In today’s rapidly evolving automotive industry, integrating electrical skills and apprenticeship experiences during K12 education offers immense value. As vehicles increasingly rely on advanced electrical systems, early exposure to electrical concepts enables students to cultivate critical skills for future careers. This approach not only enhances technical competence but also builds a bridge between schools and the automotive industry, preparing a robust talent pipeline for tomorrow’s workforce.
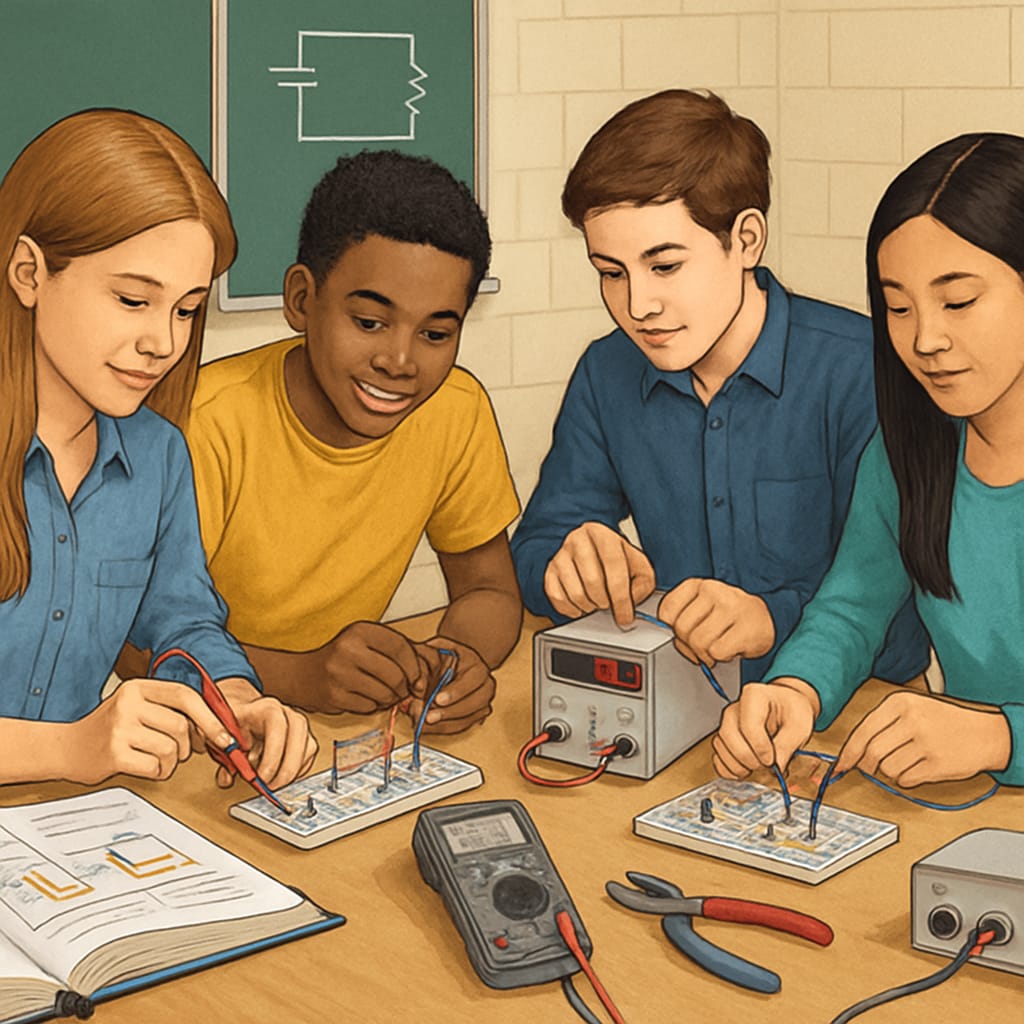

Why Electrical Skills Matter in the Automotive Industry
The automotive industry is transforming, with electric vehicles (EVs) and hybrid models becoming mainstream. This shift necessitates high-level expertise in electrical systems, including wiring, sensors, and battery technologies. By introducing electrical skills in K12, students gain foundational knowledge that aligns with the needs of the automotive sector. For example, hands-on learning experiences such as working with circuits or programming small robots can ignite interest in automotive careers.
Additionally, early exposure helps students understand the interdisciplinary nature of automotive engineering, where electrical systems play a central role alongside mechanics and software. According to Wikipedia’s overview of electric vehicles, the demand for skilled professionals in EV technology continues to rise, highlighting the importance of investing in relevant education.
The Role of Apprenticeship in Career Development
Apprenticeship programs are an effective way to bridge theoretical learning with practical application. In K12 settings, apprenticeships can include partnerships with local automotive companies, where students shadow technicians or participate in real-world projects. This hands-on experience not only reinforces classroom learning but also cultivates problem-solving skills, teamwork, and adaptability—qualities essential for thriving in the automotive industry.
Furthermore, apprenticeship programs allow students to explore career paths early on, helping them make informed decisions about higher education or vocational training. For example, schools can collaborate with industry leaders to offer workshops or internships focused on EV technologies, fostering direct connections between education and employment opportunities.
Building Bridges Between Schools and the Automotive Industry
Creating effective partnerships between schools and the automotive industry is key to developing future talent. Schools can invite industry professionals to guest-lecture, organize factory tours, or establish mentorship programs. These initiatives provide students with a real-world perspective, motivating them to pursue careers in automotive electrical engineering.
In addition, curriculum designers can incorporate industry-relevant content into K12 programs, such as basic electrical engineering principles, automotive safety standards, and EV technology fundamentals. For instance, Britannica’s insights on electric vehicles underscore the significance of specialized knowledge in EV systems, which schools can integrate into their STEM syllabi.
Conclusion: Shaping the Future Workforce
Integrating electrical skills and apprenticeship experiences in K12 education is a powerful strategy to prepare students for careers in the automotive industry. By fostering technical expertise and industry connections, schools can empower students to explore opportunities in a sector poised for innovation and growth. As a result, this approach not only benefits individual student development but also addresses the automotive industry’s growing need for skilled professionals.
With the right support, K12 education can serve as a launch pad for shaping the next generation of automotive engineers, technicians, and innovators. Schools, industry leaders, and policymakers must work collaboratively to unlock the full potential of this transformative educational model.
Readability guidance: Use concise paragraphs and clear transitions to ensure accessibility. Incorporate illustrative examples and authoritative links for credibility. Leverage apprenticeship case studies to emphasize practical benefits.


