For K-12 students with a passion for science, diving into professional medical knowledge can be an exciting yet challenging endeavor. With no prior medical background, accessing reliable and age-appropriate online resources in fields like cardiology (heart health) can open doors to future career possibilities. However, the gap between intricate medical concepts and the learning capacity of younger minds presents a unique challenge. This article provides solutions by exploring accessible resources, structured learning pathways, and tailored educational strategies for non-medical students.
Why K-12 Students Need Accessible Medical Education Resources
Medical science is often viewed as an advanced field reserved for college-level study, but introducing foundational concepts early can spark lifelong interest. For example, understanding the basics of heart health, anatomy, or diseases like heart attacks helps young learners develop critical thinking and scientific curiosity. Accessible online courses designed for students without medical backgrounds can serve as an important bridge.
Several platforms, such as Khan Academy and Coursera, offer beginner-friendly medical courses that align with K-12 education standards. These courses cover topics like human anatomy, physiology, and the cardiovascular system in ways that are engaging and understandable for younger audiences.

Building a Step-by-Step Medical Education Framework for Students
To make professional medical knowledge accessible for K-12 students, educators and parents can adopt a layered teaching approach:
- Introduction to Medical Basics: Start with fundamental concepts like the structure of the human body or the function of organs, using engaging visuals or interactive tools.
- Explore Specific Areas of Interest: Provide opportunities for students to delve deeper into areas like cardiology, neurology, or immunology based on their interests.
- Practical Learning: Incorporate hands-on activities such as virtual dissections or simulations that allow students to visualize complex concepts.
- Advanced Enrichment: Offer resources such as webinars with medical professionals or advanced online courses for students who show deeper interest.
Such a framework ensures that students progress gradually, building a solid foundation before tackling more specialized topics.
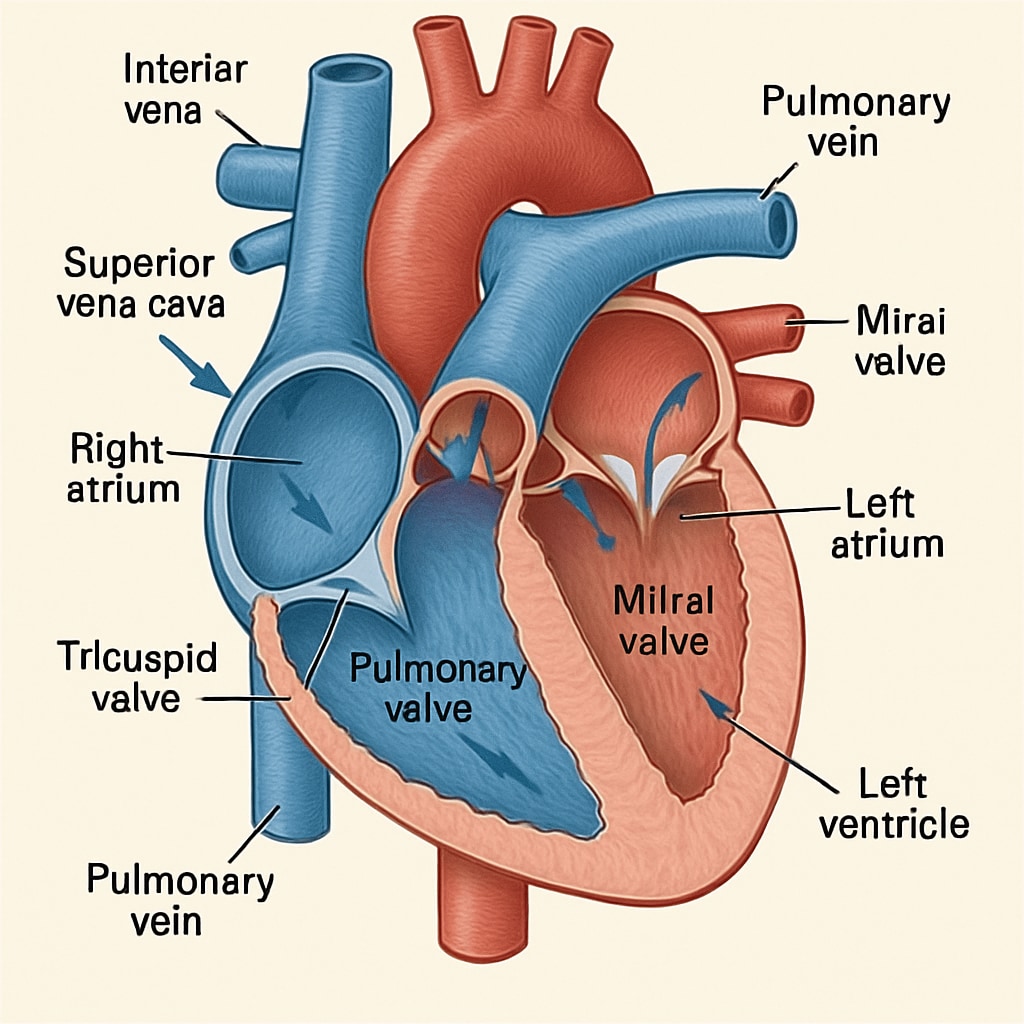
How Online Medical Courses Can Benefit Non-Medical Background Students
Online platforms have revolutionized education, making specialized knowledge accessible to learners of all ages. For students without a medical background, online medical courses offer flexibility, visual aids, and interactive content tailored to beginners.
For example, courses on heart health might use animations to explain how blood flows through the chambers of the heart or how lifestyle factors impact cardiovascular health. This approach makes complex subjects comprehensible while maintaining scientific accuracy.
Additionally, online learning allows students to explore subjects at their own pace, fostering independence and self-directed learning. Platforms like MOOCs (Massive Open Online Courses) provide free or affordable options for students to access high-quality content.
Key Benefits of Early Exposure to Medical Knowledge
Introducing students to medical education resources at an early age offers several advantages:
- Career Exploration: Early exposure can help students identify potential career paths in healthcare or research.
- Critical Thinking: Studying medical concepts encourages analytical skills and problem-solving abilities.
- Health Literacy: Understanding topics like heart health equips students to make informed decisions about their own health.
As a result, students not only gain knowledge but also develop skills that can benefit them academically and personally.
Conclusion: Bridging the Gap Between Medical Knowledge and K-12 Students
Creating accessible medical education pathways for K-12 students requires thoughtful planning and the use of engaging resources. Online courses, structured frameworks, and practical tools can make advanced subjects like cardiology approachable for young learners without medical backgrounds.
By fostering curiosity and providing age-appropriate learning opportunities, educators and parents can inspire the next generation of scientists, doctors, and researchers.
Readability guidance: Each section uses concise paragraphs and clear headings. Lists summarize key points for ease of understanding, ensuring the article remains engaging and accessible to a wide audience.


