Medical education is evolving beyond its traditional boundaries. With rising health awareness globally, the demand for accessible medical knowledge has grown significantly. Today, medical education is no longer an exclusive domain for healthcare professionals—it is becoming increasingly vital for individuals from non-medical backgrounds. Among these efforts, K12 education has emerged as a promising platform to introduce age-appropriate medical concepts through online courses, helping young learners establish a foundation for lifelong health literacy.
The Growing Need for Health Literacy in K12 Education
Health literacy refers to the ability to access, understand, and use information to make informed health decisions. According to the World Health Organization, a lack of health literacy can lead to poor health outcomes and increased healthcare costs. In response, educators are recognizing the importance of introducing medical education early in life, especially at the K12 level.
K12 students often encounter health-related topics in science or physical education classes, but these subjects typically lack the depth needed to instill practical health knowledge. By integrating structured medical education into K12 curricula, educators can provide students with tools to understand basic anatomy, nutrition, mental health, and disease prevention. This approach not only builds their knowledge but also empowers them to make healthier choices as they grow.

Online Courses: A Gateway to Inclusive Medical Knowledge
The rise of online learning platforms has revolutionized how educational content is delivered. For non-medical learners, online courses offer an engaging and flexible way to explore medical topics. Platforms like Khan Academy and Coursera have developed beginner-friendly medical courses that cater to varying age groups and educational levels.
In the K12 space, these online courses present several advantages:
- Accessibility: Students can access courses anytime, anywhere, bridging gaps in traditional classroom settings.
- Interactive Learning: Features like quizzes, animations, and interactive diagrams help simplify complex medical concepts.
- Customizability: Courses can be tailored to specific age groups, ensuring that the content is both relevant and appropriate.
For example, a middle school course may introduce basic human anatomy through interactive visuals, while a high school course could explore topics like epidemiology or mental health awareness. These tailored approaches make medical education more relatable and effective for younger audiences.
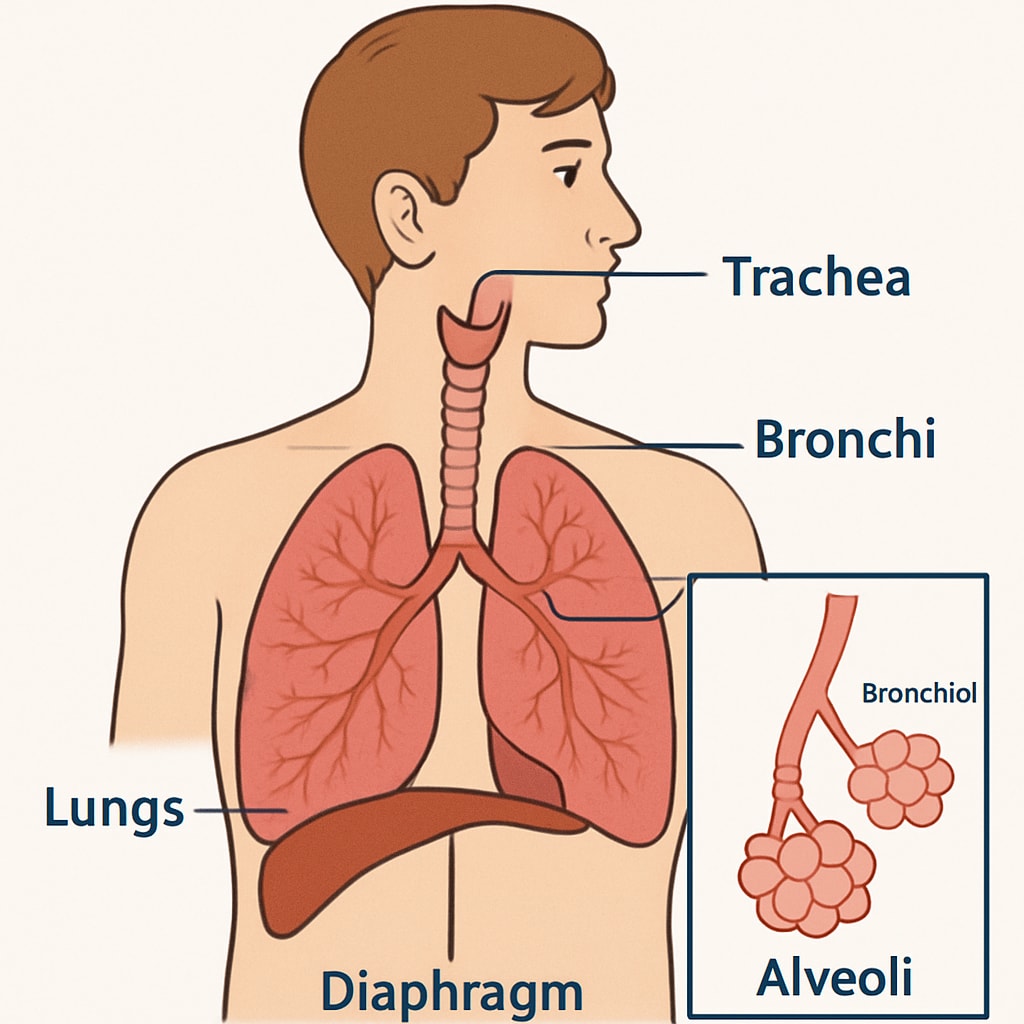
Challenges and Strategies for Effective Implementation
While the integration of medical education into K12 curricula holds immense potential, it also poses certain challenges. One significant obstacle is ensuring the accuracy and reliability of the content provided in online courses. Misleading or overly complex material can confuse students or, worse, propagate misinformation.
To overcome these challenges, educators and course developers can adopt the following strategies:
- Collaborate with Experts: Partnering with medical professionals ensures that the course content is accurate and up-to-date.
- Focus on Simplification: Use analogies, visuals, and real-life examples to make medical concepts easier to grasp.
- Encourage Critical Thinking: Include activities that prompt students to analyze health scenarios, fostering a deeper understanding of the subject.
- Prioritize Inclusivity: Ensure that the courses are accessible to students from diverse socio-economic and cultural backgrounds.
Conclusion: Paving the Way for Lifelong Learning
Integrating medical education into K12 curricula through online courses is a forward-thinking approach to enhancing health literacy among younger generations. By equipping students with essential medical knowledge early on, we empower them to make informed health decisions throughout their lives. As technology continues to advance, the opportunities for creating engaging and impactful online medical education resources for non-medical learners will only expand. Ultimately, this cross-disciplinary initiative bridges the gap between education and healthcare, fostering a healthier and more informed society.
As we move forward, it is crucial for educators, medical professionals, and policymakers to collaborate in shaping these resources. Together, we can ensure that every student—regardless of their background—has the tools they need to thrive in a world where health knowledge is more important than ever.


