Promoting mental health awareness among high school students is a crucial step in fostering emotional resilience and well-being. Organizing impactful mental health assemblies led by medical students can bridge the gap between educational institutions and healthcare expertise. This article provides a comprehensive guide for medical students to plan, design, and evaluate assemblies that address the psychological needs of teenagers effectively.
Step 1: Establishing Connections with Schools
The first step in organizing a mental health assembly is building partnerships with high schools. Medical students should initiate communication by reaching out to school administrators or counseling departments. Highlight the importance of addressing mental health challenges among adolescents, and propose an assembly as an engaging and educational approach.
- Explain the benefits: Emphasize how such assemblies can help reduce stigma, improve awareness, and provide students with tools to manage stress.
- Collaborate with counselors: Partnering with school counselors ensures the content aligns with the school’s needs and policies.
- Gain approval: Secure permission from school authorities to proceed with planning.
For additional context, explore resources on mental health education for youth at Youth Mental Health on Wikipedia.

Step 2: Designing Content for Impact
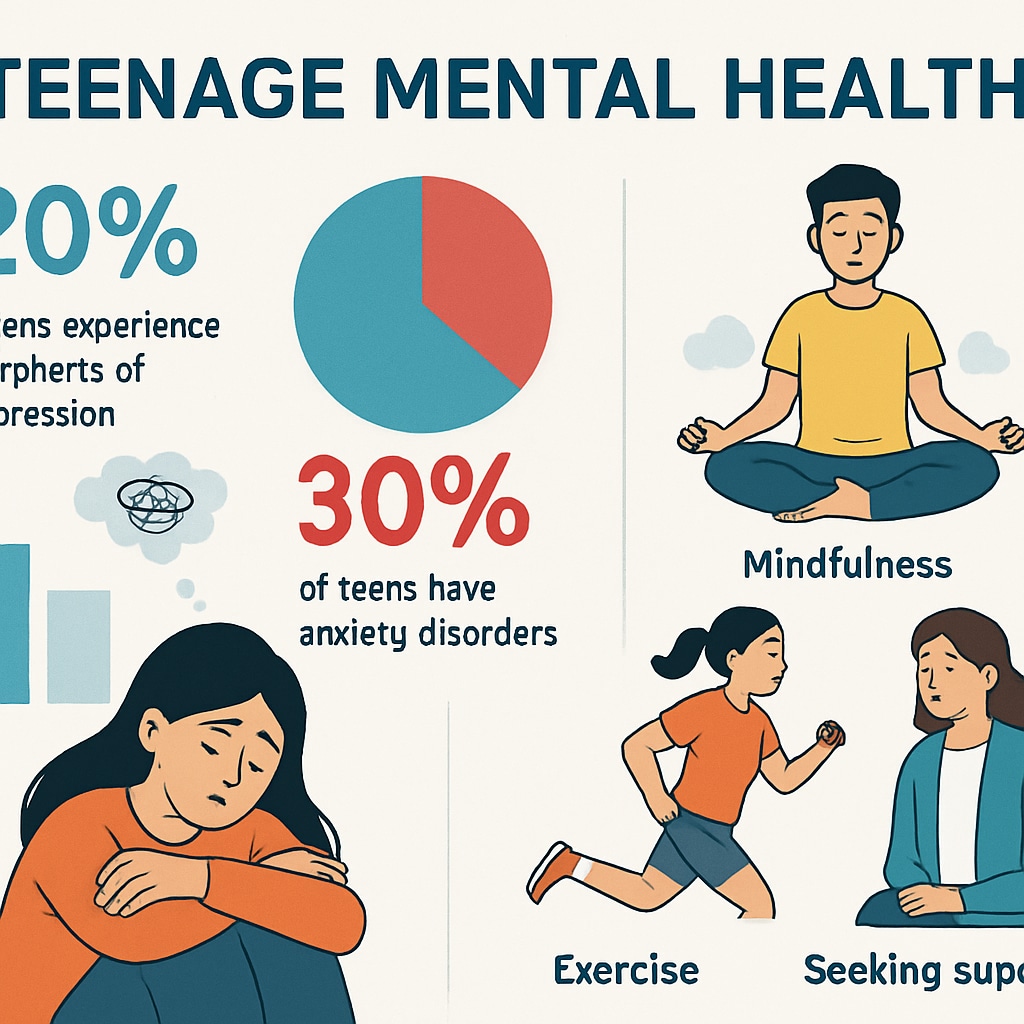
Creating meaningful and relatable content is essential for engaging high school students. The assembly should address common mental health issues such as anxiety, depression, and stress management while providing actionable strategies for coping.
- Know your audience: Tailor the content to the age group and cultural background of the students.
- Include interactive elements: Activities like role-playing, Q&A sessions, or small group discussions can make the assembly more engaging.
- Incorporate expert insights: Medical students can share relevant examples and clinical knowledge, ensuring accuracy and professionalism.
For inspiration, check out Mental Health Insights on Britannica.
Step 3: Delivering the Assembly
Effective delivery is key to ensuring the assembly’s success. Medical students should focus on clear communication, empathy, and engagement during the presentation.
- Practice beforehand: Rehearse the content to ensure smooth delivery and build confidence.
- Use visuals: Incorporate slides, videos, or diagrams to make the presentation more dynamic.
- Encourage participation: Invite students to ask questions, share experiences, or contribute to discussions.
Adding personal stories or relatable anecdotes can create a deeper connection with the audience.
Step 4: Evaluating and Improving
Post-assembly evaluation is essential to measure its impact and refine future initiatives. Gather feedback through surveys, focus groups, or informal conversations with students and staff.
- Analyze responses: Identify areas of improvement based on the feedback received.
- Track outcomes: Monitor changes in student behavior or engagement with school counseling services.
- Share results: Present findings to the school administration to build long-term partnerships.
Medical students may also consider publishing their insights or collaborating with other schools to expand the initiative’s reach.
Readability guidance: Use short paragraphs and lists to summarize key points. Distribute transition words evenly throughout the text, such as “however,” “therefore,” “in addition,” and “for example.”


