Functional English reading tests often challenge students with one key skill: determining the purpose of a given text. Whether it’s distinguishing between informational, explanatory, or persuasive writing, this skill is critical for effective comprehension. In this article, we’ll break down the common difficulties students face, provide clear strategies to identify text purposes, and analyze examples to help you master functional English reading.
Why Understanding Text Purpose Matters
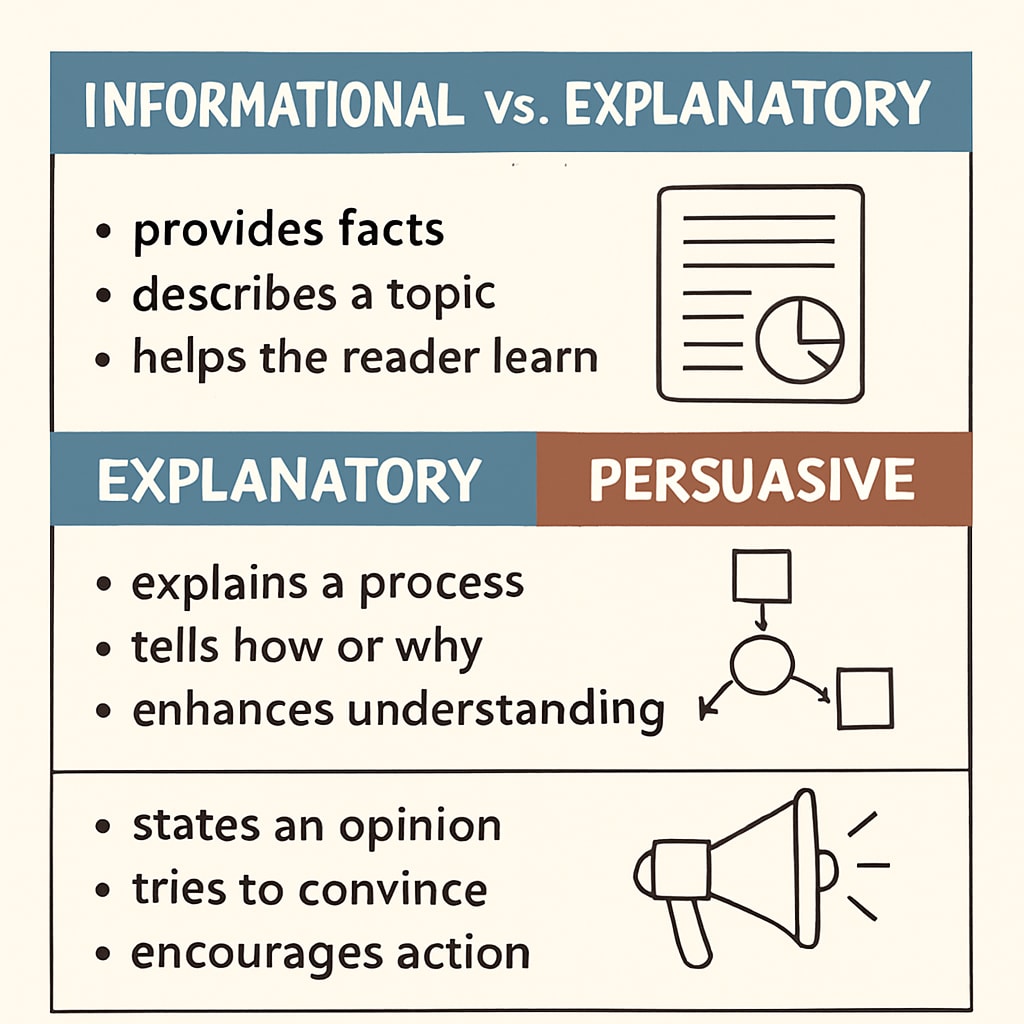
Before diving into strategies, it’s important to understand why identifying text purposes is so essential. The purpose of a text shapes its structure, language, and tone. For example, an informational text aims to deliver facts, while a persuasive text tries to influence the reader’s opinion. Misinterpreting the purpose can lead to misunderstandings and lower test scores.
Here’s a brief overview of the three main types of texts:
- Informational: Provides objective facts and data (e.g., news articles, manuals).
- Explanatory: Clarifies processes, ideas, or concepts (e.g., tutorials, how-to guides).
- Persuasive: Seeks to convince the reader (e.g., advertisements, opinion pieces).
Common Challenges in Identifying Text Purpose
Students often struggle with functional English reading tests for several reasons:
- Overlapping features: Some texts combine elements of multiple purposes, making it harder to classify.
- Unfamiliar vocabulary: Complex or unfamiliar words can distract from understanding the text’s main goal.
- Implicit purposes: Not all texts explicitly state their purpose, requiring readers to infer from context.
For example, a travel guide might include both persuasive elements (encouraging visits) and informational content (listing landmarks). In such cases, students must focus on the overall tone and intent of the author.
Practical Strategies to Decode Text Purpose
To overcome these challenges, follow these proven strategies:
- Analyze the title and headings: Titles often give clues about the text’s purpose. For instance, a title like “Top 10 Reasons to Visit Paris” signals a persuasive intent.
- Examine the tone: Is the text neutral, enthusiastic, or critical? Neutral tones suggest informational texts, while enthusiastic tones often indicate persuasive writing.
- Look for key phrases: Phrases like “studies show” or “research indicates” suggest informational content, while “you should” or “we believe” point to persuasion.
- Focus on structure: Informational texts generally follow a logical sequence, explanatory texts use step-by-step formats, and persuasive texts often include calls to action.
Practicing these strategies can significantly improve your accuracy in identifying text purposes.
Example Analysis: Applying the Strategies
Let’s analyze a sample text:
“Recycling is not just an individual obligation; it’s a global necessity. Studies show that countries with higher recycling rates have lower carbon emissions. By making small changes, like separating your waste, you can contribute to a healthier planet. Join the movement today!”
Using the strategies above:
- Title and headings: A call-to-action tone suggests persuasion.
- Tone: Enthusiastic and motivational language confirms it’s persuasive.
- Key phrases: “Join the movement today” is a clear call to action.
- Structure: Includes evidence (“Studies show…”) to support its argument, typical of persuasive texts.
From this analysis, the text’s purpose is clearly persuasive.

Final Tips for Success
Here are some final tips to ensure you’re well-prepared for functional English reading tests:
- Practice regularly: Use past test papers to familiarize yourself with common question formats.
- Expand your vocabulary: Understanding a wide range of words helps you grasp text nuances.
- Read actively: Take notes, underline key phrases, and summarize the main idea of each paragraph.
Improving your ability to identify text purposes takes time, but with consistent effort and the right strategies, you’ll see noticeable progress.
In conclusion, mastering functional English reading tests is all about understanding the author’s intent. By analyzing titles, tone, key phrases, and structure, you can confidently determine whether a text is informational, explanatory, or persuasive. Start practicing today, and watch your reading comprehension skills soar!


