In today’s rapidly evolving world, design engineering has emerged as one of the most vital fields, bridging creativity and technical expertise to solve complex problems. Aspiring professionals often ponder the best pathways to success, including degree options and career development strategies. At the heart of these choices lies K12 education, which plays a pivotal role in shaping the minds of future engineers. This article delves into how K12 education can serve as a foundation for careers in design engineering, examines the challenges within the current system, and proposes reforms to foster STEM integration, cultivate design thinking, and establish diverse evaluation frameworks.
Why K12 Education Matters for Design Engineering Careers
K12 education is the first touchpoint for students to explore their interests and abilities. For future design engineers, this stage sets the groundwork for critical thinking, problem-solving, and creativity. However, many school systems still fall short in equipping students with the necessary skills to thrive in engineering disciplines. Limited focus on STEM (science, technology, engineering, and mathematics), outdated curricula, and insufficient emphasis on design thinking hinder students from realizing their potential.
To address these gaps, schools must prioritize hands-on learning experiences. For example, introducing project-based learning modules can help students understand the interplay between science and creativity. Moreover, exposure to design engineering concepts early on encourages students to pursue specialized degrees in fields such as mechanical engineering, civil design, or industrial design.
Exploring Degree Options and Career Pathways
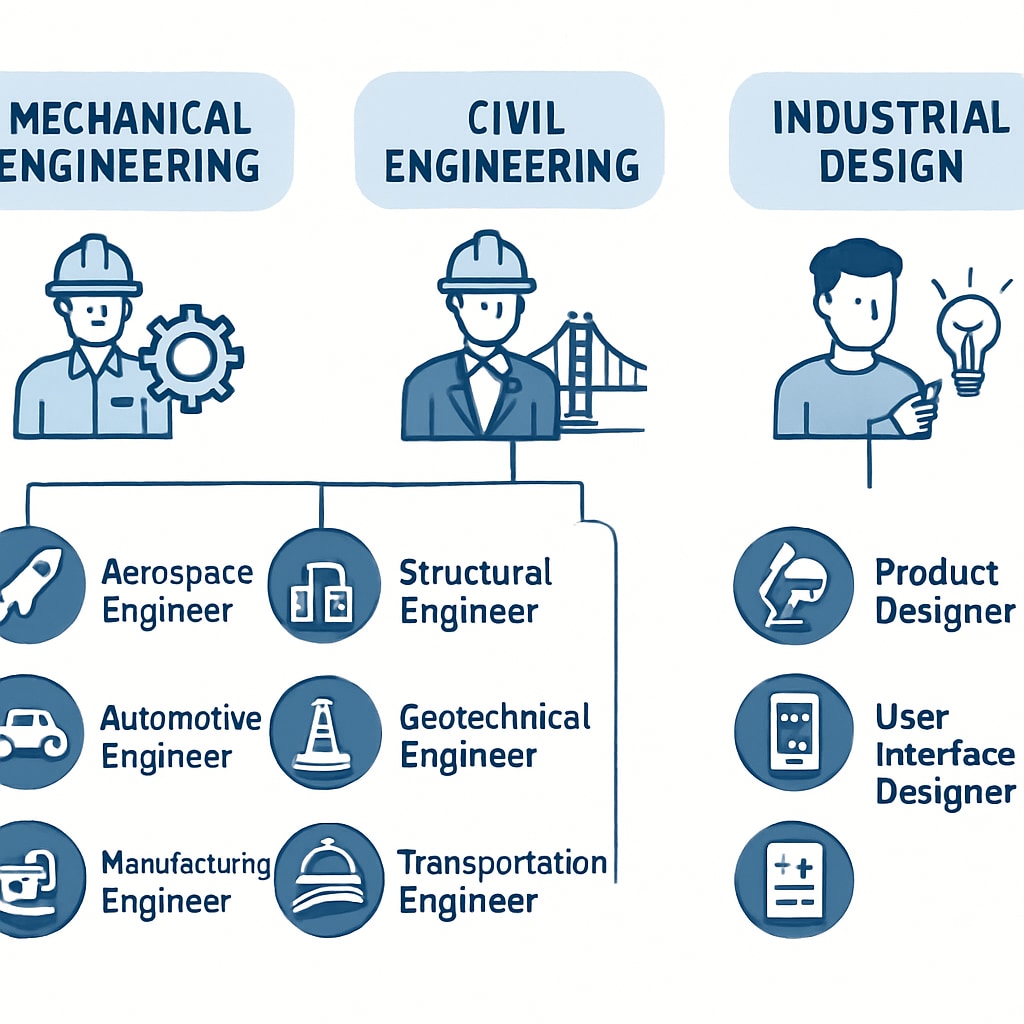
When transitioning from K12 education to higher studies, students encounter various degree pathways in design engineering. Common options include bachelor’s degrees in mechanical engineering, industrial design, civil engineering, or architectural engineering. Each path offers distinct career opportunities, ranging from product design to infrastructure development.
Choosing the right degree often depends on personal interests and career goals. For instance:
- Mechanical Engineering: Ideal for students passionate about machinery and systems design.
- Industrial Design: Focuses on creating user-friendly products that blend aesthetics and functionality.
- Civil Engineering: Perfect for those interested in large-scale infrastructure projects like bridges and buildings.
Furthermore, postgraduate degrees such as a Master’s in Design Engineering can enhance specialization and open doors to leadership roles in research, innovation, and project management.
Reforming K12 Education to Foster Design Thinking
To truly prepare students for careers in design engineering, K12 education must evolve. Integrating STEM education with design thinking principles can transform classrooms into hubs of innovation. Design thinking emphasizes empathy, creativity, and iterative problem-solving, which are essential for engineering success.
Key reforms include:
- Enhanced STEM Curriculum: Combine theoretical knowledge with practical applications, such as robotics, coding, and environmental engineering projects.
- Focus on Collaboration: Encourage team-based activities to teach communication and leadership skills.
- Diverse Evaluation Methods: Move beyond standardized tests to assess creativity, critical thinking, and project outcomes.
By adopting these reforms, schools can empower students to develop the mindset and skills necessary to excel in design engineering and related professions.
For further insights into STEM education reform, visit STEM education on Wikipedia or explore design thinking on Britannica.
Conclusion: Building a Strong Foundation
The journey to becoming a design engineer begins long before college or professional training—it starts with the foundational experiences offered in K12 education. By addressing gaps in STEM integration, nurturing design thinking, and providing diverse learning opportunities, educators can better prepare students for specialized degrees and rewarding careers. Whether aiming for mechanical engineering, industrial design, or civil projects, students will benefit from an educational framework that encourages creativity, collaboration, and innovation.
As the demand for skilled design engineers increases, the importance of cultivating talent from an early age cannot be overstated. Parents, educators, and policymakers must collaborate to ensure K12 education equips future engineers with the tools they need to succeed in a dynamic and challenging field.


