In recent years, the integration of specialized fields like medicine into K12 education has become an exciting challenge. For students without a medical background, exploring professional fields can feel daunting, but resources like online courses, mentorship, and structured programs are making this journey more accessible than ever. Bridging the gap between foundational education and advanced knowledge is critical to fostering cross-disciplinary interest and equipping young learners with tools to succeed.
Why Early Exposure to Professional Fields Matters
Introducing K12 students to specialized fields such as medicine, engineering, or technology at an early stage can spark interest and open pathways to lifelong learning. Early exposure helps them understand the relevance of academic subjects in real-world applications while developing critical thinking skills. However, accessibility to suitable resources remains a challenge for many students.
For instance, students interested in medicine may struggle to find beginner-friendly materials that explain core concepts like anatomy, biology, and medical ethics. This is where curated resources such as beginner-focused online courses and interactive workshops come into play.

Accessible Learning Options for Non-Medical Background Students
Students without a formal background in medicine can benefit significantly from resources tailored to their level of understanding. Here are some effective options:
- Online Courses: Platforms like Khan Academy and Coursera offer introductory courses in biology, anatomy, and health sciences designed for young learners.
- Virtual Simulations: Tools like Visible Body and BioDigital Human allow students to visualize human anatomy interactively, helping them grasp complex concepts in an engaging way.
- Mentorship Programs: Partnering with medical professionals or educators can provide valuable guidance and real-world insights into the field.
- Hands-On Workshops: Local science centers or STEM initiatives often host workshops tailored for K12 students exploring medicine or related fields.
These resources bridge the gap between curiosity and comprehension, allowing students to transition smoothly from foundational learning to more advanced concepts.
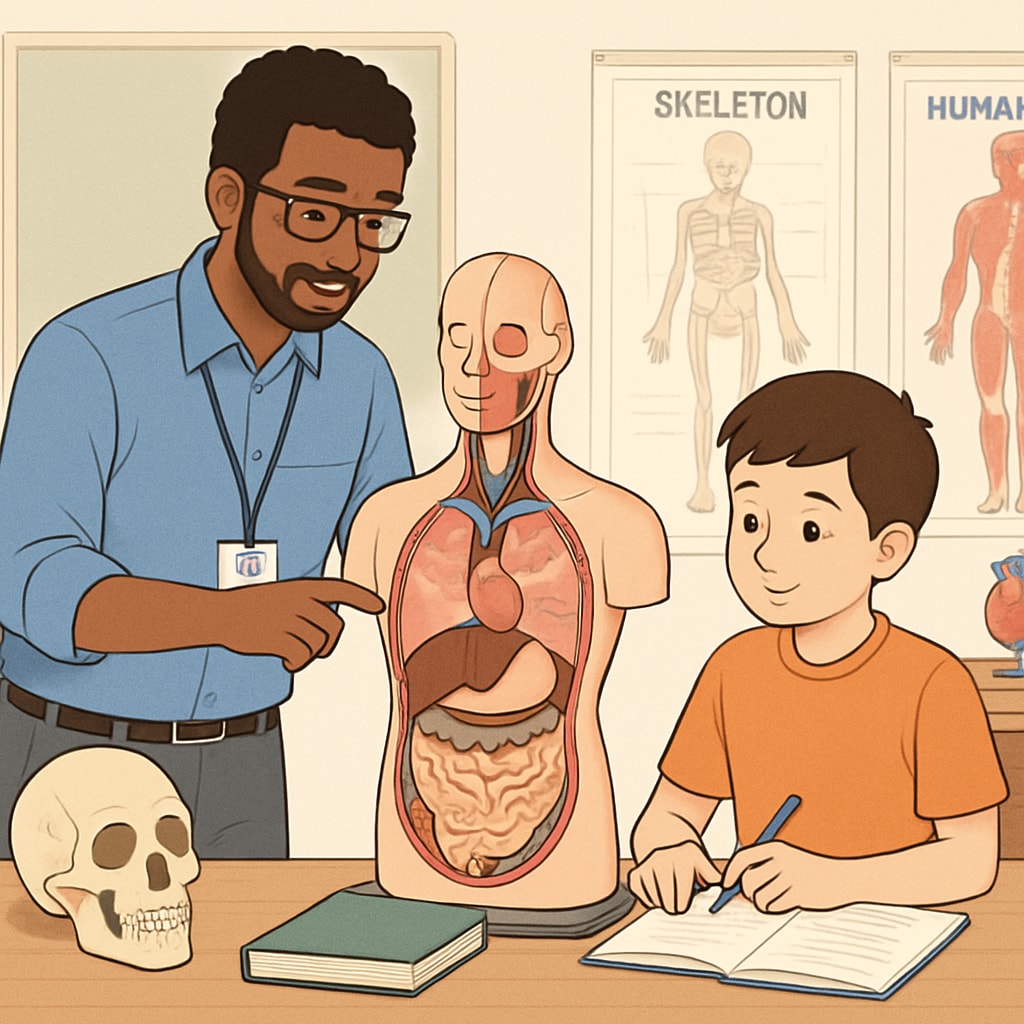
Overcoming Barriers to Medical Education
While resources for non-medical background students are increasingly available, barriers like accessibility, affordability, and relevance can limit their effectiveness. Here are actionable strategies to address these challenges:
- Accessibility: Schools and libraries can partner with organizations to ensure that online learning platforms and virtual simulations are available to students regardless of location.
- Affordability: Many platforms offer free or low-cost introductory courses to make specialized knowledge accessible to students from diverse socioeconomic backgrounds.
- Relevance: Tailoring content to align with K12 curricula ensures that learning materials complement existing studies and enhance understanding.
By addressing these challenges, educators and parents can help foster a supportive environment for students to explore specialized fields like medicine without overwhelming them.
Conclusion: Bridging the Gap Between Curiosity and Expertise
The journey for K12 students from foundational education to professional exploration requires thoughtful guidance and accessible resources. Tools such as online courses, mentorship programs, and interactive workshops play a pivotal role in bridging gaps, empowering students to pursue their interests in fields like medicine. As educational tools evolve, so does the potential for young learners to explore their passions and make informed career decisions.
For more information about how students can explore medical concepts interactively, check resources like Medical Education on Wikipedia or Medicine on Britannica.
Readability guidance: Use short paragraphs to maintain engagement, include lists for clarity, and incorporate transition words to ensure smooth flow between sections.


