Choosing the right academic pathway in design engineering can significantly impact your career trajectory. With options ranging from bachelor’s degrees to master’s programs such as MEng (Master of Engineering) and MSc (Master of Science), understanding the differences is crucial for aligning educational investments with long-term professional goals. This article breaks down the key distinctions between these degrees, highlighting how they influence employment prospects in the competitive field of design engineering.
Understanding Design Engineering Degrees: Bachelor’s vs Master’s
In design engineering, undergraduate and postgraduate degrees serve distinct purposes. A bachelor’s degree typically provides foundational knowledge and technical skills, covering areas like product development, CAD (computer-aided design), and materials science. On the other hand, master’s programs delve deeper into specialized topics, offering advanced expertise in areas such as systems engineering, sustainability, and innovation management.
For students aiming to enter the workforce quickly, a bachelor’s degree is often sufficient to secure entry-level positions. However, pursuing a master’s degree can open doors to higher-level roles, such as design manager or systems engineer, as well as opportunities in research and academia. Therefore, the choice between bachelor’s and master’s degrees depends largely on career aspirations and industry requirements.
MEng vs MSc: Which Master’s Degree is Right for You?
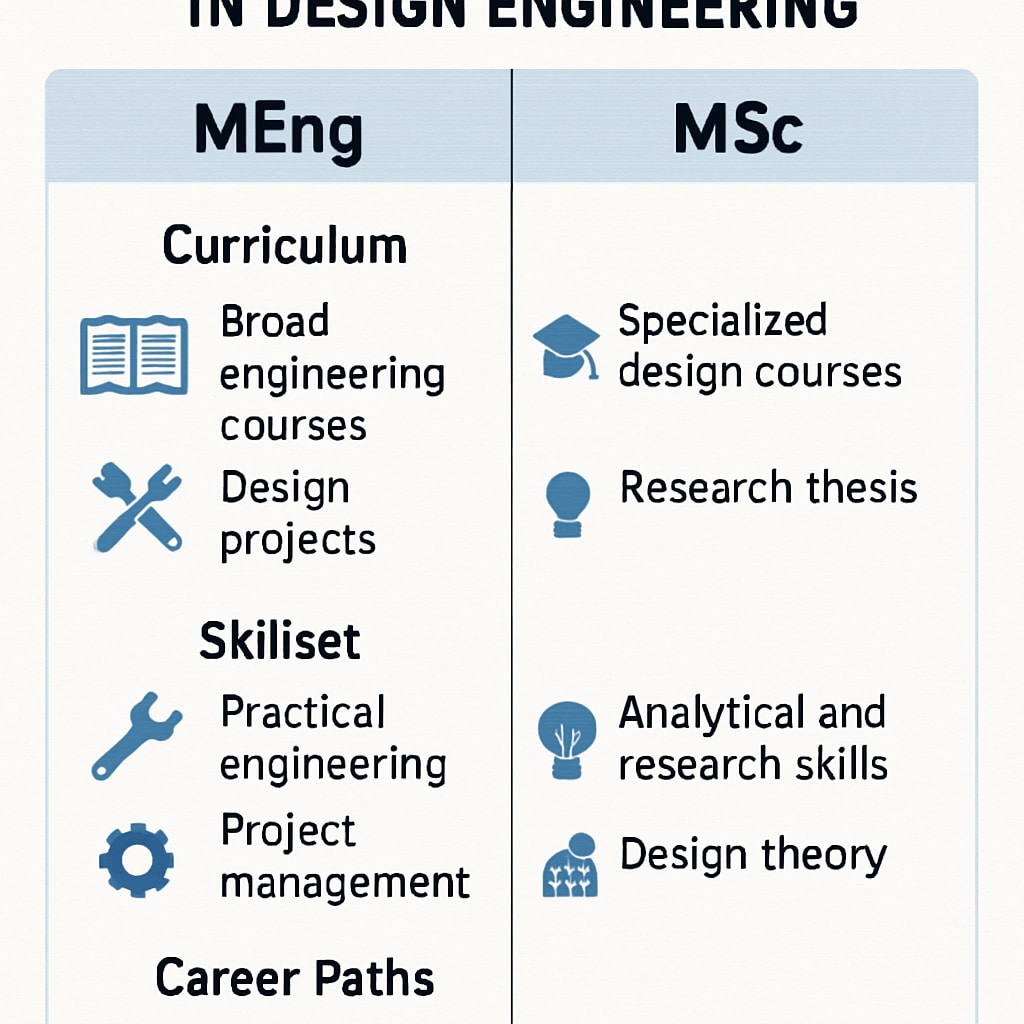
When considering postgraduate studies in design engineering, students often face the decision between an MEng (Master of Engineering) and an MSc (Master of Science). While both degrees provide advanced education, they differ in focus and application:
- MEng: This degree is typically more practical and industry-oriented, emphasizing hands-on engineering skills. It prepares students for roles in design, manufacturing, and implementation.
- MSc: This program is often research-focused and theoretical, ideal for students interested in innovation, academic research, or niche industries like aerospace engineering.
For example, an aspiring product designer may benefit more from an MEng, while someone looking to innovate in sustainable design might prefer an MSc. Understanding these distinctions is vital for selecting a program that aligns with your career objectives.
How Design Engineering Degrees Impact Employment Prospects
The type of degree you pursue in design engineering can influence your employability and earning potential. According to industry data, bachelor’s degree holders often find positions in technical roles, such as CAD technicians or junior engineers, with salaries ranging from $50,000 to $70,000 annually. Master’s degree holders, particularly those with MEng or MSc qualifications, are more likely to secure senior roles, with salaries starting at $80,000 and often exceeding $100,000.
Moreover, certain sectors, such as automotive or renewable energy design, actively seek candidates with advanced degrees, recognizing their specialized knowledge. As a result, pursuing a master’s program can be a strategic move for those aiming to enter competitive industries or achieve leadership positions.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Design Engineering Degree
To make an informed decision about your academic pathway, consider the following factors:
- Career Goals: Are you aiming for technical roles or leadership positions?
- Industry Demand: Research the qualifications preferred in your target sector.
- Cost and ROI: Assess tuition fees and potential earning outcomes.
- Program Focus: Choose between practical (MEng) and theoretical (MSc) approaches.
For example, if your goal is to work in cutting-edge technology fields like AI-driven design or robotics, an MSc may offer the depth required. Conversely, if you prioritize hands-on engineering in industries like construction or manufacturing, an MEng might be better suited.
Conclusion: Investing in Your Future
Choosing the right design engineering degree is more than an academic decision—it’s an investment in your future career. Both bachelor’s and master’s programs offer valuable opportunities, but understanding the distinctions between MEng and MSc degrees is essential for aligning your education with professional goals. By carefully evaluating your career aspirations, industry demands, and program focus, you can make a choice that positions you for long-term success in the dynamic field of design engineering.
For more detailed information about design engineering degrees, visit Engineering Design on Wikipedia or Engineering Overview on Britannica.
Readability guidance: This article uses concise paragraphs, avoids excessive jargon, and maintains an engaging tone. Key points are summarized in lists and charts where applicable, ensuring clarity and accessibility for readers.


