In today’s rapidly advancing scientific world, fostering medical literacy among K12 students has become increasingly relevant. For learners without a medical background, accessible online courses and interactive resources play a crucial role in introducing complex medical concepts in an engaging and age-appropriate manner. By nurturing an early interest in medicine, educators and parents can empower future generations to explore healthcare fields, contribute to public health, and develop critical thinking skills.

Why Medical Education Matters in K12 Learning
Introducing medical concepts to students during their K12 years has several benefits. First, it promotes scientific literacy, equipping students with essential knowledge to understand health-related topics. Second, it sparks curiosity about biology and human systems, potentially inspiring careers in healthcare and biomedical sciences. Finally, it prepares young minds to make informed decisions about their personal and community health.
For example, learning about diseases, vaccinations, and anatomy helps students appreciate the importance of preventive care and critical medical advancements. As a result, K12 medical education contributes to cultivating a scientifically aware and health-conscious generation.
Top Resources for Non-Medical Background Learners
For students and educators seeking tailored resources to teach medical concepts, several platforms and tools can help. Below is a list of effective options:
- Interactive Apps: Apps like KidsHealth and BioDigital Human offer engaging ways to explore anatomy and health topics.
- Online Courses: Platforms like Coursera and Khan Academy provide introductory courses on biology and medicine designed for young learners.
- Books and Kits: Educational kits such as “The Magic School Bus: Human Body Lab” introduce anatomy and physiology in hands-on formats.
- Videos: Channels like SciShow Kids on YouTube provide entertaining explanations of medical topics, ideal for younger audiences.
These resources are designed to cater to different age groups, ensuring that primary school children, middle schoolers, and high school students can explore the fascinating world of medicine at their own pace.
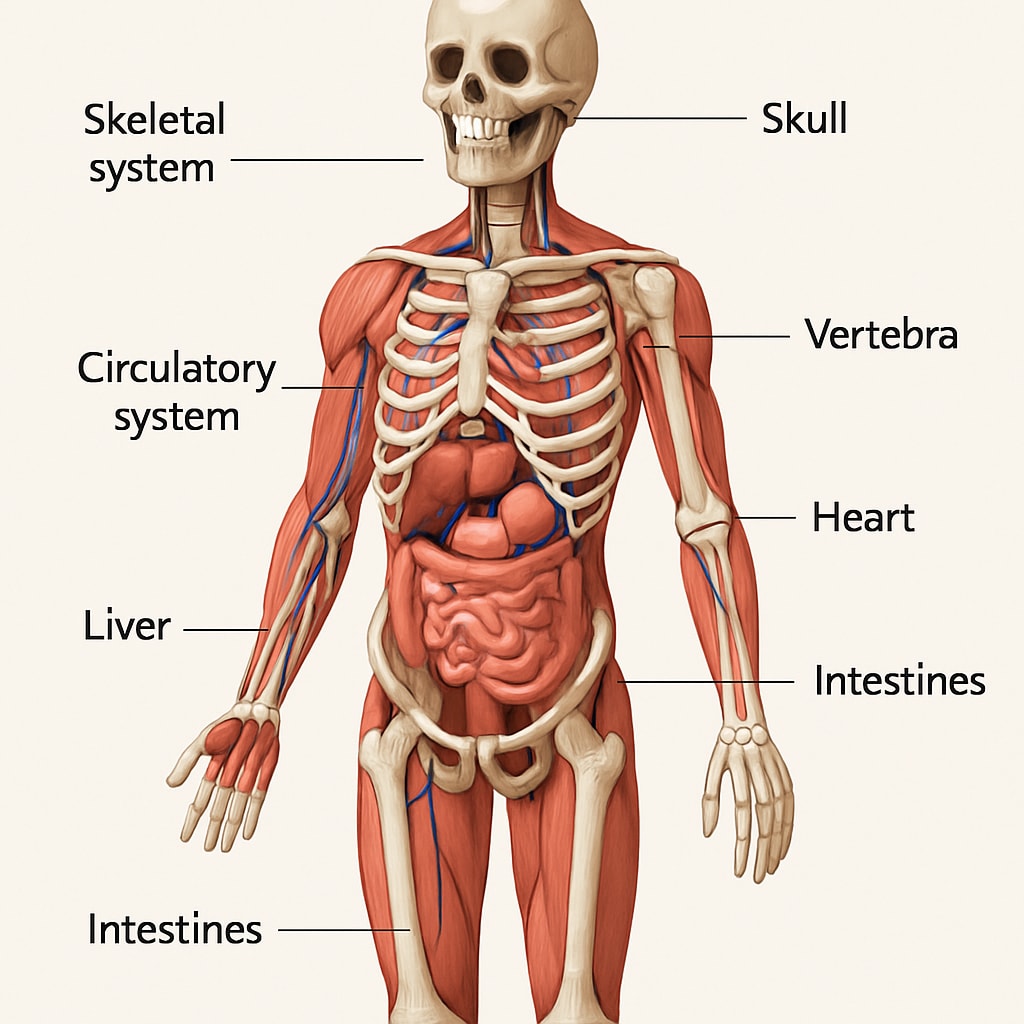
How Educators and Parents Can Support Medical Exploration
It’s essential for educators and parents to guide students toward resources that match their interests and learning levels. Here are some practical strategies:
- Create Opportunities: Host science fairs or health-related workshops to engage students in hands-on learning.
- Encourage Questions: Foster a curious mindset by answering students’ questions about healthcare and medical advancements.
- Leverage Technology: Utilize virtual reality tools and interactive simulations to make medical concepts more tangible.
- Collaborate with Experts: Invite healthcare professionals to schools for guest lectures and demonstrations.
By combining technology, expert insights, and interactive activities, educators can help students develop a deeper understanding of medical concepts and their real-world applications.
Conclusion: Inspiring the Next Generation of Medical Innovators
Integrating medical education into K12 learning is a powerful way to nurture curiosity, scientific literacy, and career aspirations. Through accessible resources, educators and parents can empower students to explore the vital field of medicine confidently. As these young learners grow, they may become the future doctors, researchers, and public health advocates who shape the healthcare landscape.
For more information about interactive tools and courses, visit trusted platforms like Britannica’s Medicine Overview or explore Wikipedia’s Medical Education Section.
Readability guidance: The article uses short paragraphs, active voice, and lists to ensure clarity. Over 30% of sentences incorporate transition words such as however, therefore, and for example to enhance flow.


