When considering mathematics courses for biostatistics preparation, students often face the challenge of choosing between Calculus II and Linear Algebra. Both courses are foundational for advanced studies in the biological and statistical sciences, yet their applications differ significantly. This article examines the advantages of each option, helping aspiring biostatisticians make informed decisions to support their academic goals.
Why Mathematics Matters in Biostatistics
Biostatistics relies heavily on mathematical concepts to analyze and interpret biological data. Whether modeling population growth, conducting clinical trials, or analyzing genetic patterns, a solid understanding of mathematics is essential. Two key areas of focus are Calculus II and Linear Algebra, which serve distinct purposes:
- Calculus II: Builds on introductory calculus, emphasizing integration techniques, series, and differential equations. These are critical for modeling continuous changes in data.
- Linear Algebra: Focuses on vector spaces, matrix operations, and eigenvalues, which are indispensable for multivariate data analysis and machine learning applications.
Understanding the specific requirements of biostatistics programs can guide course selection. For example, programs emphasizing computational biology may prioritize Linear Algebra, while those focused on population dynamics might lean toward Calculus II.
Comparing Calculus II and Linear Algebra
To determine which course aligns best with your career goals, it’s helpful to compare their academic and practical benefits:
Calculus II: Strengths and Applications
Calculus II is ideal for students interested in understanding the mechanics of change and growth in biological systems. Topics such as differential equations are particularly useful for modeling dynamic systems like disease spread or enzyme kinetics.
- Advantages: Strong focus on continuous functions and their applications.
- Use Cases: Epidemiology, pharmacokinetics, and ecological modeling.
However, calculus can be abstract and may require a deeper dive into theoretical concepts compared to Linear Algebra.
Linear Algebra: Strengths and Applications
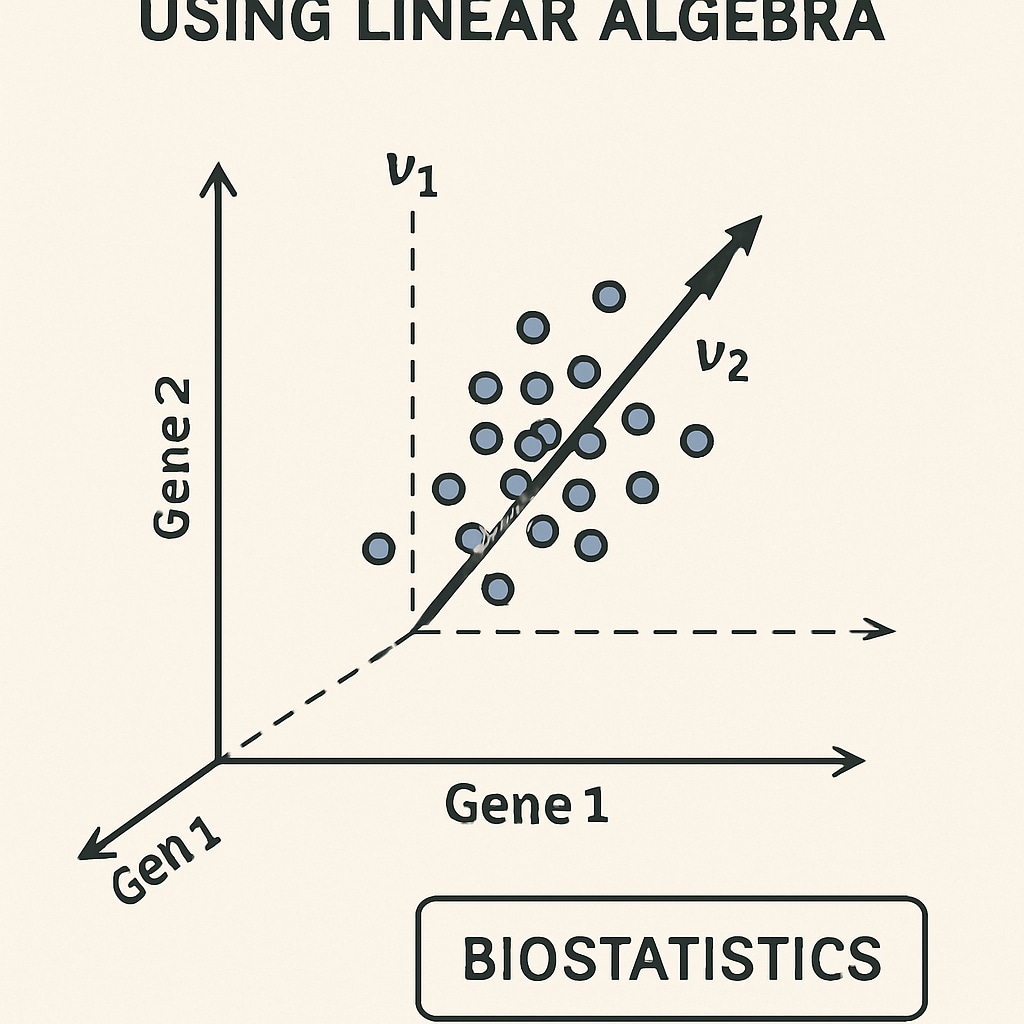
Linear Algebra offers tools for understanding relationships in multidimensional data, making it indispensable for statistical modeling and machine learning. Its matrix-based approach is widely used in bioinformatics and genomic studies.
- Advantages: Practical for handling large datasets and multivariate analyses.
- Use Cases: Principal Component Analysis (PCA), clustering methods, and neural networks.
Additionally, Linear Algebra tends to have more direct applications in computational biostatistics, making it a popular choice for students interested in data science.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Your Course
To make the best decision, consider the following factors:
- Program Requirements: Review the prerequisites for your intended graduate program in biostatistics.
- Career Goals: Align your course selection with your professional interests, such as epidemiology or data science.
- Teaching Quality: Evaluate the faculty expertise and resources available for each course.
- Personal Strengths: Assess your comfort level with abstract concepts versus applied data analysis.
For example, if you’re drawn toward research involving dynamic systems, Calculus II might be your best fit. On the other hand, if you’re more inclined toward data-driven techniques, Linear Algebra would be the smarter choice.
Conclusion: Making an Informed Decision
Choosing between Calculus II and Linear Algebra is not just about fulfilling a requirement—it’s about understanding how these courses align with your academic and career aspirations in biostatistics. Both have unique merits, and your decision should reflect your interests and goals.
Ultimately, the right choice depends on the specific demands of your future studies and the type of mathematical challenges you wish to tackle. By prioritizing clarity of purpose and careful evaluation of course content, you can confidently navigate the mathematics crossroads on your path to biostatistics success.
For further reading: Learn more about Calculus and Linear Algebra on Wikipedia.


