High-achieving STEM students often encounter a pivotal decision: choosing between computer science, bioengineering, and medicine. Each field offers unique career prospects, rigorous academic challenges, and varying degrees of personal compatibility. Understanding these aspects is crucial for students to make informed decisions that align with their long-term goals.
Understanding the Professional Landscape
Each of these fields—computer science, bioengineering, and medicine—holds distinct advantages and challenges. Below is a breakdown of their career prospects and industry demands:
- Computer Science: Known for its versatility, computer science professionals can work in areas such as artificial intelligence, software development, cybersecurity, and data science. The field is highly dynamic, with strong growth potential in sectors like tech, finance, healthcare, and more. Salaries are competitive, and remote work options are widely available.
- Bioengineering: This interdisciplinary field bridges biology and engineering, offering opportunities in medical device design, genetic engineering, and pharmaceutical development. Bioengineering professionals contribute to cutting-edge innovations, including prosthetics and tissue regeneration, but may face slower career progression compared to computer science.
- Medicine: Medicine offers the chance to directly impact lives through healthcare delivery. Physicians and specialists enjoy stable job security, high earning potential, and societal respect. However, the path involves extensive education, high financial costs, and a demanding lifestyle, especially during residency.
These career paths not only differ in their industry demands but also in their work-life balance, potential for innovation, and societal contributions.
Academic Pathways and Challenges
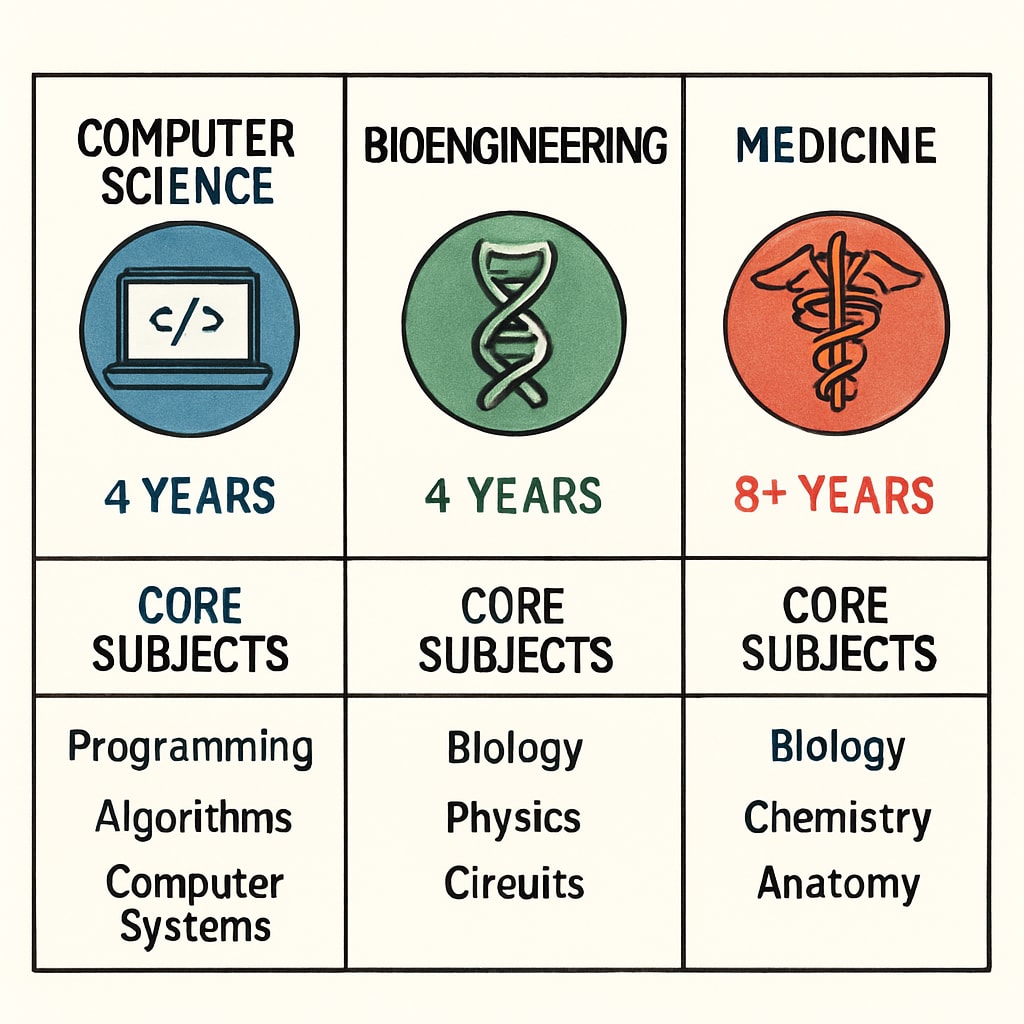
Choosing a major means committing to years of academic preparation. Below is a summary of the educational paths required for each field:
- Computer Science: A bachelor’s degree is typically sufficient to start a career. Advanced roles may require certifications or postgraduate education, but entry into the workforce can be swift compared to other STEM fields.
- Bioengineering: Undergraduate programs focus on biology, engineering principles, and mathematics. Graduate studies often become necessary for specialized roles, such as research or product development.
- Medicine: The path to becoming a physician includes a pre-med undergraduate degree, medical school, and residency. This journey can take over a decade and demands dedication to rigorous coursework and clinical practice.
While computer science offers quick entry into the workforce, bioengineering and medicine require deeper commitments to academic and professional training.
Aligning Personal Strengths and Interests
In addition to career prospects and academic challenges, personal compatibility plays a significant role in professional success. Here are factors to consider:
- Skills: Computer science favors logical thinking, programming, and problem-solving. Bioengineering requires a strong foundation in biology and engineering concepts, while medicine demands empathy, resilience, and excellent communication.
- Interests: Students passionate about technology and innovation may thrive in computer science or bioengineering. Those drawn to direct patient care and improving lives should consider medicine.
- Values: Consider whether you value creativity, scientific discovery, or societal impact. Different fields cater to different values, influencing job satisfaction.
Reflection on these aspects can help students identify which path aligns with their strengths and aspirations.
How to Make a Well-Informed Decision
To navigate this decision effectively, students can follow a structured framework:
- Research: Explore each field’s job market, required skills, and academic paths using trusted resources such as Computer Science on Wikipedia and Bioengineering on Britannica.
- Self-Assessment: Evaluate your skills, interests, and long-term goals. Personality tests or career counseling can provide valuable insights.
- Shadowing and Internships: Gain hands-on experience in each field to understand the realities of the workplace.
- Consult Experts: Speak with professionals, mentors, or alumni from each discipline for advice and insights.
Making a decision based on thorough research and self-reflection ensures a smoother academic and professional journey.
Conclusion
Navigating the crossroads between computer science, bioengineering, and medicine can be daunting for STEM students. By evaluating career prospects, academic pathways, and personal alignment, students can choose a path that resonates with their aspirations and strengths. Remember, the best decision is one that balances practicality with passion.


