The Functional Skills English reading exam challenges students to demonstrate their ability to understand and interpret various text types. A critical component of this assessment is identifying the purpose of a text—whether it is informational, explanatory, or persuasive. By mastering this skill, students can navigate the exam confidently and improve their overall reading comprehension. In this article, we will explore practical strategies for recognizing text purposes and provide examples to help you succeed in your Functional Skills English exam.
Understanding the Different Text Types
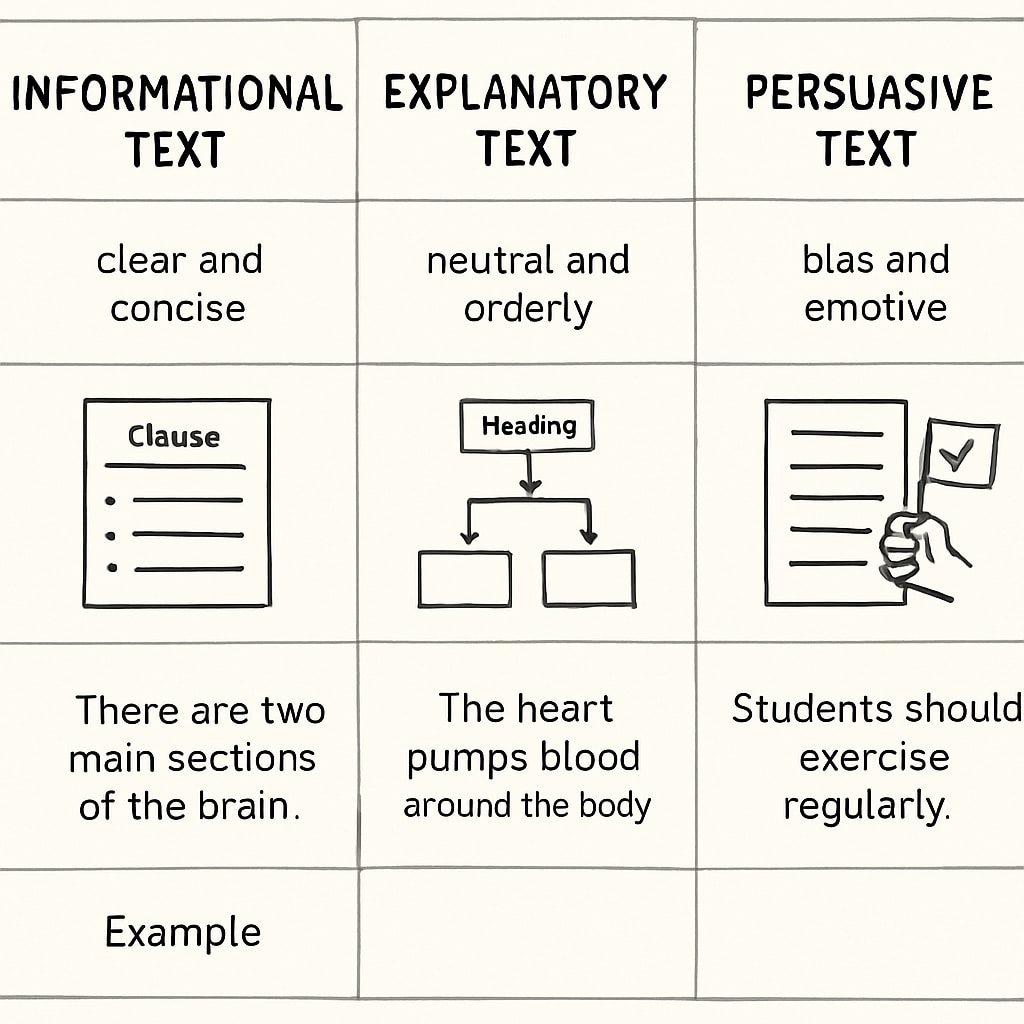
Before diving into strategies, it is essential to understand the three primary text purposes you are likely to encounter in the Functional Skills English exam:
- Informational Texts: These are designed to provide facts or data. Examples include news articles, leaflets, and instruction manuals.
- Explanatory Texts: These aim to clarify or explain concepts. Examples include how-to guides, tutorials, and reports.
- Persuasive Texts: These strive to convince the reader of a particular viewpoint. Examples include advertisements, opinion pieces, and campaign materials.
Each text type has distinct characteristics, which can help you determine its purpose. For example, informational texts focus on delivering factual content, while persuasive texts often use emotive language and rhetorical questions to influence the reader.
Key Strategies for Identifying Text Purposes
Once you understand the different text types, the next step is to apply effective strategies to identify the purpose of a given text. Below are some practical tips:
1. Analyze the Language Used
Language is a strong indicator of a text’s purpose. Look for the following:
- Informational Texts: Neutral and objective language, with a focus on facts and figures.
- Explanatory Texts: Logical sequencing and clarity, often using transitional phrases like “firstly,” “next,” and “finally.”
- Persuasive Texts: Emotional appeal, persuasive techniques such as rhetorical questions, and calls to action.
2. Examine the Structure
The organization of a text can reveal its purpose. Informational texts often follow a straightforward structure with headings and bullet points. Explanatory texts may use step-by-step instructions, while persuasive texts might include a strong opening statement and a conclusion that reinforces the argument.
3. Consider the Intended Audience
Think about who the text is addressing. Informational texts are usually targeted at a broad audience, explanatory texts are for people seeking understanding, and persuasive texts are aimed at influencing a specific group.
4. Look for Visual Cues
Pay attention to images, graphs, or formatting. For instance, a chart in an informational text provides data, while an eye-catching image in a persuasive text is designed to draw attention.

Practice Makes Perfect
To hone your skills, practice with past papers and real-world examples. Start by identifying the purpose of everyday texts such as advertisements, instruction manuals, or news articles. As you practice, apply the strategies discussed above to build confidence and accuracy.
For further reading, explore resources like the Functional Skills page on Wikipedia or consult educational guides like those provided by Britannica’s Reading section. These materials offer additional insights into text analysis and comprehension.
Conclusion
Identifying text purposes in Functional Skills English exams is a skill that can be developed with practice and attention to detail. By understanding the characteristics of informational, explanatory, and persuasive texts, analyzing language, and considering structural and visual elements, you can approach the exam with greater confidence. Remember, practice is key—so start applying these strategies today!
Whether you are preparing for an upcoming exam or looking to enhance your general reading skills, mastering text purpose identification is a valuable tool for success.


