Learning theories, cone of experience, practical learning, and multisensory learning are integral aspects of understanding how we acquire knowledge. Throughout history, scholars have sought to uncover the most effective ways of learning, and a common thread that emerges is the concept of “learning by doing”.
The Essence of Learning Theories
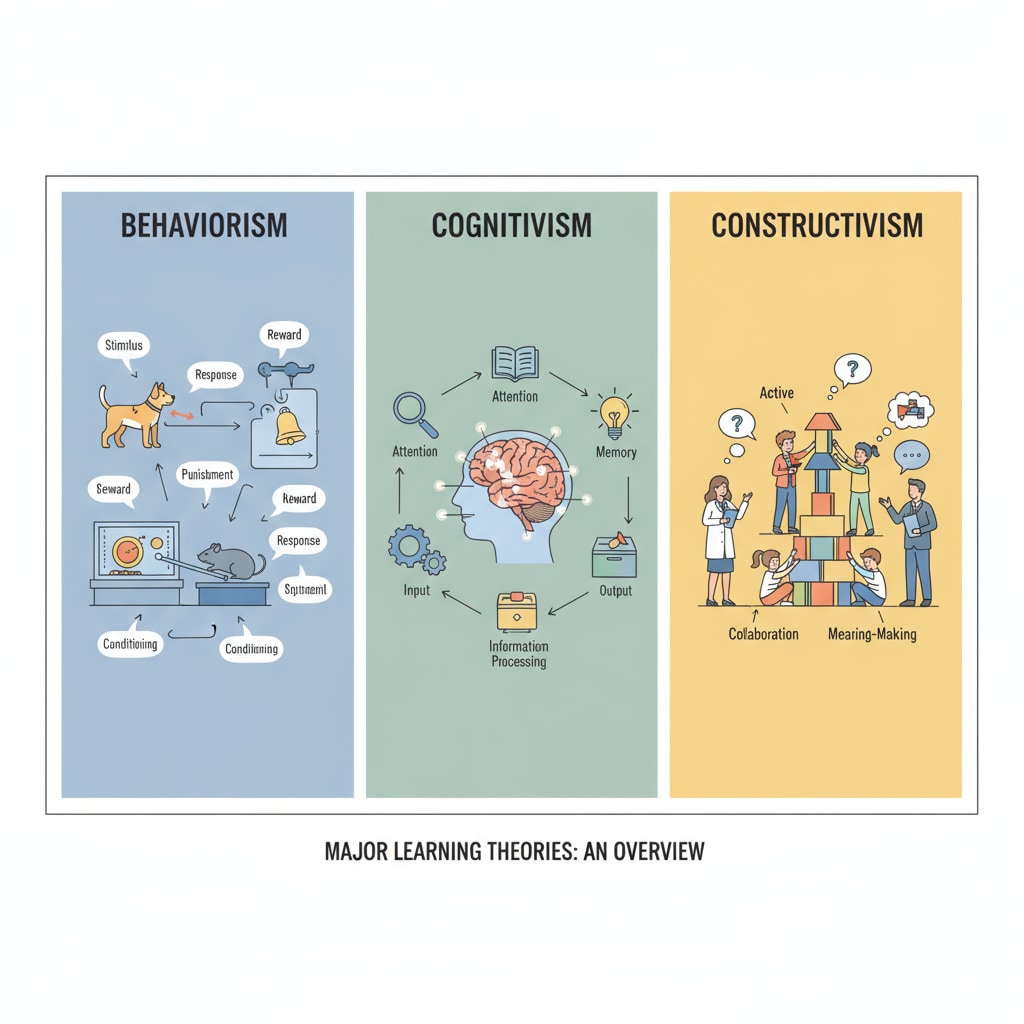
Learning theories are frameworks that attempt to explain how individuals acquire, retain, and utilize knowledge. Different theories have been proposed over time, each offering unique perspectives. For example, behaviorist theories focus on the role of external stimuli and responses in learning. Cognitive theories, on the other hand, emphasize mental processes such as perception, attention, and memory. Constructivist theories posit that learners actively construct knowledge based on their prior experiences. These theories provide a foundation for understanding the complex nature of learning.
