In the realm of educational management, ethical dilemmas and decision-making are integral parts of an administrator’s daily routine. Educational administrators are frequently confronted with complex situations that require careful navigation to balance the interests of multiple stakeholders. Let’s delve into how they can effectively handle these challenges.

The Landscape of Ethical Dilemmas in Educational Management
Ethical dilemmas in educational management can take various forms. For example, there may be conflicts between the need to maintain high academic standards and the desire to support students with diverse learning abilities. According to Wikipedia’s page on Educational Administration, administrators might also face situations where they have to decide between limited resources and the various educational programs that require funding. These dilemmas often put administrators at a crossroads, forcing them to make tough decisions.
Systematic Thinking as a Tool for Decision-Making
Systematic thinking is crucial when dealing with ethical dilemmas in educational management. Administrators need to consider all aspects of a situation, including the long-term and short-term impacts. They should analyze how a decision will affect students, teachers, parents, and the wider educational community. By taking a holistic view, as described on Britannica’s educational administration page, administrators can make more informed decisions. For instance, when deciding on a new curriculum, they need to think about how it will align with educational goals, teacher training requirements, and student interests.
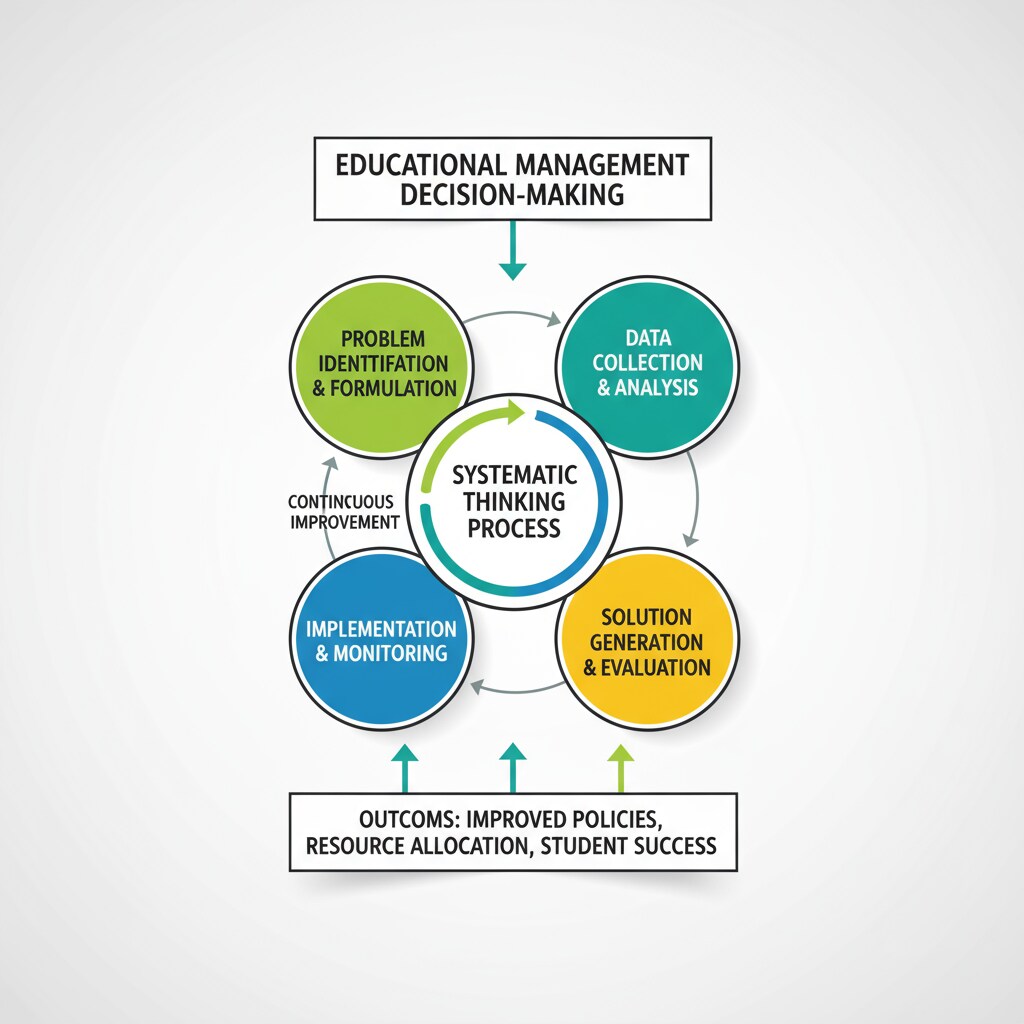
In addition to systematic thinking, values play a significant role. Administrators should be guided by principles such as fairness, equality, and the well-being of students. When faced with a dilemma, they can refer back to these values to make a morally sound decision. For example, if there is a choice between giving preferential treatment to a certain group of students or ensuring equal opportunities for all, the value of equality should prevail.
Readability guidance: As seen above, we break down complex ideas into short paragraphs. Each H2 section has a clear focus, and we use examples and external references to enhance understanding. We also incorporate transition words like ‘for example’ and ‘in addition’ to make the flow of the article smoother.


