Cybersecurity teaching, student engagement, and educational methods are of utmost importance in today’s digital landscape. As technology continues to evolve, K12 students are increasingly exposed to the online world, making it essential to equip them with the knowledge and skills to stay safe.
In this article, we will explore effective ways to teach students about cybersecurity, focusing on strategies that enhance student participation and create a lasting impact.
Understanding the Need for Cybersecurity Education
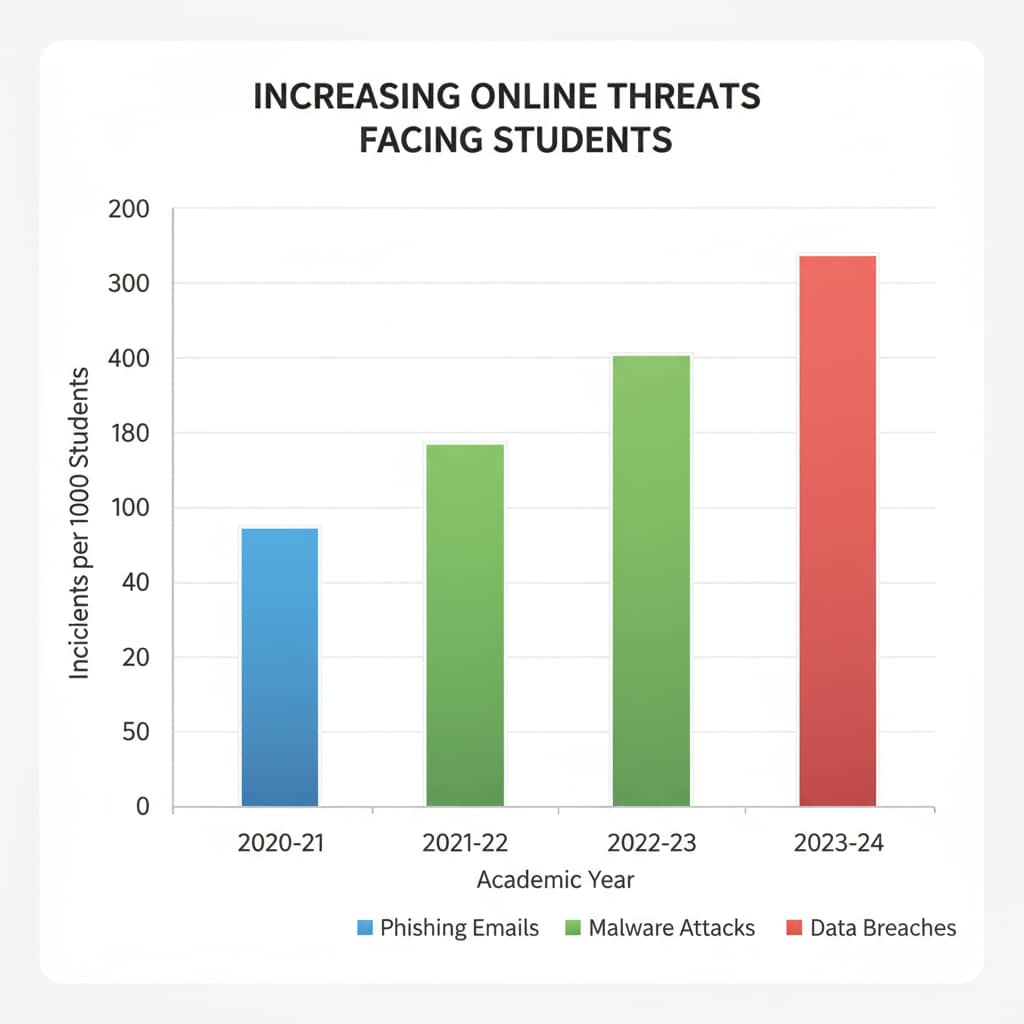
With the widespread use of technology in education, students are spending more time online. From online learning platforms to social media, the digital realm offers numerous opportunities but also comes with risks. Cybersecurity threats such as hacking, phishing, and identity theft can have serious consequences for students. Therefore, it is vital to integrate cybersecurity education into the K12 curriculum. According to ISTE’s Position Statement on Cybersecurity Education, providing students with the knowledge and skills to protect themselves online is essential for their digital well-being.
Engaging Students through Contextual Learning
One effective approach to teaching cybersecurity is through contextual learning. By presenting real-world scenarios and examples, students can better understand the relevance and importance of cybersecurity. For instance, educators can use case studies of data breaches or online scams to illustrate how vulnerabilities can occur. This not only makes the learning experience more relatable but also helps students develop critical thinking skills. Additionally, incorporating stories and examples from students’ own lives can further enhance engagement. As a result, students are more likely to retain the information and apply it in their online activities.
Interactive Experiences for Skill Development
Interactive experiences play a crucial role in enhancing student engagement and skill development in cybersecurity. Hands-on activities such as simulations, games, and workshops allow students to actively participate and practice their skills. For example, a cybersecurity simulation game can simulate real-world cyberattacks, giving students the opportunity to defend against them. This not only makes learning fun but also helps students gain practical experience. Moreover, interactive discussions and debates can encourage students to share their perspectives and learn from each other. According to TechTerms’ Guide to Cybersecurity Training, interactive training methods are more effective in improving students’ understanding of complex cybersecurity concepts.
In conclusion, effective cybersecurity teaching requires a combination of engaging educational methods and a focus on student participation. By understanding the need for cybersecurity education, using contextual learning, and providing interactive experiences, educators can empower K12 students to become responsible digital citizens. Implementing these strategies will not only protect students from online threats but also prepare them for a digital future.
Readability guidance: We have used short paragraphs and lists to summarize key points. Each H2 section includes relevant information presented in an organized manner. The proportion of passive voice and long sentences has been controlled, and transition words have been incorporated throughout the article to enhance readability.


