In the realm of language teaching, early education plays a crucial role, and the choice of teaching methods can significantly impact a child’s language acquisition journey. In the early primary school stage, teaching a second language like English requires careful consideration of various approaches. Let’s explore some of the most common and effective methods, along with their pros and cons.
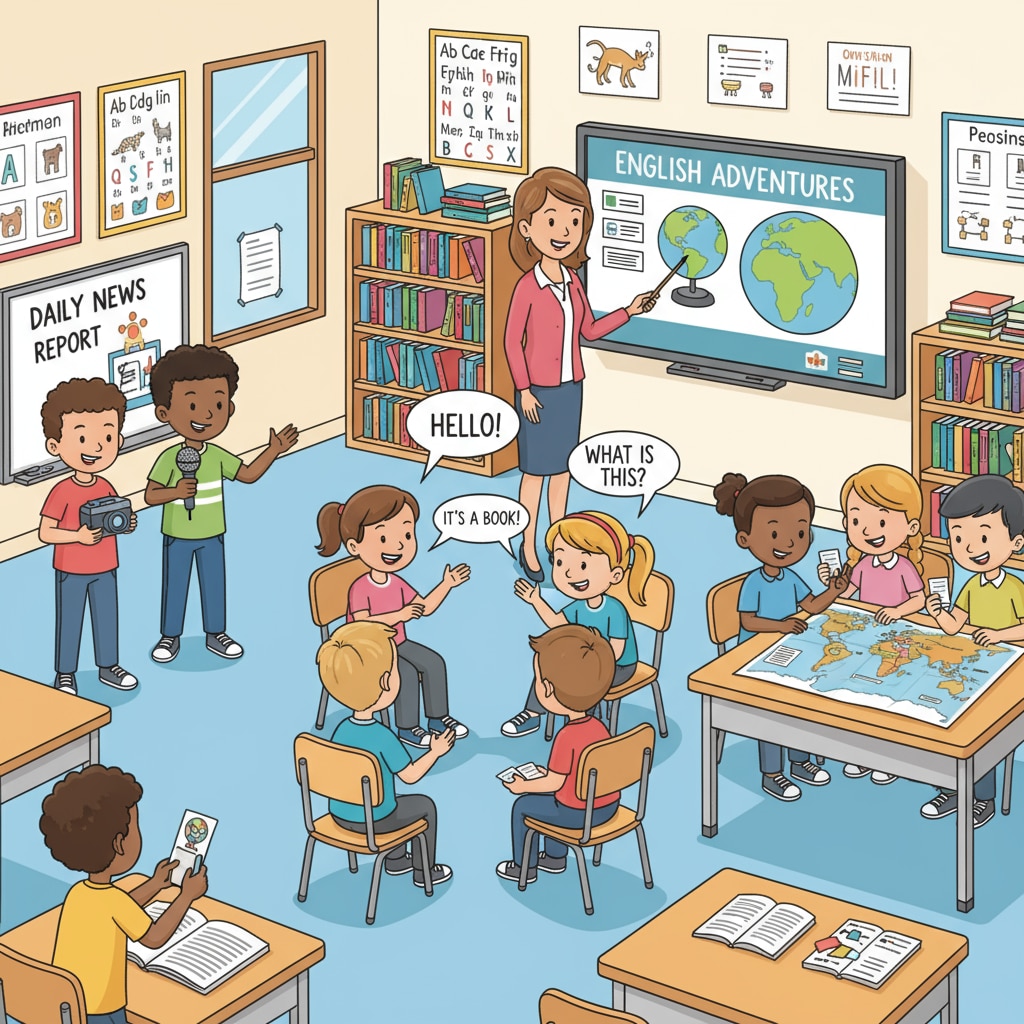

The Communicative Approach
The communicative approach emphasizes real-life communication in the target language. It aims to develop students’ ability to use the language for meaningful interaction. For example, in class, students engage in role-plays, group discussions, and problem-solving tasks. This method encourages fluency and confidence in speaking. However, it might not provide enough explicit grammar instruction. According to Wikipedia, the communicative approach has been widely adopted in language teaching around the world.
The Audio-Lingual Method
The audio-lingual method focuses on listening and speaking skills through repetition and drills. Teachers present dialogues, and students practice them repeatedly until they can respond automatically. This method helps students develop good pronunciation and intonation. But it can be rather mechanical and may not promote creativity. As explained on Britannica, the audio-lingual method was popular in the mid-20th century.
The task-based approach involves students completing various tasks, such as making a poster, writing a short story, or conducting a survey. This method integrates language learning with practical activities, enhancing students’ problem-solving and critical thinking skills. Yet, it may be challenging to design tasks that suit different proficiency levels.
In conclusion, when it comes to language teaching in early primary education, there is no one-size-fits-all approach. Educators and parents should consider the unique needs and learning styles of each child. By understanding the pros and cons of different teaching methods, they can make informed decisions to unlock the child’s language potential.
Readability guidance: Each section presents a clear teaching method, highlighting its features and limitations. Short paragraphs and simple language are used for easy comprehension. Transition words like ‘however’ and ‘but’ are employed to show contrasts.


