Teaching about mouse dolphins, marine biodiversity, and species presents a unique opportunity to spark curiosity in K12 students. These fascinating marine creatures, known for their diversity and ecological significance, can be used to introduce concepts like observation, classification, and environmental stewardship. By integrating visuals and interactive activities into lessons, educators can inspire students to explore the wonders of the ocean while cultivating critical thinking skills and a sense of responsibility toward marine conservation.
Why Mouse Dolphins Are Perfect for Teaching Marine Biodiversity
Mouse dolphins, also known as porpoises, belong to the family Phocoenidae and are small, toothed whales found in oceans and rivers worldwide. Their variety of species, including the vaquita, Dall’s porpoise, and harbor porpoise, makes them an excellent subject for teaching biodiversity and adaptation. Each species has unique physical traits, behaviors, and habitats that can be used to illustrate ecological principles and the importance of preserving marine ecosystems.
In addition, mouse dolphins are a lesser-known marine species compared to iconic animals like dolphins and whales. This provides an exciting opportunity for students to learn about creatures that are often overlooked, cultivating curiosity and expanding their understanding of ocean life.
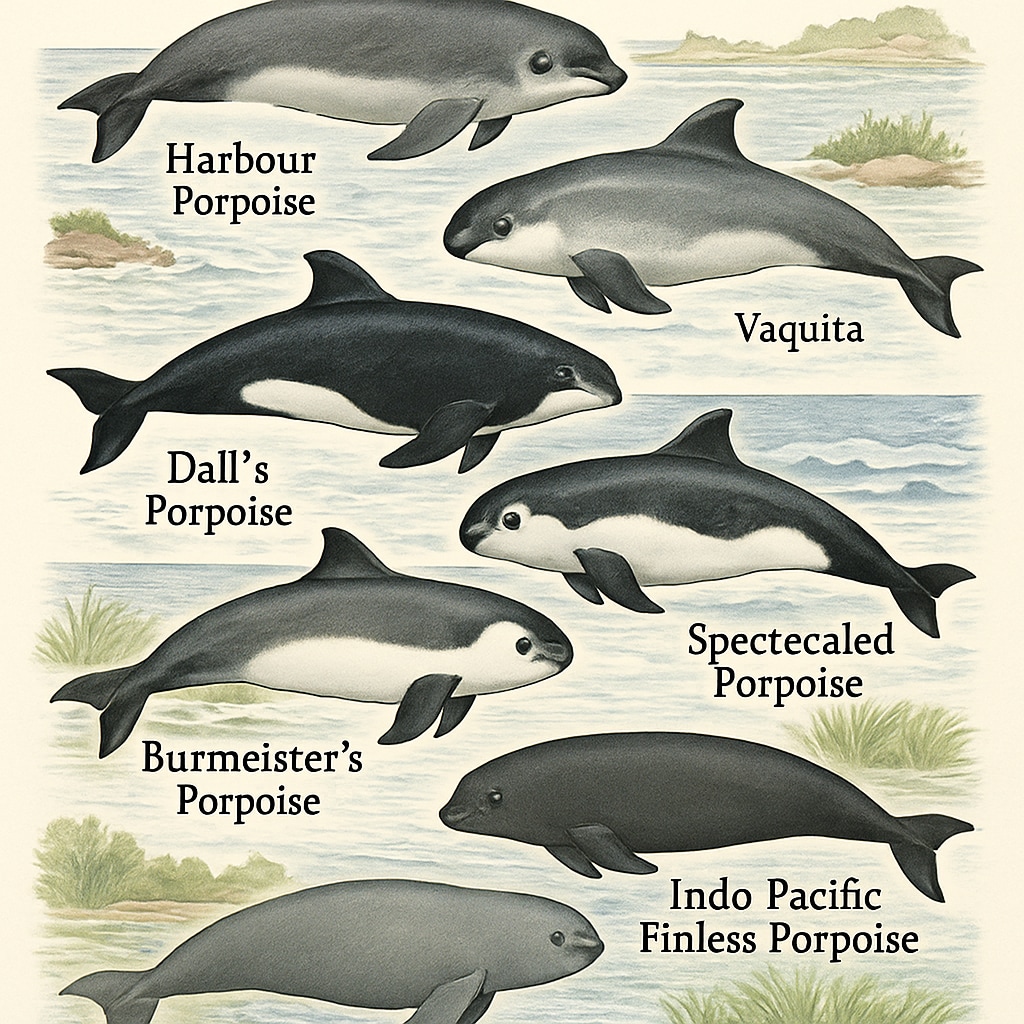

Classroom Activities to Explore Mouse Dolphin Species
To engage students effectively, incorporating hands-on activities is key. Here are some practical ideas for teaching mouse dolphin species in K12 classrooms:
- Species Identification Game: Provide students with labeled images of mouse dolphin species and challenge them to match each species to its habitat and unique characteristics.
- Habitat Mapping Exercise: Use world maps to explore the distribution of mouse dolphins and discuss how environmental factors influence their populations.
- Art and Science Integration: Ask students to draw or model different mouse dolphin species while learning about their anatomy and adaptations.
