Robotics education has become increasingly popular in K12 classrooms, yet many courses still struggle to balance foundational concepts with advanced technical skills. This article introduces a new robotics course designed for beginners, leveraging project-based learning to bridge the gap between overly simplistic and highly specialized curriculum. With this innovative approach, students can progress from zero knowledge to creating their first functional robot.
Why Robotics Education Needs a Fresh Approach
Robotics courses often fall into one of two extremes: they are either too basic to keep students engaged or too technical for beginners to follow. As a result, many students fail to develop a comprehensive understanding of robotics concepts, which undermines their interest and skill development. This dilemma highlights the need for a more balanced curriculum that provides a gradual yet comprehensive learning path.
To address this issue, a week-long project-based learning model has been developed, focusing on practical, hands-on activities. This method allows students to explore essential components such as microcontrollers, sensors, and communication systems, while simultaneously building a functional robot.

Key Components of the Beginner Robotics Course
The course integrates theoretical and practical learning, ensuring that students gain a solid foundation while staying motivated through real-world applications. Below are the core elements:
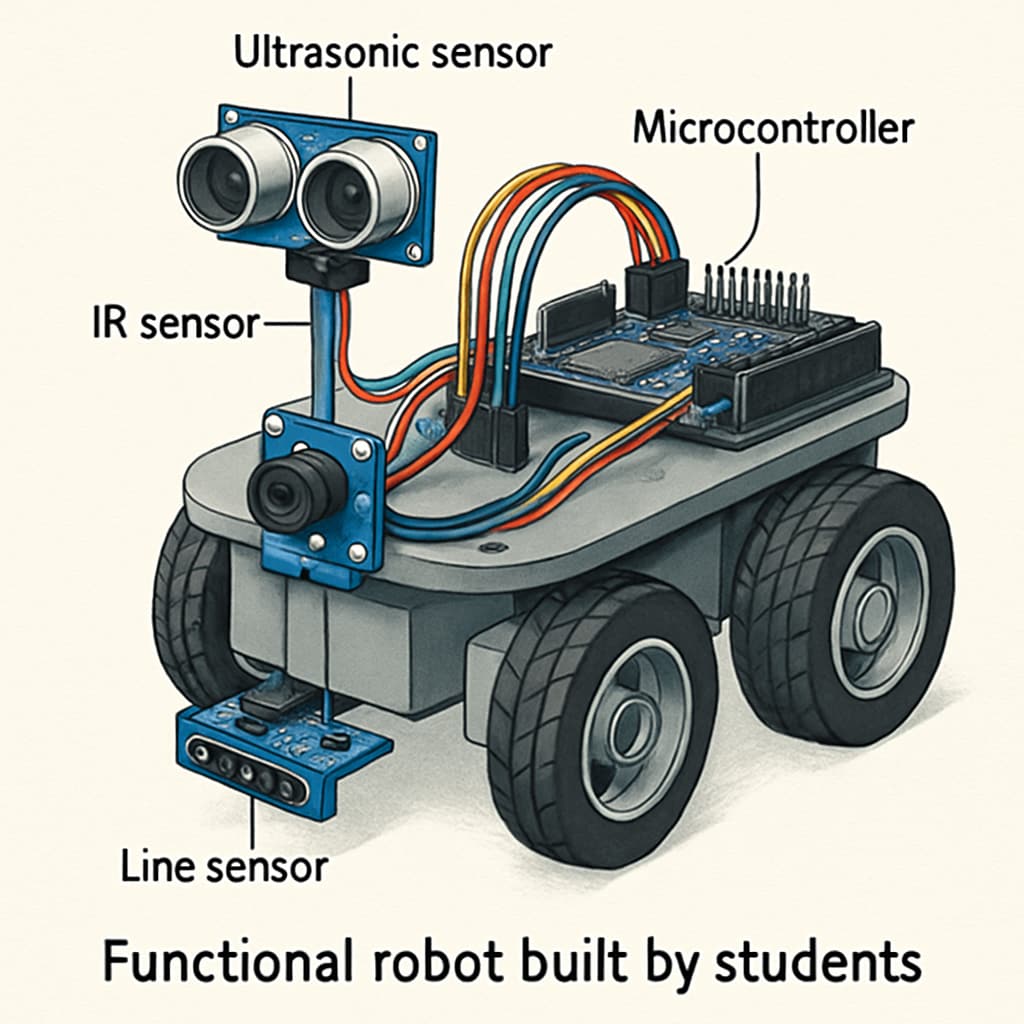
- Microcontrollers: Students learn how to program and control microcontrollers, the “brains” of their robots.
- Sensors and Actuators: Introducing tools that help robots interact with their environment.
- Communication Systems: Exploring wireless communication methods for robot control and data transfer.
- Project Assembly: Hands-on experience in assembling and testing functional robots.
By following these steps, students can transition from understanding basic concepts to applying them in a meaningful way. This approach not only builds technical skills but also fosters problem-solving and creativity.
The Benefits of Project-Based Learning in Robotics
Project-based learning has proven to be an effective teaching method in STEM education. In robotics, this approach encourages active learning and enhances student engagement. For example:
- Hands-On Experience: Students retain more knowledge by applying concepts in real-time.
- Critical Thinking: Building a robot requires troubleshooting and innovative solutions.
- Team Collaboration: Group projects teach teamwork and communication skills.
As a result, students not only gain technical expertise but also develop essential soft skills that are valuable in future education and careers. To learn more about project-based learning, explore this Wikipedia entry.
Impact on K12 Robotics Education
This beginner-friendly course has the potential to reshape K12 robotics education. By making robotics more accessible, it inspires students to pursue STEM fields and equips them with the skills needed for advanced studies. Additionally, it bridges the gap between basic and professional-level robotics, paving the way for a more inclusive and effective curriculum.
For further understanding of robotics and its applications, visit the Robotics page on Britannica.
In conclusion, the week-long robotics course provides an ideal starting point for beginners, combining theoretical knowledge with practical experience. Through project-based learning, students can transform their curiosity into expertise, creating functional robots and laying the foundation for future innovation.


