The increasing emphasis on health literacy has highlighted the importance of providing accessible medical education. For non-medical professionals, including K12 educators and students, finding structured and reliable resources for medical education can be challenging. This article explores how to navigate the diverse landscape of online courses and other educational resources to build a foundational understanding of medical concepts.
Challenges in Accessing Medical Education for Non-Professionals
One of the major hurdles faced by non-medical professionals is the complexity of medical terminology and concepts. Many resources are designed for individuals with prior medical knowledge, making them less accessible to beginners. Additionally, the uneven distribution of educational materials across schools and regions creates disparities in health literacy opportunities.
For example, while some urban schools may have access to advanced health education programs, rural schools might lack even the most basic resources. This gap underscores the need for inclusive and easily accessible platforms that cater to diverse audiences.
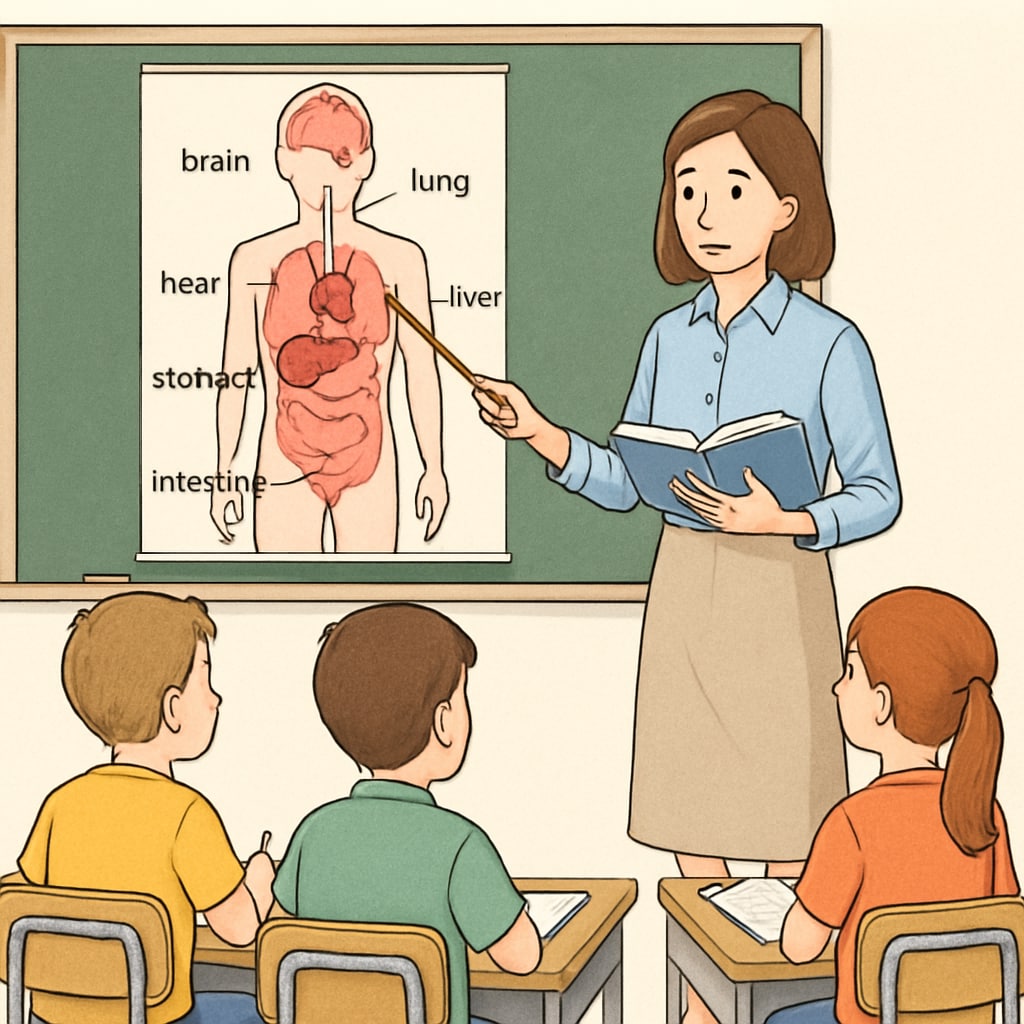
Effective Online Resources for Medical Education
Non-medical professionals can now leverage a variety of online platforms to access medical education. These platforms offer courses tailored for beginners, making scientific concepts easier to understand. Here are some recommended resources:
- Khan Academy: Known for its comprehensive library, Khan Academy provides free courses on human anatomy, physiology, and other related topics. Explore Khan Academy.
- Coursera: Partnering with top universities, Coursera offers beginner-friendly courses such as “Introduction to Healthcare” and “Understanding Medical Research.” Visit Coursera.
- OpenStax: This platform provides free, peer-reviewed textbooks on biology and health, making it an excellent resource for K12 educators.
