Technology addiction, child protection, and mental health have become interconnected challenges in raising digitally-native generations. Research from the American Academy of Pediatrics shows children aged 8-12 spend 4-6 hours daily on screens, while teens average 9 hours – time that could nurture creativity or physical activity. This digital saturation impacts developing brains in three measurable ways:
The Cognitive Consequences of Excessive Screen Time
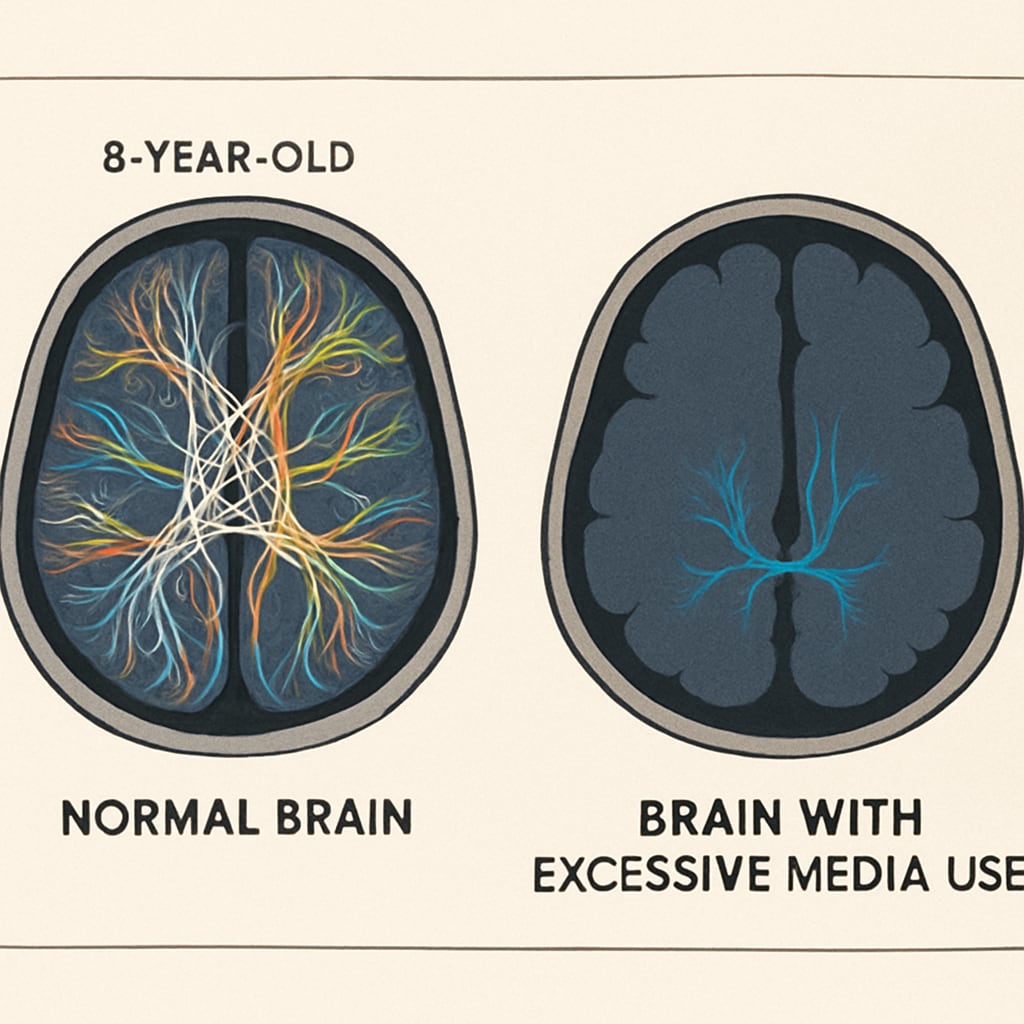
Neuroscience reveals that passive screen consumption alters brain structure in children. A JAMA Pediatrics study found that preschoolers with >1 hour daily screen time showed:
- Reduced white matter integrity affecting language skills
- Shorter attention spans during offline activities
- Decreased problem-solving creativity by 23%
Protecting Emotional Wellbeing in Digital Environments
Social media platforms design features that trigger dopamine responses, creating dependency loops in young users. The mental health correlation appears strongest when:
- Nighttime usage disrupts sleep cycles
- Social comparison replaces real-world interactions
- Algorithmic content replaces self-directed play
However, balanced technology use shows benefits. The key lies in implementing “tech-healthy” habits:

Practical Strategies for Balanced Digital Exposure
Parents and educators can implement these research-backed approaches:
- Create tech-free zones: Designate meal areas and bedrooms as device-free spaces
- Schedule analog time: Ensure 2+ hours daily of unstructured play using physical objects
- Model behavior: Children mirror adult screen habits – practice mindful usage
As technology becomes more embedded in education, protecting children’s mental health requires conscious effort to maintain balance. Small, consistent changes yield significant developmental benefits.


