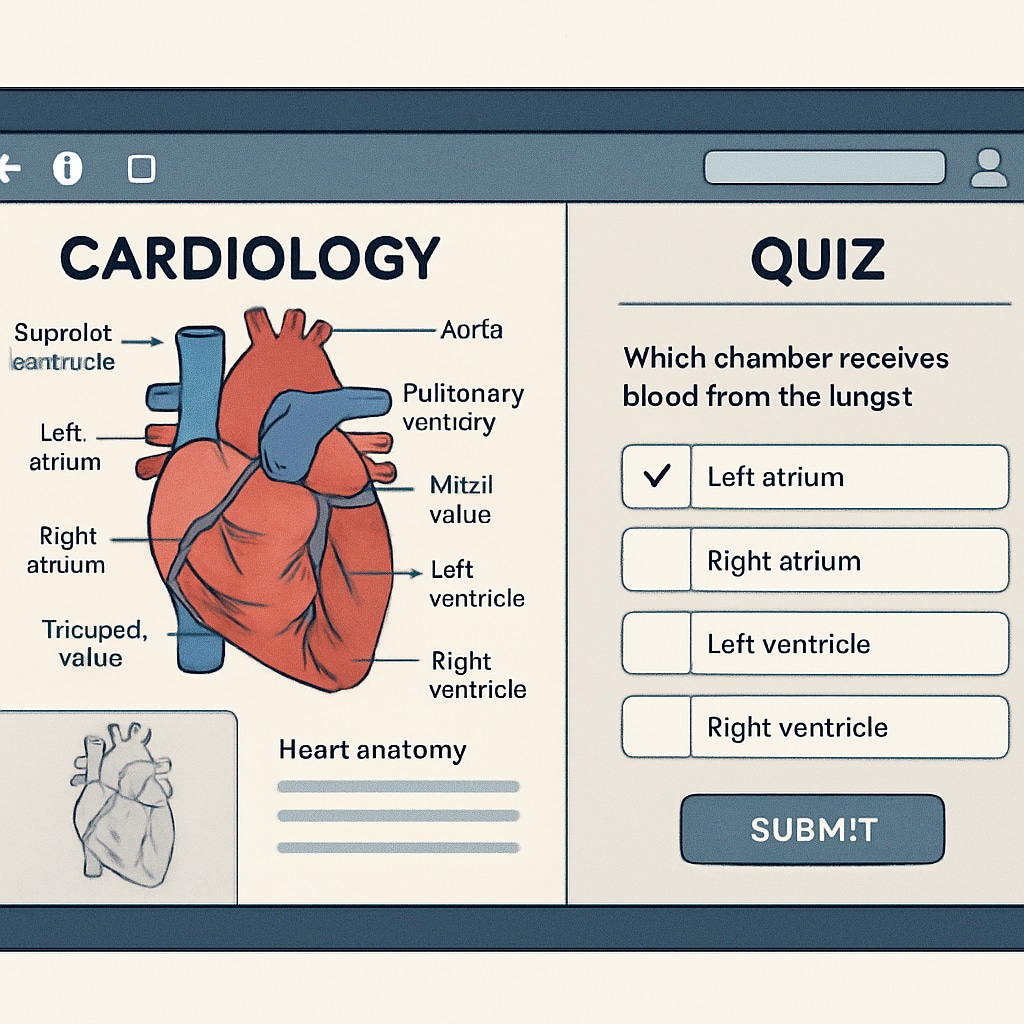
Benefits of Cross-disciplinary Medicine in K12 Education
Integrating cross-disciplinary medicine into K12 education offers numerous benefits:
- Improved Health Literacy: Students develop the ability to understand and apply medical knowledge in real-life situations.
- Enhanced Scientific Thinking: Exploring medical topics fosters curiosity and analytical skills, preparing students for careers in STEM fields.
- Empowered Decision-making: Knowledge about topics like cardiology enables students to make informed choices about their health and lifestyle.
- Community Impact: Health-literate individuals contribute to a more informed and resilient society, capable of addressing public health challenges.
Ultimately, the goal is to equip students with practical skills that enhance their personal growth and societal contributions.
Final Thoughts: Preparing for a Health-literate Future
As health challenges become more complex, the need for a well-rounded education that includes medical knowledge is undeniable. By introducing a cross-disciplinary medicine curriculum in K12 education, schools can empower students to take charge of their health, understand scientific principles, and contribute positively to society. Whether through interactive online courses or classroom activities focused on cardiology and other medical fields, this innovative approach has the potential to shape a healthier, more informed future generation.
Learn more: Explore health literacy resources on Health Literacy on Wikipedia and Health Literacy on Britannica.


