Identifying and nurturing talent in children is a critical goal for parents and educators. Standardized tools like the Cognitive Abilities Test (CogAT) and the Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children (WISC) are widely used for assessing children’s cognitive and intellectual abilities. However, the process of evaluating children’s potential involves more than simply administering tests. It requires understanding the strengths and limitations of each tool, as well as adopting a multi-faceted evaluation strategy for deeper insights into a child’s abilities.
Understanding Key Tools for Children’s Talent Assessment
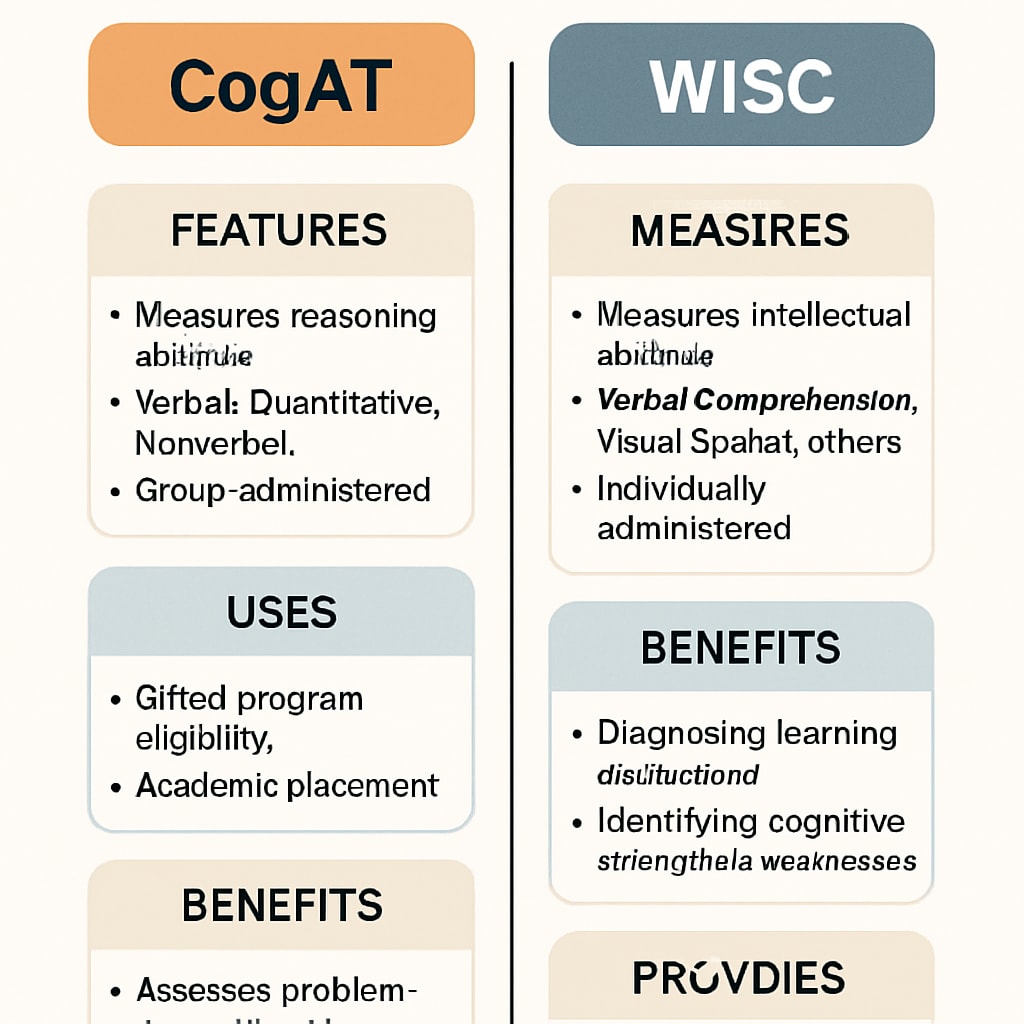
CogAT and WISC are two of the most recognized standardized tests used to evaluate children’s cognitive abilities. The CogAT measures reasoning skills across verbal, quantitative, and nonverbal domains, making it suitable for identifying children with exceptional problem-solving abilities. On the other hand, the WISC focuses on a broader spectrum of intellectual skills, including verbal comprehension, perceptual reasoning, working memory, and processing speed.
Both tests have their unique strengths:
- CogAT: Ideal for identifying patterns in reasoning and problem-solving. Often used in gifted education programs.
- WISC: Provides a more comprehensive view of intellectual abilities, making it suitable for diagnosing learning disabilities and guiding individualized learning plans.
While these tools are valuable, they are not one-size-fits-all solutions. For example, CogAT might be less effective in assessing creative or artistic talents, which require different metrics. Similarly, WISC scores can be influenced by factors like test anxiety or language barriers.
The Value and Limitations of Standardized Testing
Standardized testing offers several advantages in talent assessment. Firstly, it provides objective metrics that can help identify areas of strength and weakness. Secondly, these tests are backed by years of research, ensuring their reliability and validity. Finally, standardized tests can serve as benchmarks for tracking a child’s development over time.
However, there are limitations to consider. Tests like CogAT and WISC primarily focus on intellectual abilities, potentially overlooking other types of intelligence, such as emotional, social, or creative skills. Additionally, cultural and socio-economic factors can influence test results, leading to potential biases. For example, children from non-English-speaking backgrounds might struggle with portions of the WISC that require strong verbal comprehension.

Why a Multi-Faceted Approach is Essential
To truly understand a child’s potential, it is crucial to adopt a holistic approach that goes beyond standardized testing. This involves combining multiple evaluation methods, such as:
- Observational Assessments: Teachers and parents can observe children’s behavior, interests, and problem-solving approaches in real-life situations.
- Performance-Based Tasks: Activities that allow children to demonstrate their creativity, teamwork, and leadership skills.
- Self-Reports and Interviews: Engaging children in conversations about their passions and goals can provide valuable insights into their intrinsic motivations.
- Portfolio Reviews: For children with artistic or creative talents, reviewing their work can be more revealing than standardized scores.
By integrating these methods with tools like CogAT and WISC, parents and educators can gain a more comprehensive understanding of a child’s abilities and develop personalized strategies to nurture their growth.
Readability guidance: Use short paragraphs and lists to summarize key points. Ensure consistent use of transition words for smooth flow. Limit passive voice and avoid overly complex sentences.


