High school geometry in the US education system is a fascinating area that encompasses a rich array of teaching resources. It plays a crucial role in shaping students’ spatial reasoning and mathematical understanding.
As educators strive to impart knowledge, the availability and utilization of these resources are key factors. In this article, we will explore the various aspects of US high school geometry, from its curriculum to teaching methods and the emerging digital trends.
The Foundation of US High School Geometry Curriculum
The US high school geometry curriculum is built on several fundamental concepts. It typically starts with an introduction to basic geometric shapes such as points, lines, and angles. According to Wikipedia’s entry on Geometry education in the United States, students then progress to more complex topics like congruence and similarity of triangles. This foundation is essential for developing logical thinking skills. For example, understanding the properties of parallel lines helps students solve problems related to angles in geometric figures.
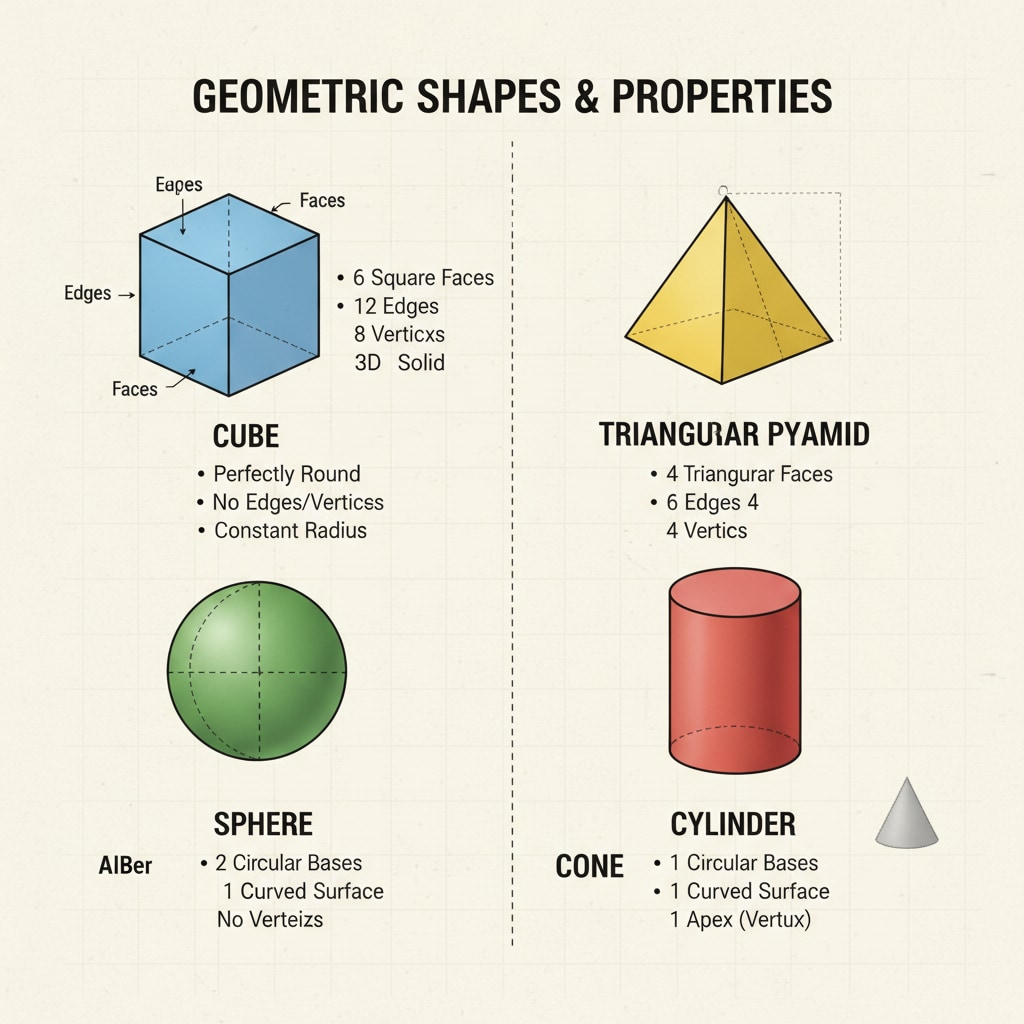
Teaching Resources in US High School Geometry
In addition to textbooks, there is a wide range of teaching resources available. Online platforms offer interactive lessons, virtual manipulatives, and video tutorials. These resources make learning more engaging. For instance, websites like Khan Academy provide free geometry courses with detailed explanations. Educators also use physical manipulatives such as geometric solids to help students visualize 3D shapes. As per Britannica’s information on geometry education, the combination of these resources caters to different learning styles among students.
The digital age has brought about significant changes in US high school geometry education. Interactive software allows students to explore geometric concepts in a dynamic way. For example, they can manipulate shapes in real – time and observe how changes in one parameter affect others. This hands – on approach enhances understanding. Moreover, digital assessment tools provide immediate feedback, enabling students to identify areas for improvement quickly.
Readability guidance: By using short paragraphs and lists, we can clearly present the key points. For example, in the section on teaching resources, we list different types of resources. The use of transition words like ‘for example’ and’moreover’ helps in smooth flow. Also, we keep the passive voice to a minimum and control the length of sentences for better readability.


