In today’s rapidly evolving world, understanding basic medical concepts is no longer reserved for healthcare professionals. For non-medical background individuals, cardiology and online courses provide accessible ways to learn essential medical knowledge. This shift is especially vital in K12 education, where fostering health literacy and scientific thinking can prepare students for future challenges in personal and public health.
Why Medical Education Matters for Non-Medical Learners
Medical education has traditionally been tailored for professionals, but the increasing importance of health literacy makes it essential for everyone. For example, cardiology—the study of the heart and its diseases—can help students understand conditions such as heart disease, a leading global health issue. Teaching these concepts early equips students with the knowledge to make informed decisions about their health and empowers them to advocate for healthier communities.
Introducing medical education to K12 students involves challenges, but online courses have emerged as a practical solution. Platforms like Khan Academy and Britannica offer interactive resources that simplify complex topics for young learners.
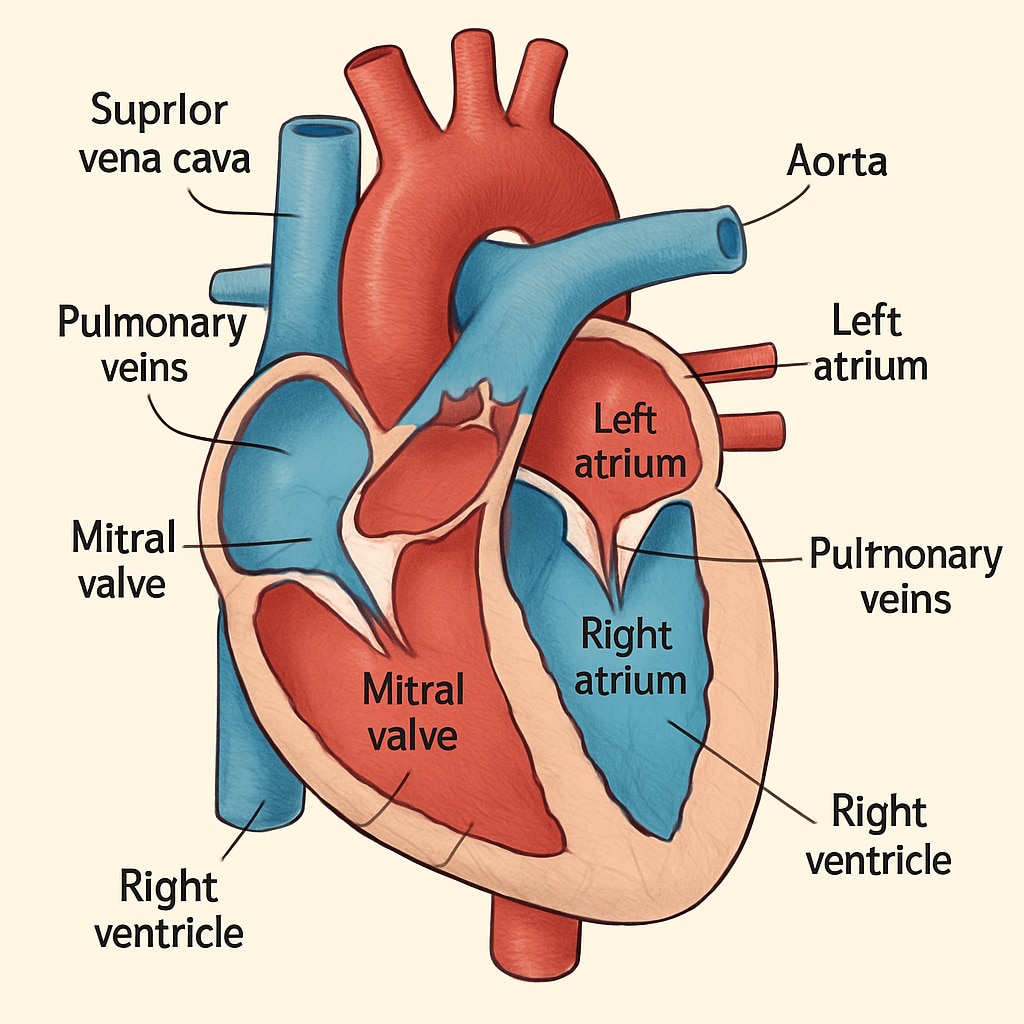
Building the “Cross-Disciplinary Medicine” Curriculum
To effectively integrate medical knowledge into K12 education, a specialized curriculum called “Cross-Disciplinary Medicine” could be developed. This curriculum would combine elements of biology, health science, and ethics to teach medical concepts in an age-appropriate manner. For example:
- Basic Anatomy: Understanding body systems like the cardiovascular system.
- Common Diseases: Exploring conditions such as diabetes and hypertension.
- Preventative Health: Teaching habits that promote long-term well-being.
Online courses can complement this curriculum by offering video tutorials, quizzes, and interactive simulations. These resources ensure accessibility for students from diverse backgrounds, making medical education inclusive and engaging.

The Role of Technology in Medical Learning
Technology plays a crucial role in bringing medical education to non-medical learners. Platforms like virtual labs and augmented reality applications allow students to explore complex medical concepts in a hands-on environment. For example, a virtual heart dissection can teach the anatomy of the heart without the need for physical specimens.
Moreover, online courses offer flexibility, enabling students to learn at their own pace. This approach caters to individual learning styles and ensures that students grasp foundational concepts before moving on to advanced topics.
As a result, integrating technology into medical education not only enhances learning outcomes but also prepares students for a future where digital tools are central to healthcare.
Benefits of Early Medical Education for Society
Incorporating medical knowledge into K12 education has long-term benefits for society. Students who develop health literacy at an early age are more likely to adopt healthy lifestyles and contribute to public health initiatives. Additionally, exposure to medical concepts can inspire careers in healthcare, filling critical gaps in the workforce.
For instance, understanding cardiology can spark interest in becoming a cardiologist, nurse, or medical researcher. These professionals play vital roles in addressing global health challenges and advancing medical science.
As a result, medical education for non-medical learners is not just an educational innovation—it’s a societal investment.
Readability guidance: This article uses concise paragraphs, lists, and transitions like “for example,” “as a result,” and “in addition” to improve clarity. It minimizes passive voice and long sentences to maintain reader engagement.


