Porpoises are fascinating marine mammals that play a critical role in maintaining the balance of ocean ecosystems. As part of the toothed whale family, porpoises are smaller and more compact compared to their dolphin relatives. Understanding the classification of porpoises is essential to appreciating their diversity and ecological significance. This article delves into the various species of porpoises, their unique characteristics, and their contribution to marine biodiversity.
What Are Porpoises? An Overview of Marine Life
Porpoises belong to the family Phocoenidae and are classified under the order Cetacea, which includes whales, dolphins, and porpoises. These aquatic mammals are often confused with dolphins due to their similar appearance, but porpoises are distinct in several ways. For instance, they have spade-shaped teeth, a triangular dorsal fin, and a shorter, more robust body.
Currently, there are seven recognized species of porpoises, each with unique adaptations to their environment. These species include:
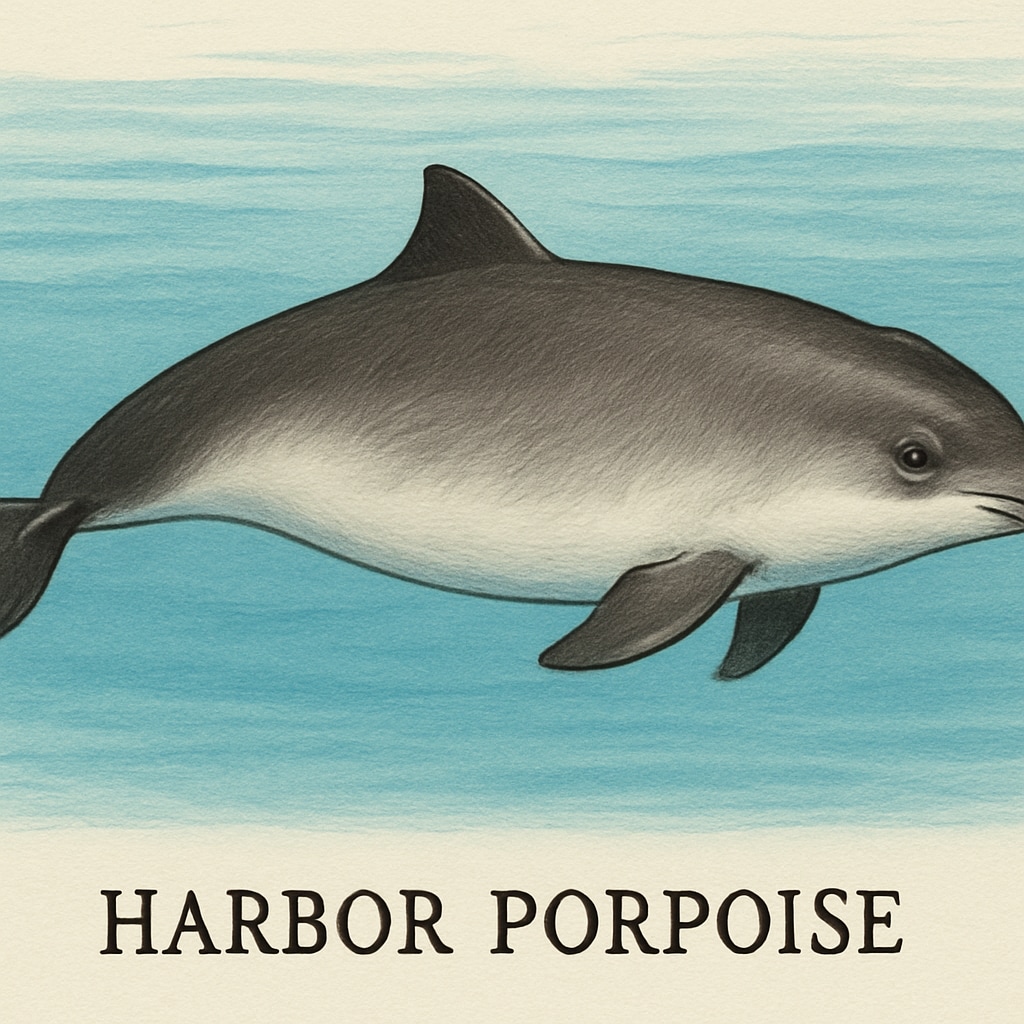
- Harbor Porpoise (Phocoena phocoena)
- Vaquita (Phocoena sinus)
- Dall’s Porpoise (Phocoenoides dalli)
- Burmeister’s Porpoise (Phocoena spinipinnis)
- Spectacled Porpoise (Phocoena dioptrica)
- Finless Porpoise (Neophocaena phocaenoides and Neophocaena asiaeorientalis)
The Classification of Porpoises: Understanding the Diversity
Porpoises are classified based on their physical traits, genetic differences, and ecological habitats. For example, the harbor porpoise (Phocoena phocoena) is one of the most widespread species, found in the coastal waters of the Northern Hemisphere. In contrast, the vaquita (Phocoena sinus), which is critically endangered, is endemic to the northern part of the Gulf of California.
Another notable species, the Dall’s porpoise (Phocoenoides dalli), is known for its striking black-and-white coloration, often resembling a small killer whale. Meanwhile, the finless porpoise (Neophocaena spp.) lacks a dorsal fin altogether and is adapted to warmer, shallow waters in Asia.
Each species plays an essential role in its respective ecosystem, contributing to the food chain and maintaining the health of marine environments. However, many porpoise species face threats from habitat loss, bycatch in fishing nets, and pollution.

Why Protecting Porpoises Matters
Porpoises are indicators of ocean health. Their presence in a habitat often reflects the availability of prey and the overall condition of the marine ecosystem. Protecting porpoises ensures the stability of food webs and supports the biodiversity of ocean environments.
Efforts to conserve porpoises include reducing bycatch through the use of safer fishing gear, establishing marine protected areas, and raising awareness about the ecological importance of these marine mammals. For example, organizations like the World Wildlife Fund (WWF) and the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) are actively working to protect species like the vaquita from extinction.
In addition, research on porpoise behavior, migration patterns, and genetic diversity continues to provide valuable insights into their conservation needs. By supporting such initiatives, we can help ensure that porpoises thrive in their natural habitats for generations to come.
Conclusion: Appreciating the Diversity of Porpoises
Porpoises are remarkable marine mammals with unique adaptations and an essential role in ocean ecosystems. By understanding their classification and the challenges they face, we can contribute to their conservation and the health of our oceans. From the widely distributed harbor porpoise to the critically endangered vaquita, each species reminds us of the beauty and fragility of marine life.
As stewards of the planet, it is our responsibility to protect these creatures and the habitats they call home. Through collective efforts in research, conservation, and sustainable practices, we can ensure a future where porpoises continue to thrive.
Readability guidance: This article uses short paragraphs and clear headings to enhance readability. It includes lists for concise information delivery and incorporates transitional phrases to maintain a smooth flow of ideas.


