Research, evaluation, social inequality, and education are intertwined concepts that significantly impact the K12 education landscape. In today’s society, ensuring educational equity is a pressing concern, and research and evaluation play pivotal roles in this pursuit.

The Professional Definitions of Research and Evaluation in K12 Education
Research in K12 education refers to the systematic investigation of educational phenomena. It aims to generate new knowledge, understand teaching and learning processes better, and identify effective educational practices. For example, researchers might study how different teaching methods affect students’ learning outcomes. Evaluation, on the other hand, is the process of making judgments about the value, effectiveness, or quality of an educational program, policy, or practice. It helps determine whether educational initiatives are achieving their intended goals. As stated on Educational research on Wikipedia, these two concepts, while related, have distinct focuses.
Key Differences between Research and Evaluation
One key difference lies in their purposes. Research is often exploratory, seeking to expand our understanding of educational issues. Evaluation, however, is more focused on assessing the performance and impact of existing programs. Another difference is in their methods. Research may use a wide range of qualitative and quantitative methods, such as surveys, interviews, and experiments. Evaluation typically relies on specific evaluation criteria and metrics to measure success.
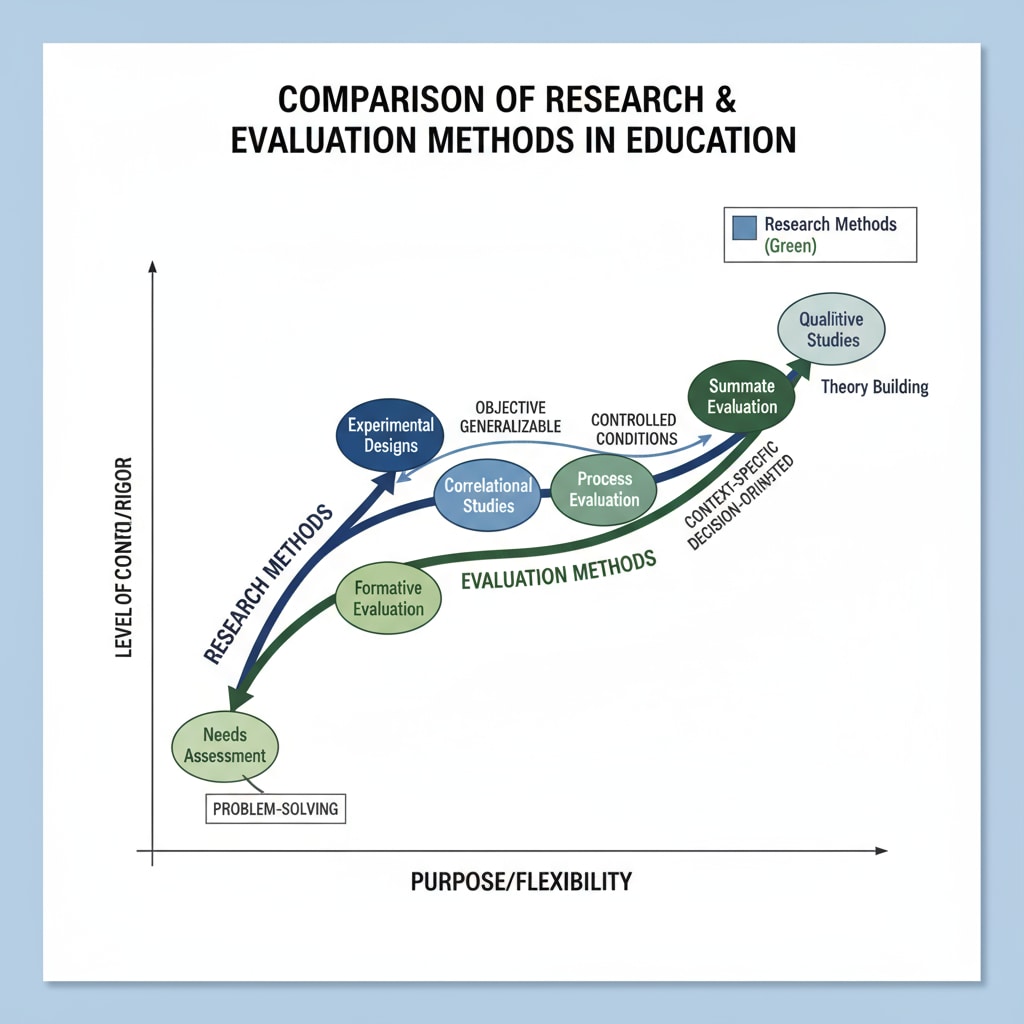
For more insights, refer to Educational evaluation on Britannica.
Research and Evaluation as Tools for Addressing Social Inequality in K12 Education
Research can identify the root causes of social inequality in education, such as disparities in funding, access to resources, and teacher quality. By understanding these issues, policymakers can develop targeted interventions. Evaluation, on the other hand, can measure the effectiveness of these interventions. For instance, it can determine whether a new program aimed at reducing achievement gaps is actually making a difference. In addition, both research and evaluation can provide evidence to advocate for policy changes that promote educational equity.
Readability guidance: This article uses short paragraphs and lists to summarize key points. Each H2 section provides a clear focus, and the use of passive语态 is minimized. Transition words like ‘however’, ‘for example’, and ‘in addition’ are used throughout to enhance the flow of the text.