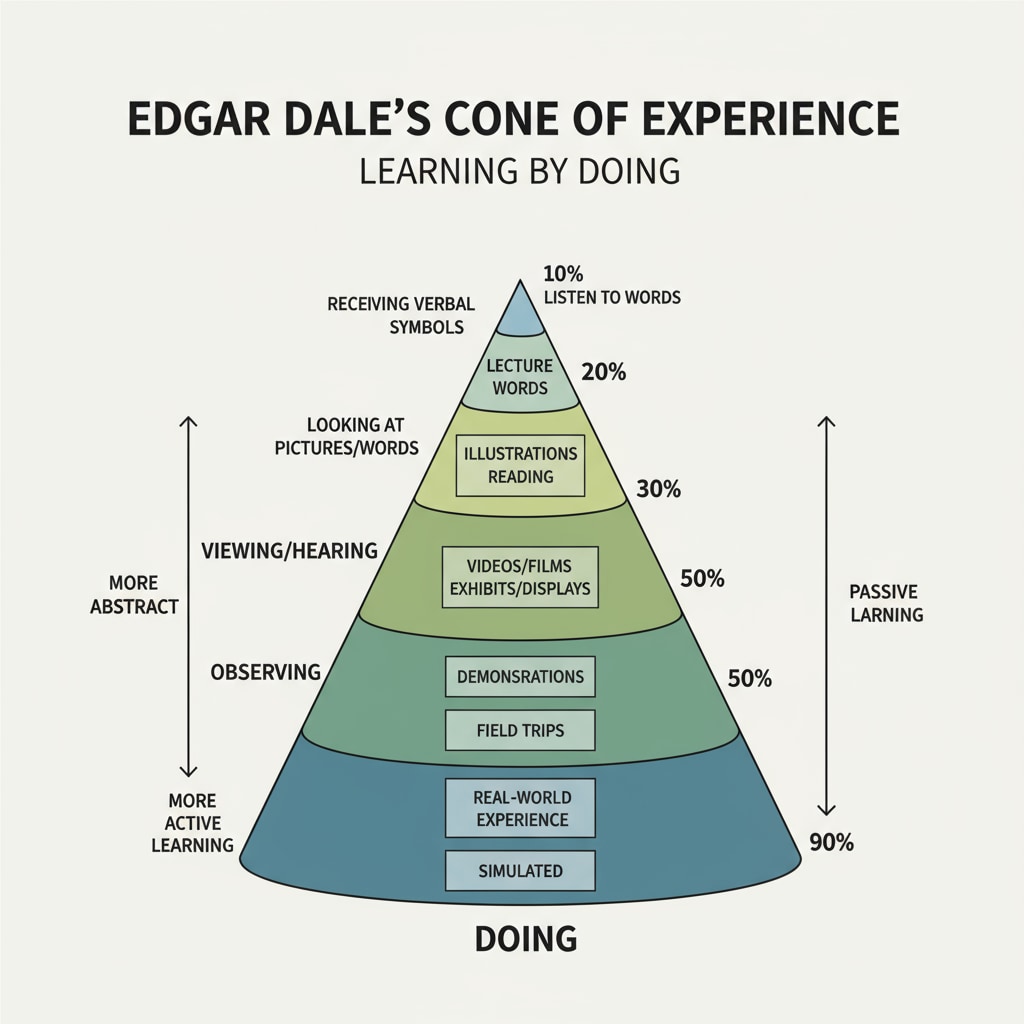
The Cone of Experience: A Modern Perspective
Edgar Dale’s Cone of Experience is a well-known model in the field of education. It represents different types of learning experiences on a cone-shaped diagram. At the base of the cone are the most concrete and direct experiences, such as doing a hands-on activity. As we move up the cone, the experiences become more abstract, like listening to a lecture. According to Dale, the more concrete the experience, the more effective the learning. This aligns with the idea of practical learning, where learners engage in real-world tasks to gain knowledge and skills. Cone of Experience on Wikipedia
The concept of “learning by doing” has been echoed by various thinkers across different cultures and time periods. In ancient China, the philosopher Xun Kuang, or Xunzi, proposed a theory of learning levels. He believed that true learning involved not just hearing and seeing but also putting knowledge into practice. This is remarkably similar to Dale’s ideas in the modern era. Both emphasize the importance of active engagement in the learning process.
In modern education, the principles of practical learning and multisensory learning are being increasingly recognized. Multisensory learning involves engaging multiple senses, such as sight, hearing, touch, and smell, in the learning process. For example, in a science experiment, students not only observe the results visually but also feel the textures, hear the sounds, and sometimes even smell the substances involved. This multi-sensory approach enhances memory retention and understanding.
With the advancement of technology, virtual reality (VR) has emerged as a powerful tool for multisensory learning. VR allows learners to immerse themselves in realistic scenarios, providing a highly engaging and concrete learning experience. For instance, medical students can use VR to practice surgical procedures in a safe and controlled environment. This combines the principles of practical learning and multisensory learning to create a more effective learning environment.
Readability guidance: The article has presented different aspects of learning theories, the cone of experience, practical learning, and multisensory learning. By highlighting the connection between ancient and modern ideas, as well as the role of technology, it showcases the evolving nature of learning. Each section has used short paragraphs and clear explanations to enhance readability. Transition words have been used to connect ideas, and external links have been provided for further exploration.


