The blended teaching cycle theory, a significant concept in educational theories that combines transmissive and facilitative teaching, has revolutionized the way educators design learning environments. This theory offers a unique approach to education by integrating different teaching methods in a cyclical structure.
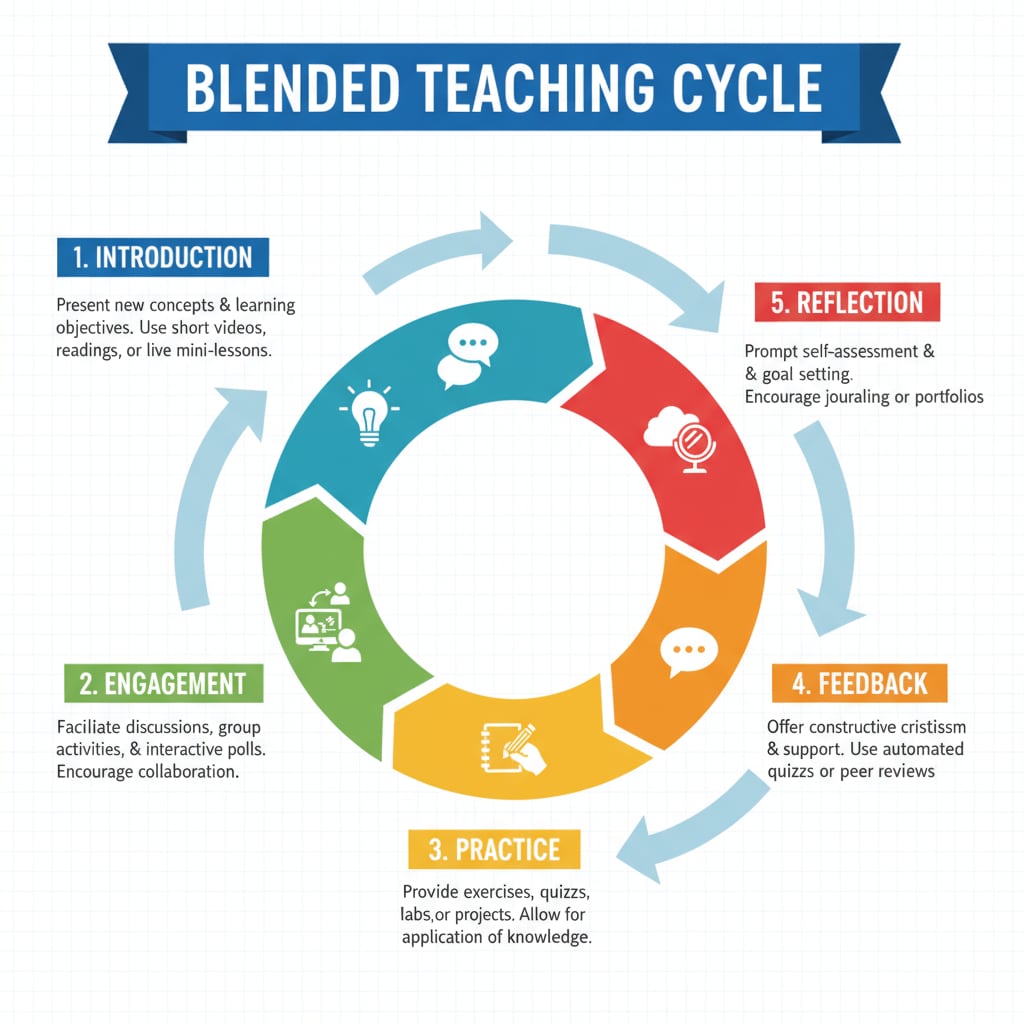
The Structure of the Blended Teaching Cycle
The blended teaching cycle consists of five key steps. First is the “Introduction” phase, where educators present new knowledge to students, similar to the transmissive teaching method. This provides a foundation for the learning process. Next is the “Engagement” step. Here, students actively interact with the new information, often through group discussions or hands-on activities, which is more in line with facilitative teaching.
Following engagement is the “Practice” stage. Students apply what they have learned in real – world or simulated scenarios. This helps them solidify their understanding. The “Feedback” step is crucial as educators provide constructive feedback to students, guiding them on areas for improvement. Finally, the “Reflection” phase allows students to think about their learning journey, identify what they have mastered and what needs further attention.
Theoretical Basis of the Blended Teaching Cycle
The blended teaching cycle draws on multiple educational theories. Behaviorist theories, for example, support the transmissive part of the cycle. In behaviorism, learning is seen as a response to stimuli, and the introduction of new knowledge can be considered a form of stimulus. On the other hand, constructivist theories underpin the facilitative aspects. Constructivism posits that learners build their own knowledge through active interaction with the environment.
Cognitive theories also play a role. They emphasize the importance of mental processes in learning. The feedback and reflection steps in the blended teaching cycle are in line with cognitive theories, as they encourage students to process and internalize their learning experiences. Educational Psychology on Wikipedia provides more in – depth understanding of these underlying theories.
Another important aspect is social learning theory. The engagement and practice steps, which often involve group work, are based on the idea that learning occurs through social interaction. By working together, students can learn from each other’s perspectives and experiences. Social Learning Theory on Britannica offers valuable insights into this concept.
Advantages of the Blended Teaching Cycle in K12 Education
In K12 education, the blended teaching cycle has several advantages. Firstly, it caters to different learning styles. Students who prefer direct instruction can benefit from the transmissive elements, while those who thrive in active learning environments can engage with the facilitative parts. This inclusivity ensures that more students can effectively learn.
Secondly, it enhances student engagement. The cycle’s structure encourages students to be actively involved in their learning process. Through group discussions, hands – on activities, and reflection, students are more likely to stay interested and motivated. Additionally, the feedback step helps students feel supported and guided, which boosts their confidence.
Disadvantages of the Blended Teaching Cycle in K12 Education
However, the blended teaching cycle also has some drawbacks. One challenge is the need for significant teacher training. Educators need to be proficient in both transmissive and facilitative teaching methods, as well as in managing the different steps of the cycle. This requires additional time and resources for professional development.
Another potential issue is the time management. The five – step cycle can be time – consuming, especially in a K12 classroom where there is a fixed curriculum to cover. Balancing the different steps while ensuring that all necessary content is taught can be a difficult task for teachers.
Readability guidance: The article uses short paragraphs to present clear ideas. Each section provides a summary of key points. The passive voice is kept to a minimum, and transition words like “firstly”, “secondly”, “however” are used to make the flow smooth. Lists are used to organize information for better readability.


