In recent years, there has been a noticeable rise in demand for professional medical education among individuals with non-medical backgrounds. This trend reflects a growing health awareness, especially in specialized fields like cardiology. While the availability of resources has expanded significantly, the accessibility and suitability of these materials for laypeople remain a challenge. In this article, we’ll explore the current state of medical education resources and propose innovative solutions to make professional medical learning more inclusive and approachable.
Professional Medical Resources: Bridging the Knowledge Gap
Historically, medical education has been tailored almost exclusively to healthcare professionals, leaving a significant gap for non-medical individuals seeking foundational or advanced knowledge. This gap is particularly evident in areas such as cardiology, where understanding complex systems like the human heart can feel overwhelming without prior training. While medical textbooks and academic journals offer in-depth content, their technical language often alienates beginners.
However, the rise of online platforms has opened new avenues for learning. Websites like Britannica and Wikipedia provide accessible and reliable overviews of cardiology topics. Additionally, platforms like Coursera and Udemy have developed beginner-friendly courses taught by qualified professionals. These courses often include interactive modules and real-world examples, making complex topics more digestible for non-medical learners.
Innovative Solutions for Non-Medical Learners
To address the challenges faced by non-medical background individuals, innovative approaches in medical education are necessary. One promising solution is the creation of hybrid learning models that combine online courses with interactive simulations and community forums. For example, cardiology-focused platforms can integrate 3D modeling of the human heart, enabling learners to visualize its anatomy and functions.
Additionally, targeted programs designed specifically for non-medical learners are becoming more common. These programs focus on simplifying medical jargon and using relatable analogies to explain complex concepts. For instance, understanding blood flow can be illustrated using everyday plumbing systems as metaphors, making the subject more intuitive for beginners.
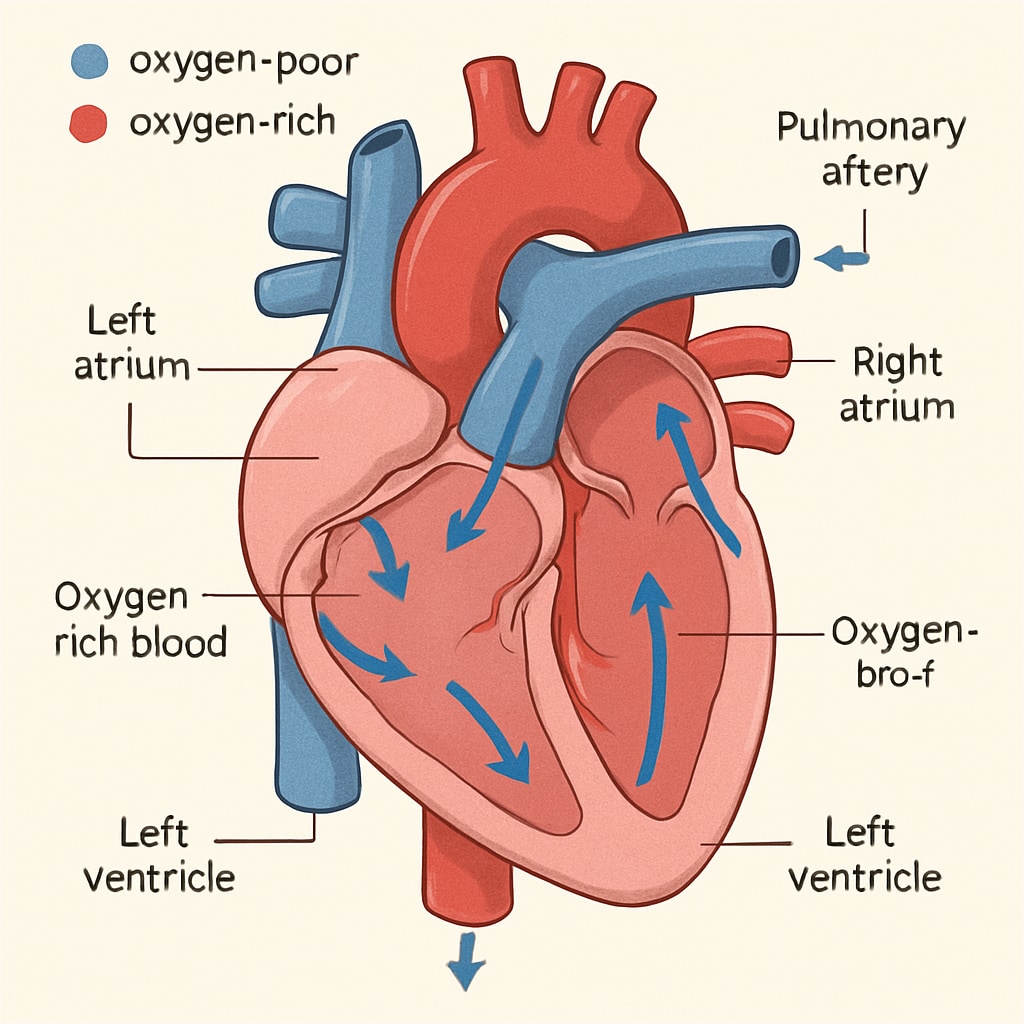
Why Cardiovascular Health Matters
Cardiology is one of the most sought-after fields among non-medical learners due to the widespread prevalence of heart-related conditions globally. Acquiring knowledge in this area not only empowers individuals to better understand their own health but also equips them to support loved ones who may face cardiovascular challenges.
For example, understanding the symptoms of a heart attack or the importance of maintaining healthy cholesterol levels can make a significant difference in early detection and prevention. By accessing online courses or reliable resources, non-medical individuals can learn these critical skills without the need for formal medical training.
How to Get Started with Medical Learning
If you’re interested in diving into professional medical knowledge without a formal background, here are some practical steps to get started:
- Choose beginner-friendly courses: Look for programs designed specifically for non-medical learners, often labeled as “basic” or “introductory.”
- Leverage multimedia resources: Opt for courses that include videos, visual aids, and simulations to enhance understanding.
- Join online forums: Participate in communities where learners and professionals exchange insights and answer questions.
- Set clear goals: Identify specific areas of interest, such as cardiology, and focus on acquiring targeted knowledge.
Ultimately, the key is to start small and build your understanding incrementally. With the right resources and dedication, anyone can gain valuable medical insights to improve their health and well-being.
Readability guidance: The article uses short paragraphs, active voice, and accessible language to ensure clarity and engagement. Lists and multimedia suggestions further simplify complex topics for non-medical learners.


