Choosing the right academic path in design engineering is a pivotal decision that influences not only educational experiences but also long-term career outcomes. Whether to pursue a Master of Engineering (MEng) or follow a Bachelor of Science (BSc) combined with a Master of Science (MSc) route is a question many students and parents face during high school planning. This article explores the advantages and challenges of each option, offering insights into how these choices align with professional goals in the field of design engineering, master’s degrees, and career development.
Understanding the Structure of MEng and BSc+MSc Programs
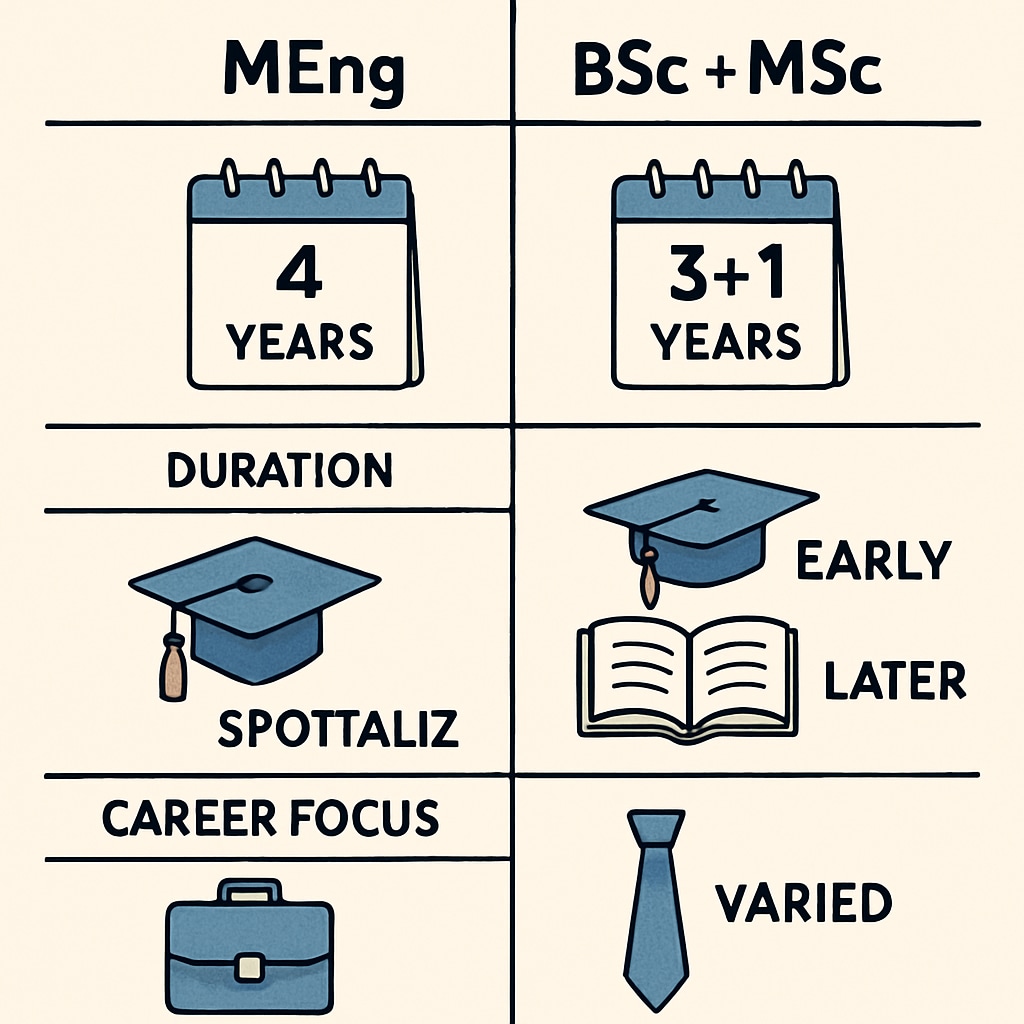
MEng programs are typically integrated courses that combine undergraduate and postgraduate study into a single streamlined curriculum over four to five years. They are designed to provide a deep immersion into engineering principles while maintaining a practical, industry-focused approach. On the other hand, the BSc+MSc pathway involves completing a standard undergraduate degree (typically three years) followed by a separate master’s program (one or two additional years).
The choice between these two paths often depends on individual priorities. MEng programs are ideal for students seeking a fast-tracked, intensive route to advanced qualifications. However, the BSc+MSc combination offers greater flexibility, allowing students to specialize further in their chosen field during the master’s stage.
Career Prospects: MEng vs BSc+MSc
When it comes to career development, the choice of degree can significantly impact job opportunities. According to industry trends, many employers value the comprehensive training provided by MEng programs, especially in roles requiring immediate application of advanced engineering techniques. This is particularly true for design engineering positions that demand interdisciplinary knowledge and leadership capabilities.
However, the BSc+MSc route may appeal to students aiming for niche specializations or academic research roles. The ability to tailor MSc coursework to specific interests—such as sustainable design, biomedical engineering, or robotics—can enhance employability in highly specialized sectors.
Key factors to consider include:
- Industry Expectations: Certain companies may prefer candidates with MEng qualifications due to the program’s integrated nature.
- Specialization Opportunities: BSc+MSc allows greater flexibility in choosing specialized fields during postgraduate study.
- Time and Cost: MEng programs might require fewer years overall, but BSc+MSc could offer more diverse experiences and networking opportunities.

How to Decide: Key Considerations for High School Students
For high school students and their families, several factors should be evaluated before deciding on a degree path:
- Academic Strengths: Students with strong mathematical and technical skills may thrive in MEng programs, while those seeking broader foundational knowledge could benefit from a BSc.
- Career Goals: Consider whether immediate industry placement or further academic research aligns better with long-term aspirations.
- Financial Planning: Compare tuition costs, scholarships, and potential return on investment for each program.
- Program Reputation: Research the specific universities offering MEng or BSc+MSc degrees and their connections to industry leaders and internship opportunities.
Ultimately, both paths can lead to rewarding careers in design engineering. The key is to align educational choices with personal interests and professional objectives.
Readability guidance: Short paragraphs, bullet points, and images enhance clarity. Overuse of complex sentences is avoided, and transitions like “however” and “as a result” are used throughout the text.


