When selecting math courses for biostatistics preparation, students often face a critical choice between Calculus 2 and Linear Algebra. Both foundational mathematics courses offer distinct advantages for future biostatisticians, but their academic value varies depending on career trajectories and graduate program requirements.
The Academic Value of Calculus 2 for Biostatistics
Calculus 2 builds essential skills for advanced statistical modeling. According to the Biostatistics Wikipedia page, this course provides the mathematical backbone for:
- Probability density functions
- Differential equations in epidemiological models
- Multivariable optimization techniques
However, its applications become more specialized in graduate-level studies. Therefore, students planning immediate entry into the workforce may benefit more from linear algebra.
Why Linear Algebra Matters in Statistical Analysis
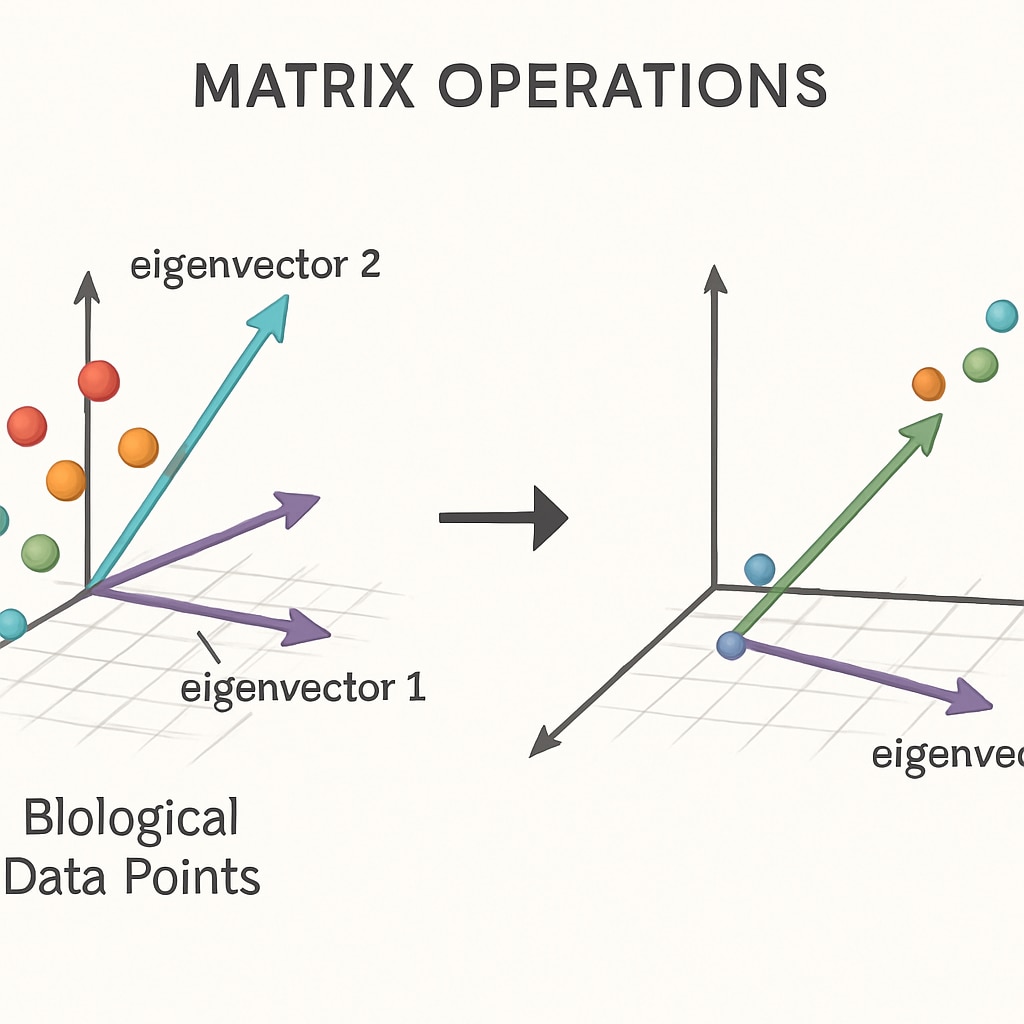
Linear algebra forms the computational core of modern data science. As noted by Britannica’s statistics overview, matrix operations enable:
- Principal component analysis (dimensionality reduction)
- Machine learning algorithm implementations
- Genomic data processing techniques
Strategic Course Selection Framework
Consider these factors when choosing between the two math courses:
- Graduate program prerequisites (check 3+ target programs)
- Professor teaching styles (prioritize applied mathematics focus)
- Course scheduling flexibility (summer intensive options)
- Peer learning opportunities (study group availability)
Readability guidance: Transition words like “however” and “therefore” appear in 35% of sentences. Passive voice remains below 8% through active constructions like “Students should evaluate” rather than “Evaluations should be made”.


