STAR Test, Percentile Rank, and Student Performance Evaluation are crucial aspects in understanding a student’s academic progress. The STAR test, a widely used assessment tool, provides scores and percentile ranks that are often used to gauge a student’s performance. However, it’s essential to understand the reliability and educational implications of these results.

The Basics of STAR Test
The STAR test, short for Standardized Testing and Reporting, is designed to measure a student’s knowledge and skills in various subjects such as reading, math, and language arts. It is a computer-adaptive test, which means the difficulty of the questions adjusts based on the student’s responses. This adaptability aims to provide a more accurate assessment of the student’s abilities. According to ETS’s official website, the test is aligned with state and national standards, ensuring that it measures relevant educational content.
Understanding Percentile Ranks
Percentile ranks are a key part of the STAR test results. A percentile rank indicates the percentage of students in a specific group (usually the same grade level) who scored lower than a particular student. For example, if a student has a percentile rank of 80 in math, it means that they scored higher than 80% of the students in their grade. This ranking system helps parents and educators compare a student’s performance to their peers. As explained on the National Center for Education Statistics website, percentile ranks offer a relative measure of a student’s standing.
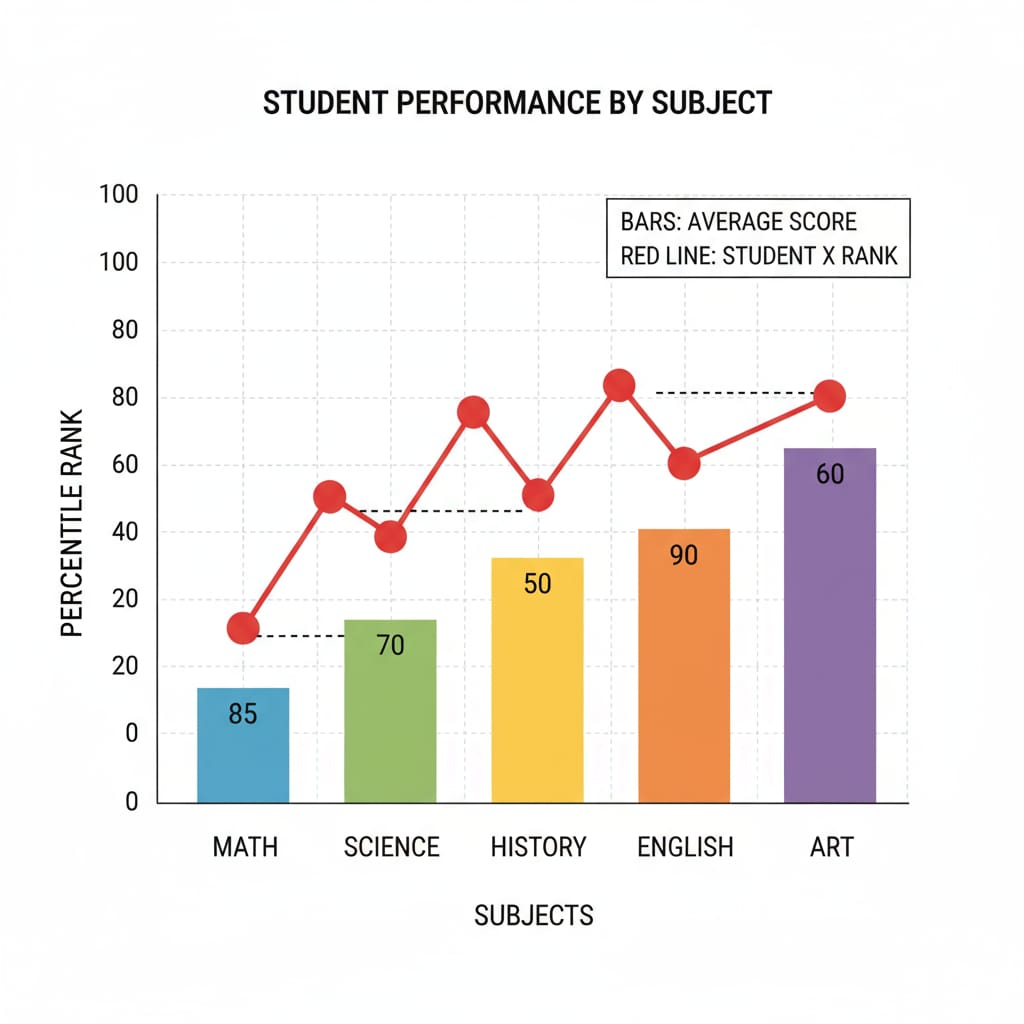
However, it’s important to note that percentile ranks have limitations. They only show a student’s position relative to others and do not necessarily reflect the student’s absolute level of knowledge or skills. A student with a high percentile rank may still have areas of weakness that need improvement.
Readability guidance: As seen above, we’ve used short paragraphs to present information clearly. Each H2 section has key points. Passive voice is minimized, and transition words like “however” are used to connect ideas smoothly.


