Porpoises, unique marine species often mistaken for dolphins, hold a captivating place in ocean biodiversity. Their classification and biology offer exciting opportunities for K12 educators to inspire curiosity and conservation awareness in students. In this article, we will explore how vivid images and structured lessons on porpoise species can enhance science education while promoting a deeper understanding of marine ecosystems.
Introducing Porpoises: Distinctive Marine Species
Porpoises belong to the Phocoenidae family, a group of small cetaceans (marine mammals) that differ from dolphins in physical characteristics and behavior. For example, porpoises have rounded heads, shorter snouts, and spade-shaped teeth compared to dolphins’ conical teeth. They are found in various oceans and coastal areas around the world.
Educators can use high-quality images to introduce porpoises to K12 students. These visuals help highlight key features such as their subtle coloration, streamlined bodies, and unique dorsal fins. Visual aids spark curiosity and provide a tangible connection to marine biology topics.
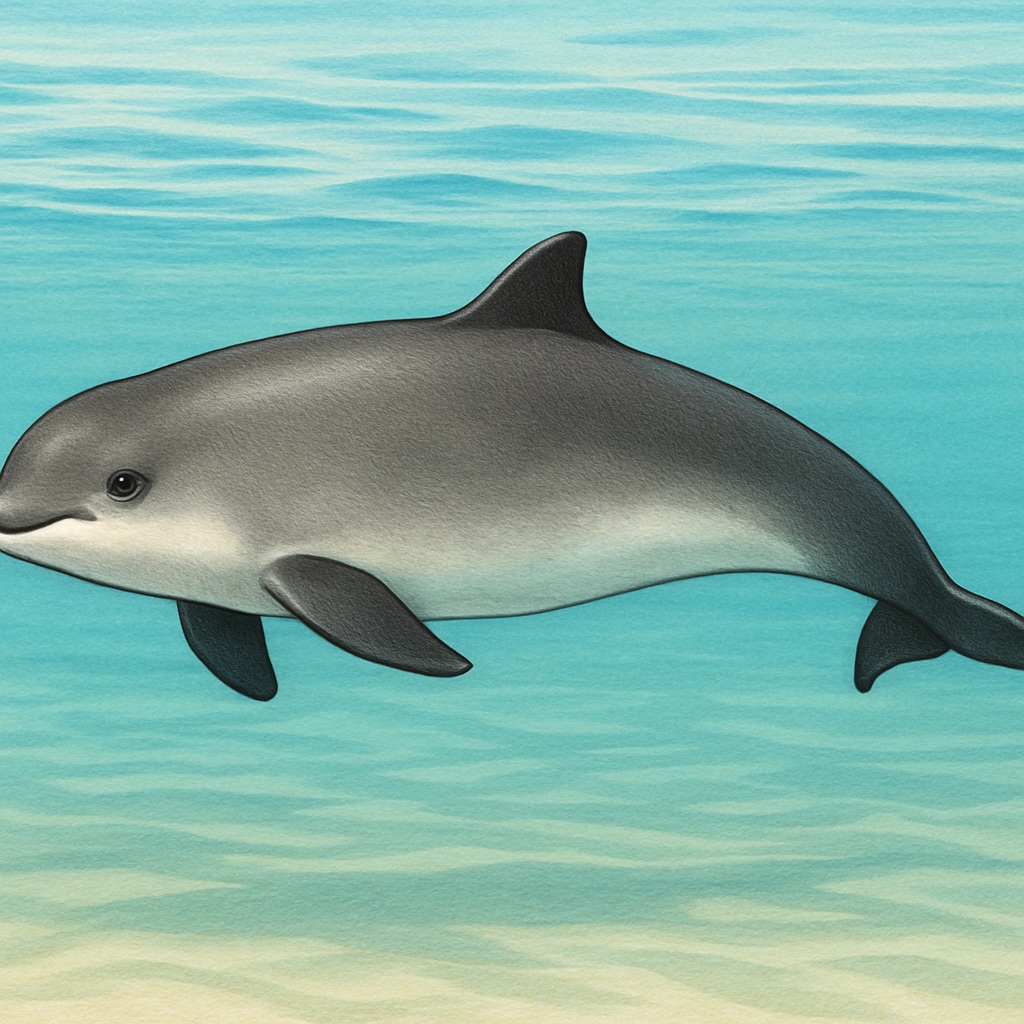
Classifying Porpoises: A Lesson in Biodiversity
Understanding porpoise classification helps students grasp broader concepts of taxonomy and biodiversity. The Phocoenidae family is composed of six recognized species, including the Harbor Porpoise (Phocoena phocoena), Dall’s Porpoise (Phocoenoides dalli), and Vaquita (Phocoena sinus). Each species is adapted to specific habitats and has unique traits.
Teachers can create engaging classroom activities by asking students to compare and contrast different porpoise species. For example:
- Harbor Porpoise: Found in cold, temperate waters; known for its shy behavior.
- Dall’s Porpoise: Distinguished by striking black-and-white coloration; found in the North Pacific.
- Vaquita: Critically endangered; native to the northern part of the Gulf of California.
By examining these species, students learn about the importance of preserving vulnerable habitats and protecting endangered marine animals.

Inspiring Ocean Conservation Through Education
Porpoises serve as an excellent introduction to conservation topics. By showing students the delicate balance of marine ecosystems, educators can foster a sense of responsibility toward protecting ocean life. Incorporating lessons on threats such as pollution, climate change, and fishing nets that endanger porpoises can deepen students’ understanding of environmental challenges.
For example, the critically endangered Vaquita has fewer than 20 individuals left in the wild due to habitat loss and bycatch in illegal fishing. Discussing such cases with students can encourage empathy and motivate action for conservation efforts.
Interactive tools like quizzes, group discussions, and hands-on projects (e.g., creating posters or presentations on porpoises) further enhance learning experiences while nurturing students’ creativity.
Using Images to Enhance Learning
Images play a critical role in science education, especially for visual learners. For porpoises, educators can use photos, diagrams, and infographics to illustrate anatomy, species differences, and habitats. Additionally, videos showing porpoises in their natural environment provide dynamic and engaging content for students.
These visual aids not only make lessons more accessible but also leave a lasting impression, encouraging students to explore marine biology and conservation beyond the classroom.
Conclusion: Porpoises are a fascinating subject for K12 science education, offering valuable lessons in marine species classification and environmental stewardship. By leveraging vivid images and interactive teaching methods, educators can inspire students to appreciate ocean biodiversity and take action to protect it.


