School statistics, PISA, and education data are essential tools in the complex landscape of K12 education. These elements provide valuable insights that can shape educational strategies and enhance student outcomes.

As we delve into the world of educational data, it becomes evident that understanding how to collect, interpret, and apply this information is key.
The Significance of Education Data
Education data serves as a window into the effectiveness of educational systems. It offers a comprehensive view of student performance, teaching methods, and overall school progress. For example, by analyzing data on student achievement, educators can identify areas where students are struggling and develop targeted interventions. This data-driven approach ensures that resources are allocated more efficiently, leading to improved educational quality. Education statistics on Wikipedia
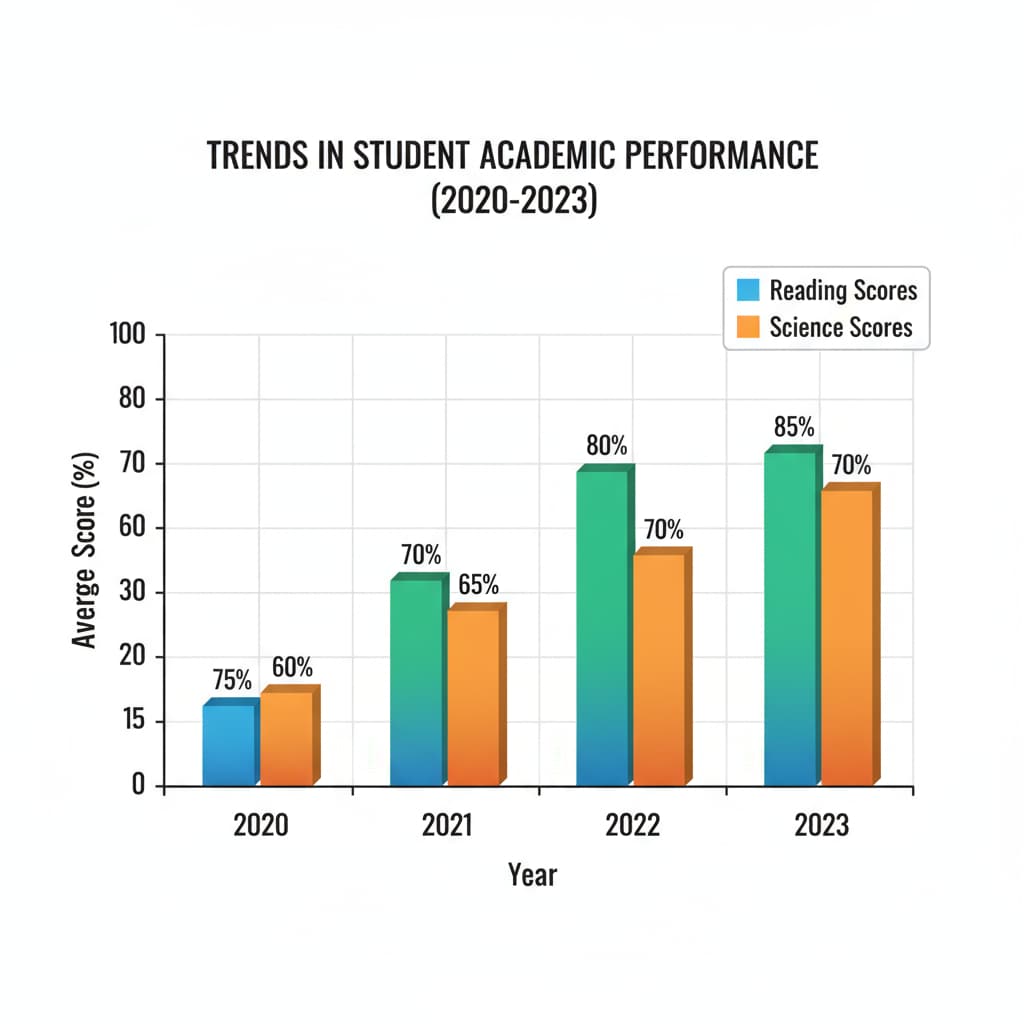
PISA: A Global Benchmark
PISA, or the Programme for International Student Assessment, is a renowned international assessment that measures the skills and knowledge of 15-year-old students across the globe. It assesses students in reading, mathematics, and science, providing a comparative analysis of educational systems worldwide. The data collected through PISA allows countries to benchmark their performance against others, identify areas for improvement, and learn from successful practices. PISA official website
Understanding the data from PISA can inform educational policies and reforms. For instance, if a country performs poorly in a particular subject area, it can use the insights from PISA to adjust its curriculum, teaching methods, or teacher training programs. This international perspective helps in setting high standards and striving for educational excellence.
Moreover, PISA data can also shed light on factors outside of the classroom that may influence student performance, such as socioeconomic background, family support, and access to resources. By considering these factors, educators and policymakers can develop more inclusive and effective educational strategies.
Readability guidance: In this article, we have used short paragraphs to convey information clearly. Each H2 section presents key points in a structured manner. We have also incorporated transition words like “for example” and “moreover” to enhance the flow of the text. The focus is on making the content accessible and understandable for readers interested in education data and its implications for K12 education.