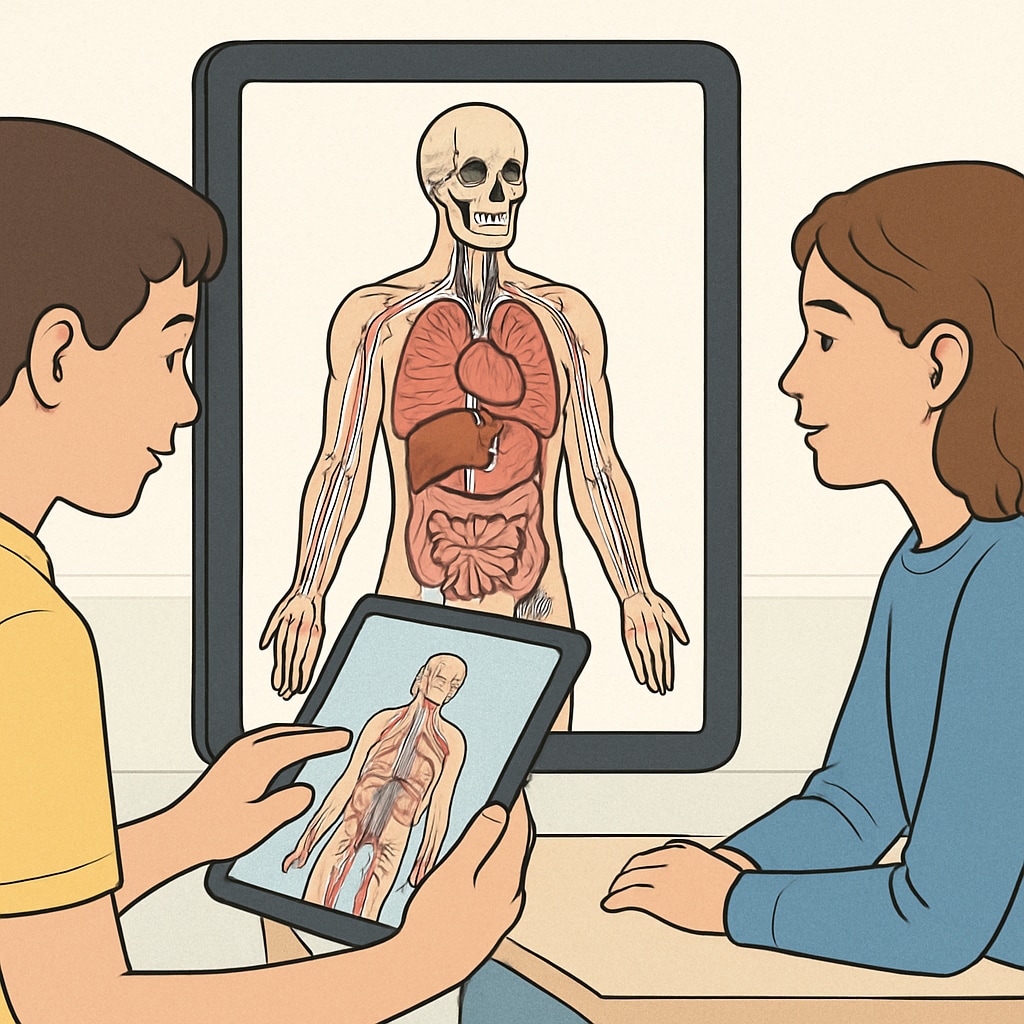
In addition to these platforms, there are interactive tools like 3D anatomy apps and virtual labs, which can help students visualize complex concepts more effectively.
Building a Scientific Knowledge Framework in K12 Education
Introducing medical education at the K12 level not only enhances health literacy but also fosters critical thinking and scientific inquiry. Here are some strategies to build a structured framework:
- Integrate Health Topics into Science Curricula: Encourage teachers to include topics such as nutrition, basic anatomy, and disease prevention within biology lessons.
- Use Age-Appropriate Resources: Tailor content to the developmental stage of students. For instance, elementary students might learn through storytelling, while high school students can engage with case studies.
- Promote Hands-On Learning: Activities like creating simple medical models or participating in first aid workshops can make medical concepts more tangible.
Looking Ahead: Bridging the Gap in Medical Education
As the demand for health education grows, it is essential to address the challenges faced by non-medical professionals in accessing quality resources. Governments, educational institutions, and private organizations must collaborate to develop inclusive, well-structured programs that cater to diverse learning needs.
For non-medical professionals eager to begin their journey, starting with free and beginner-friendly platforms is a practical first step. Over time, these foundational resources can pave the way for deeper exploration and a more comprehensive understanding of medical science.
By equipping K12 students and educators with the right tools, we can foster a scientifically informed generation, capable of making better health decisions for themselves and their communities.
Readability guidance: Use short paragraphs and bulleted lists to summarize key points. Ensure accessibility by avoiding overly complex language and maintaining a logical flow of ideas.