- Conservation Debate: Organize a classroom discussion on the threats facing mouse dolphins, such as pollution and bycatch, and brainstorm solutions for protecting these animals.
These activities can foster collaboration, enhance observation skills, and deepen students’ understanding of marine biodiversity.
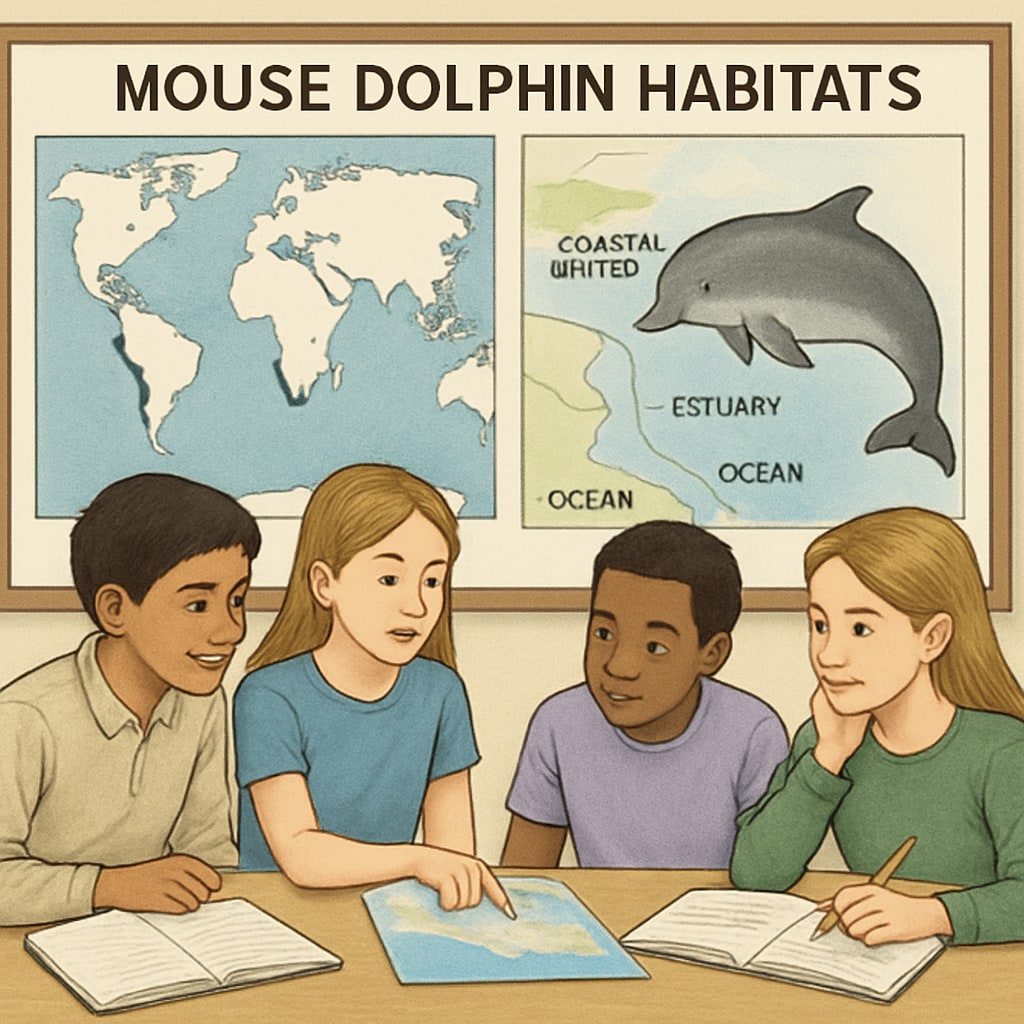
Fostering Environmental Awareness Through Marine Education
Teaching about mouse dolphins also creates an opportunity to address broader environmental issues. For example, educators can introduce topics such as habitat destruction, ocean pollution, and the impact of climate change on marine life. By connecting these issues to the lives of mouse dolphins, students can develop a personal connection to environmental challenges and feel empowered to take action.
In addition, lessons on mouse dolphins can emphasize the importance of conservation efforts. Educators can highlight organizations working to protect marine species, such as the World Wildlife Fund and International Union for Conservation of Nature, encouraging students to explore ways they can contribute to preserving biodiversity.
Recommended Resources for Teaching Mouse Dolphin Species
To support educators in implementing these lessons, here are some recommended resources:
- Books: “Marine Mammals of the World” by Thomas A. Jefferson, Marc A. Webber, and Robert L. Pitman offers detailed information on mouse dolphins and other marine mammals.
- Websites: Porpoise on Wikipedia provides a comprehensive overview of mouse dolphin species.
- Educational Videos: Documentaries like “Ocean Giants” include segments on porpoises and their ecological roles.
- Interactive Tools: Online platforms like National Geographic Kids offer interactive content to explore marine biodiversity.
By using these resources, educators can access accurate information, engaging visuals, and interactive tools to enhance their lessons.
Readability guidance: Use concise paragraphs, interactive lists, and vivid descriptions to maintain student engagement. Ensure language remains accessible while introducing scientific concepts, and incorporate visuals to support comprehension.


