The blended teaching cycle theory, which combines transmissive and facilitative teaching methods, has become a significant concept in the field of education. This theory aims to create an effective learning environment through a five-step cyclic structure. Let’s delve into its details.
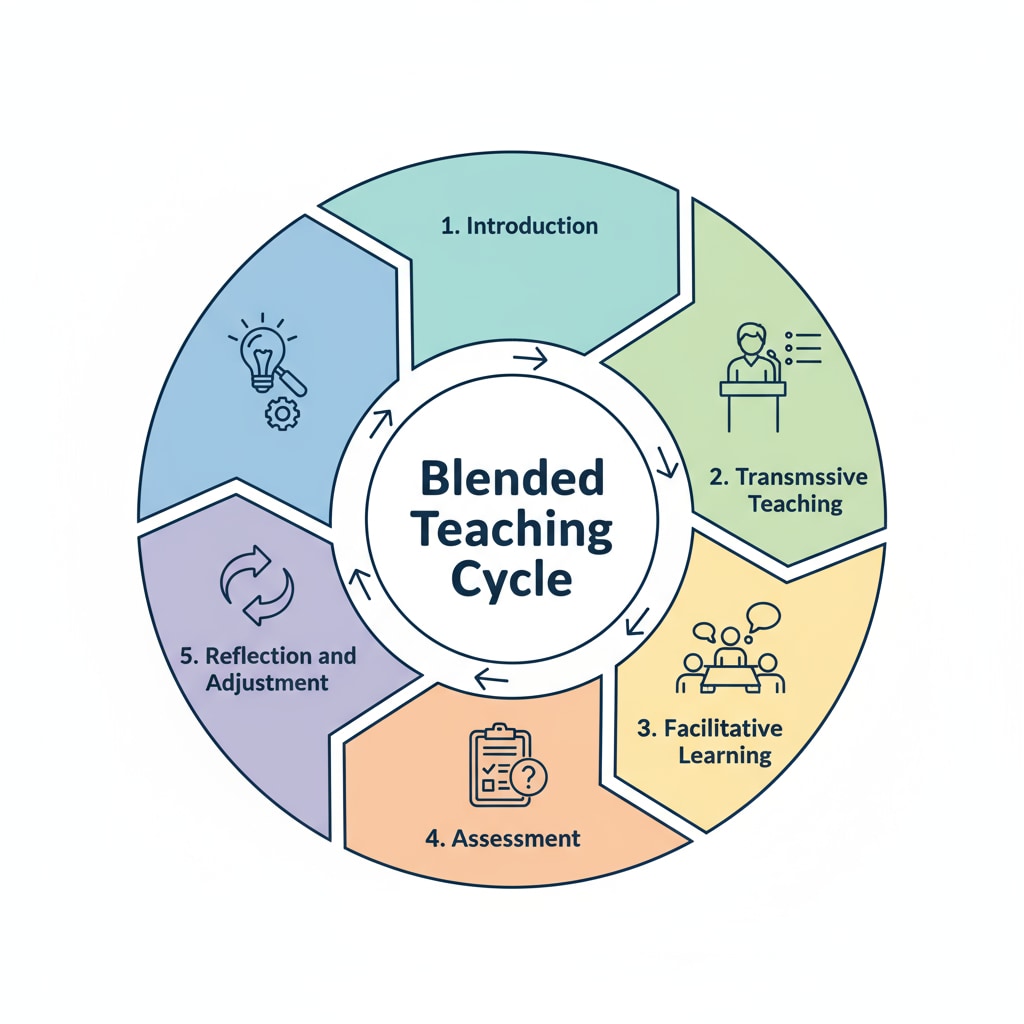
The Structure of the Blended Teaching Cycle
The blended teaching cycle consists of five key steps. First is the “Introduction” phase, where the teacher presents the learning objectives and provides the necessary background knowledge. This sets the stage for the learning process. Next is the “Transmissive Teaching” step. Here, the teacher imparts information, facts, and concepts in a more traditional way, ensuring students have a solid foundation.

After that comes the “Facilitative Learning” phase. In this step, students are encouraged to engage in activities such as group discussions, problem-solving, and hands-on projects. The teacher acts as a facilitator, guiding students to explore and discover knowledge on their own. Then is the “Assessment” stage, where the teacher evaluates students’ understanding and progress. This assessment can be in various forms, like quizzes, tests, or project evaluations. Finally, the “Reflection and Adjustment” step allows both the teacher and students to reflect on the learning process. Based on the assessment results, adjustments can be made to the teaching and learning strategies.
The Theoretical Basis of the Blended Teaching Cycle
The blended teaching cycle theory is grounded in several educational theories. One of the main bases is the constructivist theory. Constructivism posits that learners actively construct their own knowledge through experiences and interactions. In the blended teaching cycle, the facilitative learning phase aligns with this theory as students build their understanding through hands-on activities and discussions. Another important theory is the cognitive load theory. This theory emphasizes the importance of managing the cognitive load on students during learning. The transmissive teaching phase helps in presenting information in an organized manner, reducing the cognitive load on students initially.
Constructivism on Wikipedia provides more in-depth information on the constructivist theory. Also, Cognitive Load Theory on Britannica offers a detailed explanation of this theory.
The Advantages of the Blended Teaching Cycle in K12 Education
In K12 education, the blended teaching cycle has numerous advantages. Firstly, it caters to different learning styles. Some students may benefit from the structured transmissive teaching, while others thrive in the facilitative learning environment. For example, visual learners may enjoy the hands-on projects in the facilitative phase, while auditory learners may appreciate the transmissive teaching where information is clearly explained. Secondly, it promotes active learning. The facilitative learning step encourages students to take an active role in their learning, enhancing their critical thinking and problem-solving skills. In addition, the continuous assessment and reflection steps allow for timely feedback. Teachers can adjust their teaching methods, and students can improve their learning strategies.
The Disadvantages of the Blended Teaching Cycle in K12 Education
However, the blended teaching cycle also has some drawbacks. One issue is the time management. Implementing all five steps requires a significant amount of time. Teachers may find it challenging to cover all the content within the given time frame. Another problem is the resource requirement. The facilitative learning phase often needs additional resources such as materials for hands-on projects and space for group activities. Moreover, not all teachers may be well-trained in both transmissive and facilitative teaching methods. This could lead to an uneven implementation of the blended teaching cycle.
Readability guidance: By using short paragraphs and lists, we have presented the key points clearly. Each H2 section has a list of related aspects. We have also controlled the proportion of passive voice and long sentences, and added transitional words like “firstly”, “secondly”, “however” to enhance the flow of the article.


