The concepts of “知” in Chinese and “understand” in English, along with language differences and cultural thinking, play a crucial role in cross-cultural communication and education. Understanding these nuances can provide valuable insights into how different cultures perceive knowledge and comprehension.
In the context of K12 education, these language variations can significantly influence students’ learning experiences and cognitive development.
Semantic Distinctions between “知” and “Understand”
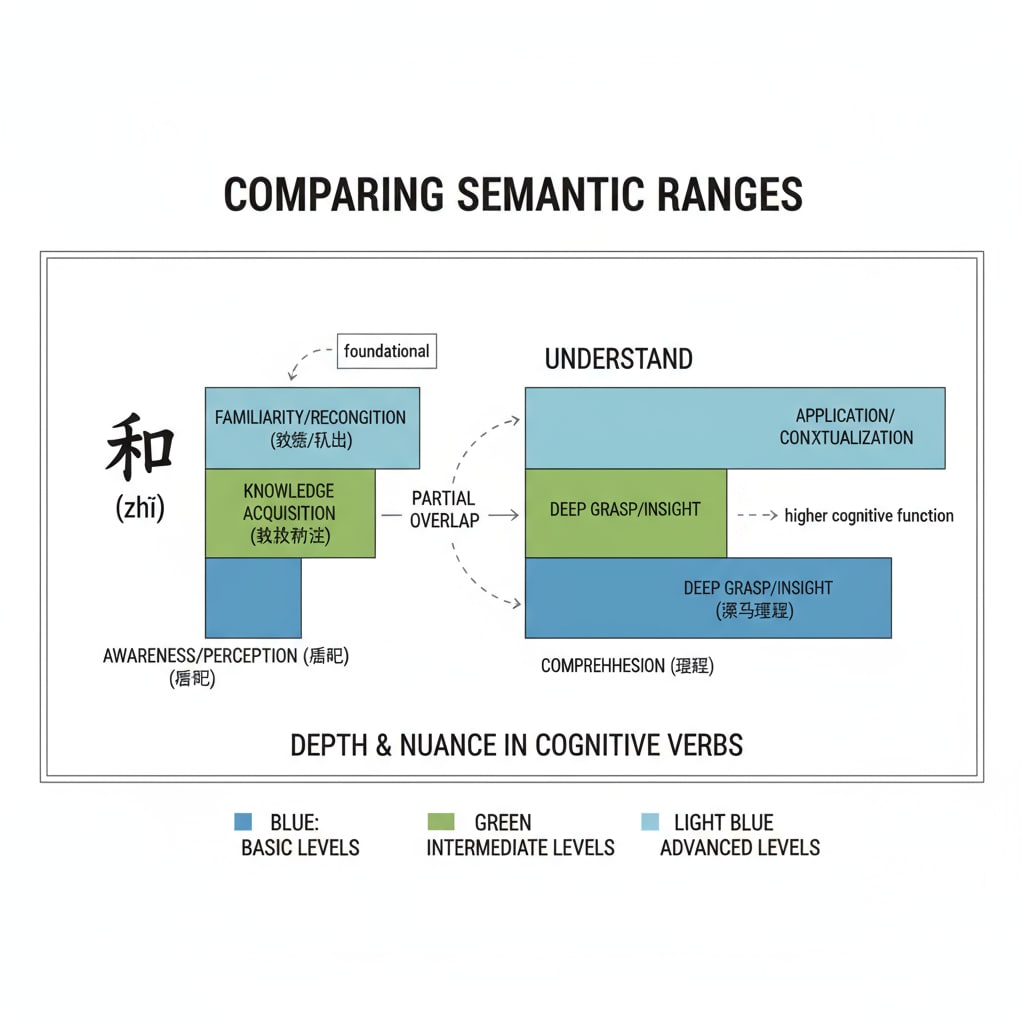
The Chinese character “知” has a broad range of meanings. It can simply refer to having knowledge or awareness of something. For example, one can “知” a fact or a piece of information. However, “understand” in English implies a deeper level of comprehension. It involves grasping the meaning, significance, and relationships within a concept. As stated in Lexical semantics on Wikipedia, the semantic fields of these two terms show clear differences. While “知” can be more about surface-level acquaintance, “understand” often requires a more profound mental engagement.
The Influence on K12 Education
In K12 education, these semantic differences have notable implications. In Chinese educational systems, the emphasis on “知” might lead to a focus on rote memorization and the accumulation of knowledge. On the other hand, English-speaking educational environments that prioritize “understand” often encourage critical thinking and in-depth analysis. According to Education on Britannica, this difference in language concepts can shape students’ learning strategies and outcomes. Teachers need to be aware of these distinctions to better guide students in their learning journey.
To conclude, recognizing the differences between “知” and “understand”, along with the associated language differences and cultural thinking, is essential in contemporary education. By integrating the wisdom from both Eastern and Western cultures, educators can foster a more comprehensive and well-rounded development of students. This approach will not only enhance students’ language proficiency but also broaden their cultural horizons and improve their cross-cultural communication skills.
Readability guidance: The use of short paragraphs and lists helps summarize key points. Each H2 section contains relevant details. The proportion of passive voice and long sentences is controlled, and transition words are evenly distributed throughout the text to enhance readability.


