As health awareness continues to grow worldwide, many individuals without a medical background are eager to learn professional medical knowledge. This demand is particularly noticeable in specialized areas like cardiology, where understanding can empower people to make informed decisions about their health and the health of their loved ones. Despite the availability of medical education, resources often seem polarized—either too technical for non-professionals or overly simplistic. This article explores the educational gap and suggests innovative solutions, including online courses, to make professional medical knowledge accessible to all.
Understanding the Challenges for Non-Medical Learners
For non-medical professionals, diving into medical studies can feel overwhelming. Traditional medical education focuses on training healthcare professionals, so the content is rich in technical jargon, in-depth anatomy, and complex procedures. For example, cardiology—a field dedicated to the heart and circulatory system—requires understanding intricate topics like arrhythmias, myocardial infarction, and hemodynamics. Non-medical learners might struggle to find resources that are both accessible and accurate.
On the other end of the spectrum, many online resources or health-related articles simplify medical knowledge to a point where critical details are lost. This creates a gap for those seeking a deeper understanding without committing to years of formal education. Addressing this gap requires a middle-ground approach—education that is accurate yet approachable for non-medical backgrounds.
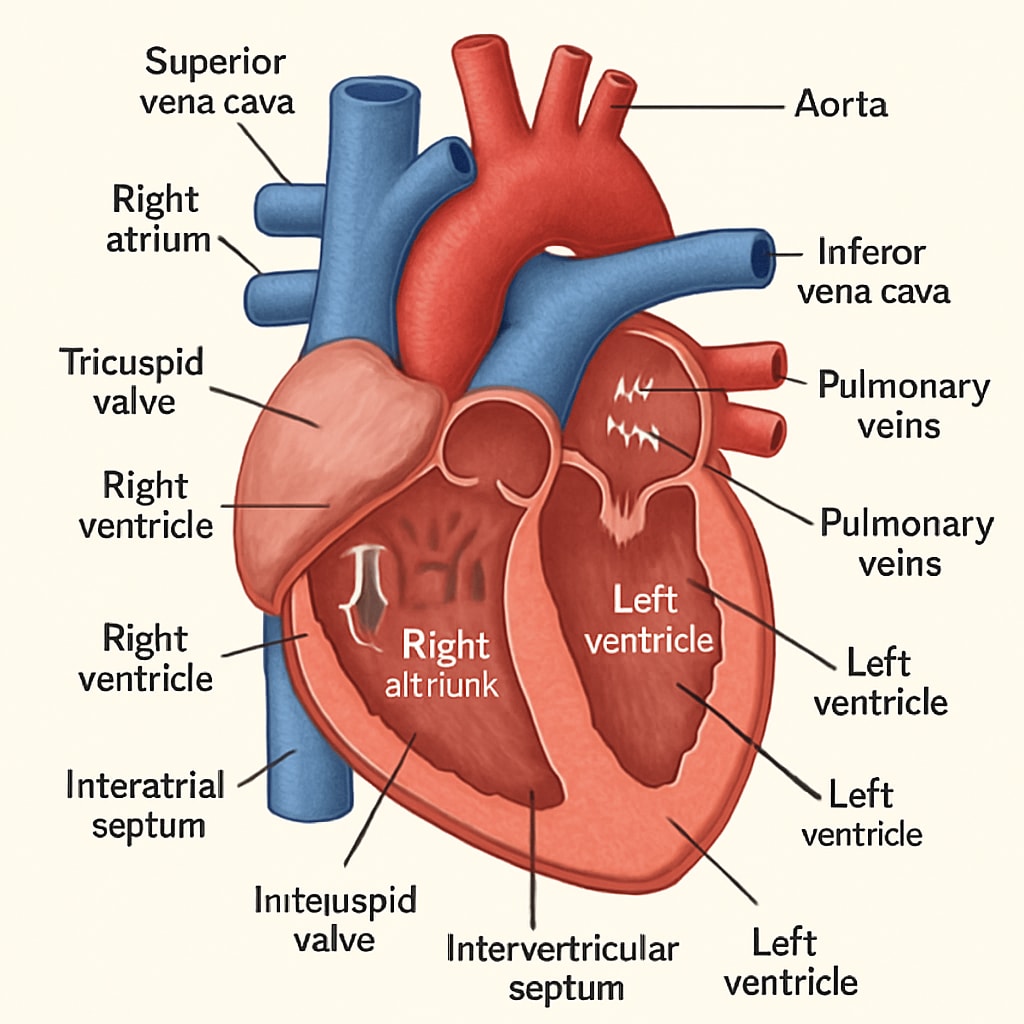
How Online Courses Are Revolutionizing Medical Education
The rise of online learning has opened doors for non-medical learners to explore specialized topics in medicine. Platforms like Coursera, edX, and Udemy offer courses created by leading universities and healthcare professionals. These courses often blend visual aids, interactive modules, and simplified explanations, making them ideal for beginners. For example, an introductory cardiology course might include:
- Basic heart anatomy and functions
- Common cardiovascular diseases and symptoms
- Preventative measures and lifestyle modifications
- Interpreting basic diagnostic tools like ECGs
Interactive features such as quizzes, videos, and discussion forums allow learners to engage deeply with the material while receiving feedback. Many courses also offer certifications, which can be valuable for professionals in related fields like fitness, nutrition, or emergency response.
Innovative Solutions to Close the Educational Gap
Innovative approaches are emerging to bridge the gap between professional medical education and the needs of non-medical learners. These solutions include:
- Hybrid Learning Models: Combining self-paced online courses with live Q&A sessions hosted by medical experts allows learners to clarify doubts in real-time.
- Medical Simulations: Virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) tools enable learners to explore anatomy and physiological processes interactively, providing a hands-on experience.
- Specialized Communities: Online forums and communities dedicated to specific topics, such as cardiology, can provide peer support and expert insights.
These methods not only make learning more engaging but also help ensure that the information is accurate and applicable. For example, learners interested in cardiology can benefit from virtual tools that simulate heart functions, helping them visualize concepts like blood flow or arrhythmia patterns.
Why Accessible Medical Knowledge Matters
Accessible medical knowledge can empower individuals to take charge of their health. It can also create a ripple effect, as informed individuals share their knowledge with family and community members. For those working in adjacent fields, such as fitness trainers or caregivers, understanding medical basics can enhance their professional skill set.
Moreover, in an era where misinformation spreads rapidly, providing reliable and clear medical education is crucial. Online platforms can serve as a counterbalance, equipping learners with credible information from trusted sources. For example, resources such as the cardiology section on Britannica offer reliable foundational knowledge, while platforms like edX provide structured courses for deeper learning.
As we look to the future, it’s clear that the demand for professional medical knowledge among non-medical learners will only grow. By embracing innovative educational models, we can ensure that everyone—regardless of their background—has the opportunity to learn and thrive.
Readability guidance: Short paragraphs and lists are used to summarize key points. Overly technical jargon is avoided, ensuring clarity for non-experts.


