In resource-limited environments, designing engaging and effective student projects for undergraduate AI courses can be challenging. However, with creative approaches, educators can craft interactive learning experiences that allow students to grasp key AI concepts while solving practical problems. This article explores diverse project ideas, from implementing foundational algorithms to exploring low-resource applications of large language models (LLMs), aimed at second-year undergraduate students. Through these projects, students can develop both technical skills and problem-solving abilities, laying the groundwork for future AI expertise.
Foundational Algorithms: Building Blocks for Problem-Solving
One of the most effective ways to introduce students to artificial intelligence is through foundational algorithms. These algorithms are the backbone of many AI systems and provide a tangible way for students to understand basic concepts such as search, optimization, and classification.
- Sorting Algorithms: Students can implement and compare sorting algorithms like bubble sort, merge sort, and quicksort. This project develops their coding skills while teaching algorithm efficiency.
- Pathfinding Algorithms: Explore algorithms like A* or Dijkstra’s algorithm through projects such as maze-solving or route optimization. These tasks demonstrate practical applications of AI in navigation and logistics.
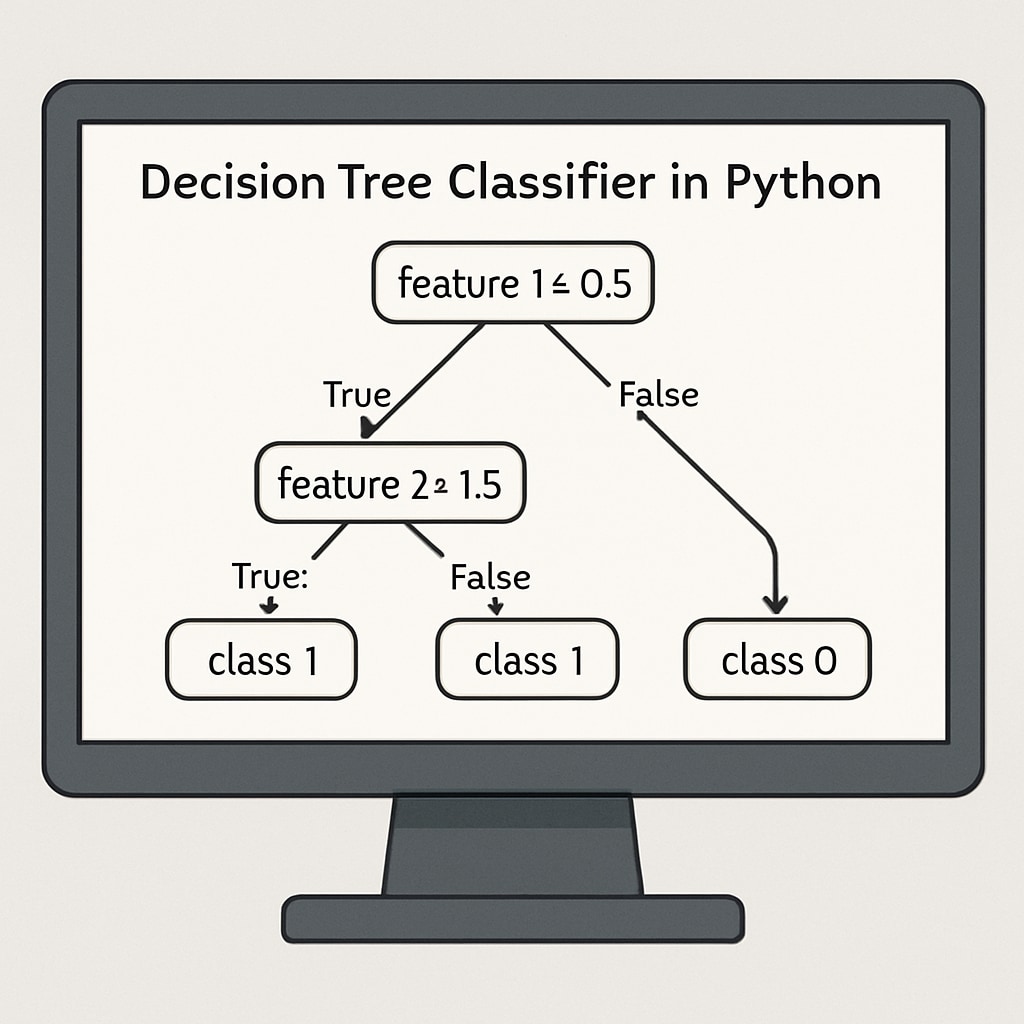
- Decision Trees: Students can build simple decision tree classifiers using small datasets, such as predicting weather conditions or student performance.
These projects are highly adaptable to limited resources since they primarily rely on coding environments and datasets that are readily available online.
Low-Resource LLM Applications: Bridging AI and Real-World Problems
Large language models (LLMs) like GPT have revolutionized the field of AI. However, many universities face constraints in accessing high-end computational resources for implementing these models. Low-resource LLM applications offer an excellent alternative for interactive learning while keeping costs manageable.
- Fine-Tuning Pre-Trained Models: Students can use open-source LLMs to perform limited fine-tuning for specific tasks such as sentiment analysis or text summarization. This project introduces them to transfer learning without requiring extensive hardware.
- Prompt Engineering: Teach students the art of crafting effective prompts to achieve specific outputs from pre-trained LLMs. For example, they can design prompts for automated customer service responses or generating creative writing.
- Ethical AI Discussions: Incorporate group discussions on ethical considerations in LLM applications, such as data privacy, biases, and responsible use.
These projects emphasize creativity and critical thinking, enabling students to make the most of limited computational resources while understanding the broader implications of AI technology.

Collaborative Learning: Team-Based Interactive Challenges
Team-based projects encourage collaboration and communication, two essential skills in AI and data science careers. These projects can be designed to simulate real-world challenges and promote peer learning.
- AI for Social Good: Assign teams to design AI solutions for local community issues, such as waste management or improving public transportation. This encourages creativity and real-world problem-solving.
- Hackathons: Organize small-scale AI hackathons where students work in teams to develop prototypes for specific applications, like recommendation systems or chatbots.
- Data Analysis Competitions: Provide students with datasets and challenge them to uncover actionable insights using AI tools. This fosters healthy competition and analytical thinking.
By focusing on teamwork and practical applications, these projects instill a sense of purpose and accomplishment in students, preparing them for collaborative work environments.
Tips for Effective Project Implementation
Designing and executing successful undergraduate AI projects requires careful planning and alignment with course objectives. Here are some tips:
- Focus on Simplicity: Ensure projects are straightforward and achievable within the constraints of the course schedule and available resources.
- Provide Clear Guidelines: Offer structured instructions and examples to help students understand project requirements.
- Encourage Creativity: Allow flexibility for students to explore their interests within the project scope.
- Incorporate Feedback: Regularly review student progress and provide constructive feedback to refine their understanding.
By following these strategies, educators can maximize the impact of interactive projects and foster a deeper understanding of AI concepts.
In conclusion, designing interactive projects for undergraduate AI courses, even in resource-limited environments, is both feasible and rewarding. From foundational algorithms to low-resource LLM applications, these projects offer students hands-on experience and prepare them for the challenges of advanced AI studies and applications. With creativity and thoughtful planning, educators can break resource barriers and create meaningful learning opportunities in artificial intelligence.


