Traditional school systems often face challenges with learning retention, especially after extended summer breaks. Year-round schooling, learning retention, and summer break alternatives have emerged as innovative solutions to tackle this issue. By reimagining how school calendars function, educators can provide students a more consistent learning experience that enhances memory retention and academic performance.
Why Year-Round Schooling Matters
The traditional school calendar, with a long summer vacation, has been criticized for contributing to the “summer slide”—a phenomenon where students forget much of what they learned during the school year. Cognitive research shows that extended breaks disrupt the learning process, making it harder for students to retain key concepts. Year-round schooling, which alternates shorter sessions of learning with consistent breaks, minimizes this disruption.
One popular alternative is the 45-15 model, where students attend school for 45 days followed by a 15-day break. This consistent rhythm keeps students engaged while allowing sufficient time for rest and recuperation. As a result, year-round schooling can significantly reduce learning loss and ensure smoother transitions between academic sessions.

The Science Behind Learning Retention
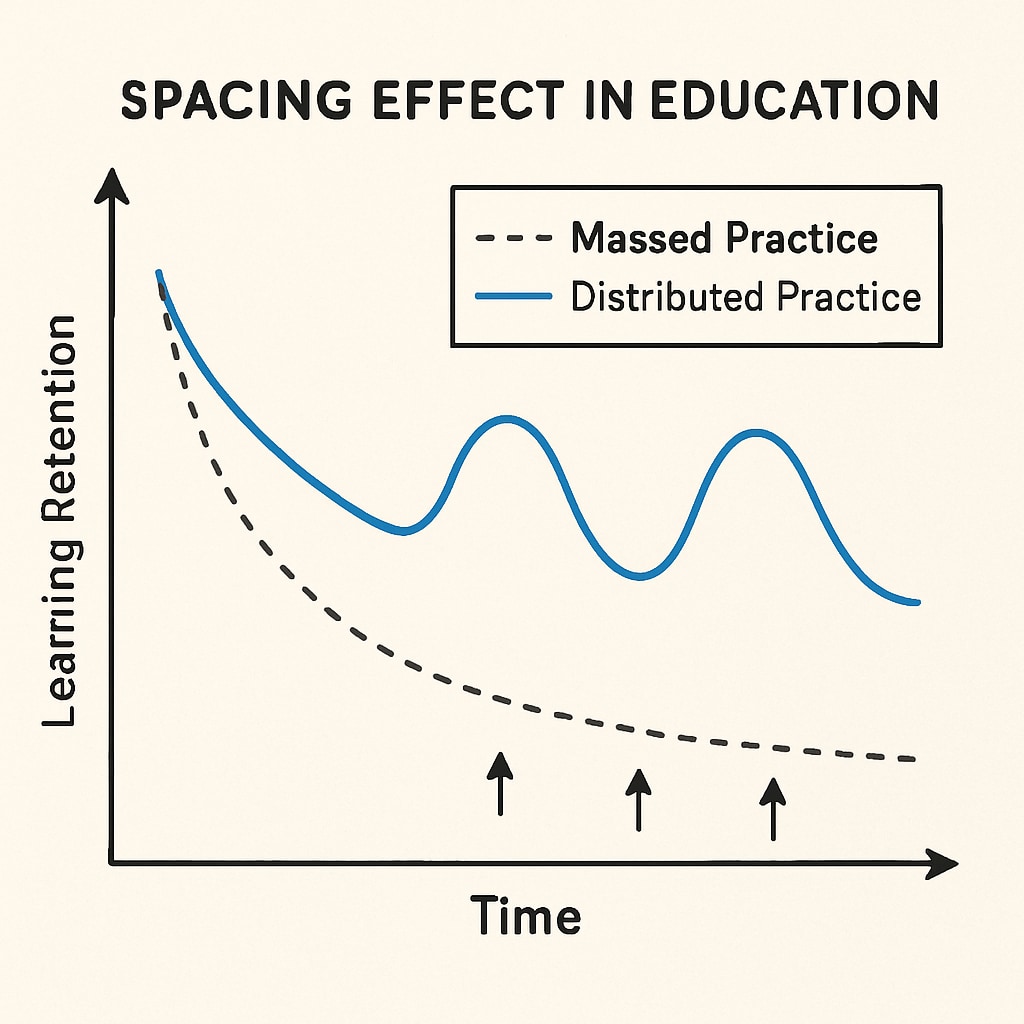
From a cognitive science perspective, spacing out learning and revision improves memory retention. Known as the “spacing effect,” this principle demonstrates that knowledge retention increases when learning is distributed over time, rather than crammed into condensed periods. Year-round schooling aligns perfectly with this principle, offering students the chance to revisit and reinforce concepts more frequently throughout the year.
Moreover, shorter breaks decrease the need for extensive review sessions at the start of each term, freeing up valuable instructional time. This approach not only bolsters academic outcomes but also reduces stress for students and educators alike.
Addressing Social and Practical Concerns
While the advantages of year-round schooling are evident, implementing this model requires addressing practical concerns. Families often plan vacations during summer breaks, and some parents worry about the impact of year-round schedules on work-life balance. Schools can mitigate these concerns by providing flexible schedules and aligning breaks with community needs.
Additionally, year-round schooling can reduce the strain on school infrastructure, spreading out occupancy and maintenance costs more evenly across the year. This model may also benefit students from disadvantaged backgrounds, who rely on school-provided meals and resources during the academic year.
As education reform continues to prioritize equity and accessibility, year-round schooling emerges as a promising solution to address diverse challenges in modern education.
Looking Ahead: The Future of School Calendars
Year-round schooling is not just a solution for learning retention—it represents a shift toward a more sustainable and student-centered education system. As more schools experiment with alternative calendars, data on student performance, well-being, and community impact will pave the way for widespread adoption.
For example, countries like Australia and Japan have already implemented year-round schedules with positive results, demonstrating the feasibility of this model on a larger scale. By leveraging insights from cognitive science and global practices, educators can design systems that prioritize long-term learning outcomes and adaptability.
Year-round schooling challenges the status quo, offering a practical and research-backed alternative to traditional calendars. With its potential to enhance learning retention, reduce stress, and foster equity, this model is undoubtedly worth exploring further.
Readability guidance: This article uses short paragraphs for clarity, includes lists for summarization, and maintains an active voice to ensure accessibility for a broad audience. Transition words and examples enhance the flow of ideas, while external links provide credibility and depth.


