Medical education is often reserved for specialized training within higher education or professional development contexts. However, introducing professional medical knowledge in K-12 education could bridge the gap between non-medical professionals and critical health literacy. This approach is particularly relevant to fields like cardiology, where understanding fundamental health concepts may empower individuals to make informed decisions about their well-being. By addressing the polarization of medical knowledge—either overly simplified or highly technical—K-12 systems can foster a middle ground that promotes accessibility and interdisciplinary thinking.
Why Medical Knowledge Should Be Accessible in K-12 Education
The polarization of medical knowledge creates significant barriers for non-medical professionals. On one hand, basic health education tends to oversimplify critical concepts such as cardiovascular health, leaving students ill-equipped to understand or apply them in real life. On the other hand, advanced medical resources are often inaccessible to individuals without specialized training. This lack of intermediate-level education leaves a gap that K-12 systems are uniquely positioned to fill.
Integrating medical topics such as cardiology into K-12 curricula could benefit students in several ways:
- Improved Health Literacy: Students learn practical skills like understanding symptoms of heart disease, promoting preventative health habits, and recognizing medical emergencies.
- Enhanced Interdisciplinary Skills: Medical education fosters critical thinking by connecting biology, chemistry, and statistics to real-world applications.
- Career Exploration: Early exposure to professional-level concepts could inspire students to pursue careers in medicine or related fields.
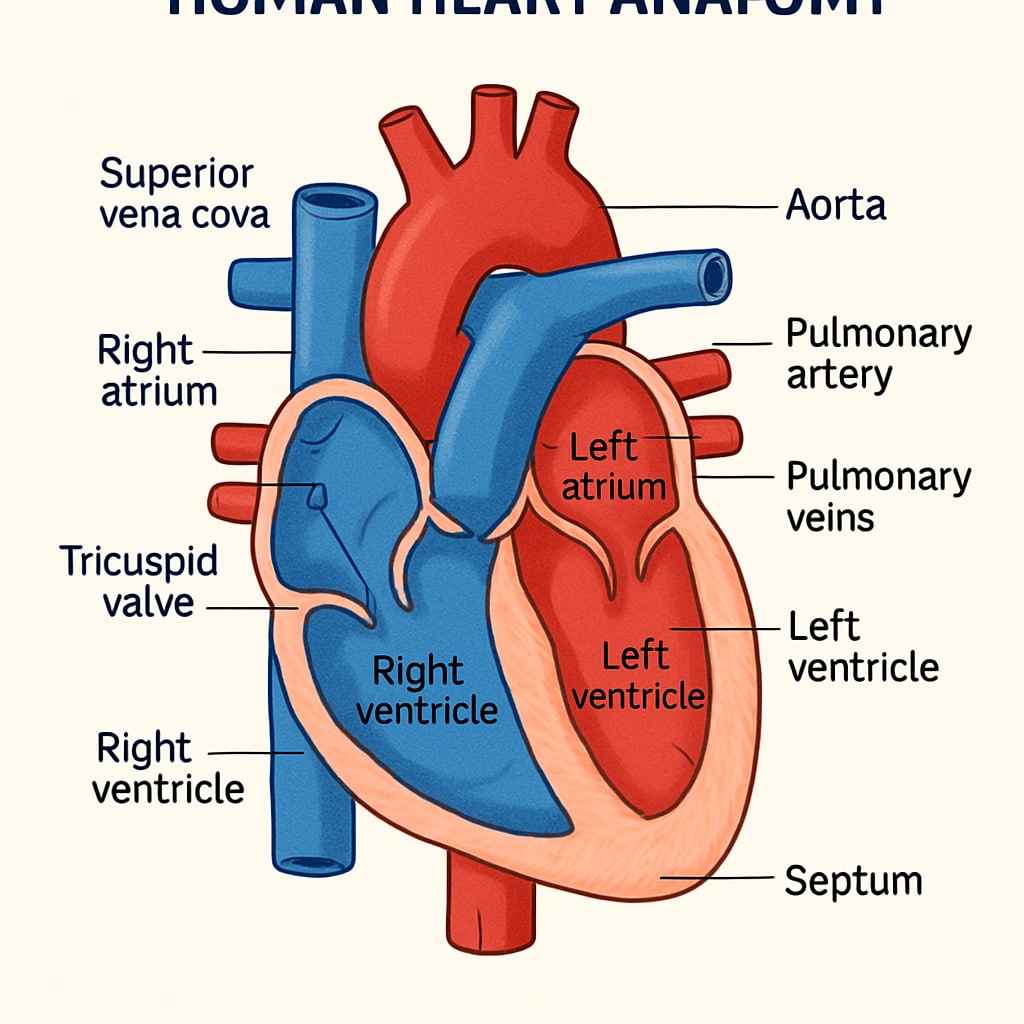
Practical Steps to Introduce Medical Knowledge in K-12
Incorporating medical topics into K-12 curricula requires thoughtful planning to ensure age-appropriate and engaging content. Schools could consider the following approaches:
- Modular Learning: Develop short modules on topics such as cardiology, covering basic anatomy, common conditions, and preventative care.
- Collaborative Projects: Encourage students to work on interdisciplinary projects, such as designing a campaign for heart health awareness.
- Guest Lectures: Invite healthcare professionals to give talks or workshops, offering practical insights and fostering interest in medical fields.
- Leveraging Technology: Use interactive tools to simulate medical scenarios, such as diagnosing symptoms or exploring human anatomy.
For example, initiatives like Khan Academy’s Health and Medicine resources provide accessible content tailored to younger audiences.

Potential Challenges and How to Overcome Them
While the benefits of introducing medical education at the K-12 level are clear, potential challenges need to be addressed:
- Curriculum Overload: Adding medical modules may strain already packed schedules. Schools can integrate them into science or health classes instead of creating standalone subjects.
- Teacher Training: Educators may feel unprepared to teach medical concepts. Training programs and partnerships with healthcare professionals can provide support.
- Funding Constraints: Developing specialized resources requires investment. Schools can seek partnerships with medical organizations to offset costs.
As a result, strategic planning and community collaboration are essential for successful implementation.
The Future of K-12 Medical Education
By introducing professional medical knowledge into K-12 education, schools can empower students with the skills to navigate health-related challenges, both personally and professionally. This approach not only enhances health literacy but also fosters interdisciplinary thinking and innovation in future generations. As society increasingly prioritizes preventative healthcare and holistic well-being, early medical education could play a pivotal role in shaping healthier communities.
To learn more about the importance of health literacy and its impact, visit Health Literacy on Wikipedia.
Readability guidance: This article uses concise paragraphs, avoids excessive jargon, and incorporates transitional phrases to maintain a smooth flow. Lists are utilized to simplify complex ideas, and passive voice is minimized to ensure clarity and engagement.


