Understanding education spending in the United States is pivotal for analyzing the nation’s commitment to its K-12 education system. Whether you’re working on an academic paper, conducting policy research, or exploring trends in education funding, accessing accurate and reliable data is essential. The key lies in identifying authoritative data sources and employing effective research methods. In this article, we will guide you through the primary sources for U.S. K-12 education spending data, explain how to access these datasets, and offer tips for integrating this information into your academic work.
Key Sources for U.S. Education Spending Data
Education spending in the United States is tracked and reported at multiple levels: federal, state, and local. Each level provides valuable insights into how funds are allocated, distributed, and utilized. Below are the most reliable sources for accessing this data:
- U.S. Department of Education (ED): The National Center for Education Statistics (NCES), part of the ED, provides comprehensive data on education spending. The NCES’s “Digest of Education Statistics” and the annual “Condition of Education” report are particularly valuable resources. Visit NCES here.
- Census Bureau: The Census Bureau offers detailed data on public education finances through its Annual Survey of School System Finances. This dataset includes information on revenue sources, spending categories, and per-pupil expenditures. Explore the Census Bureau’s data.
- State Education Departments: Each state maintains its own education department, which often publishes reports on school funding, budget allocations, and financial audits. For example, California’s Department of Education provides a “School Fiscal Services” section on its website.
- Local School Districts: Many school districts publish their budgets and financial reports online. These documents can provide granular details about spending priorities and challenges at the local level.
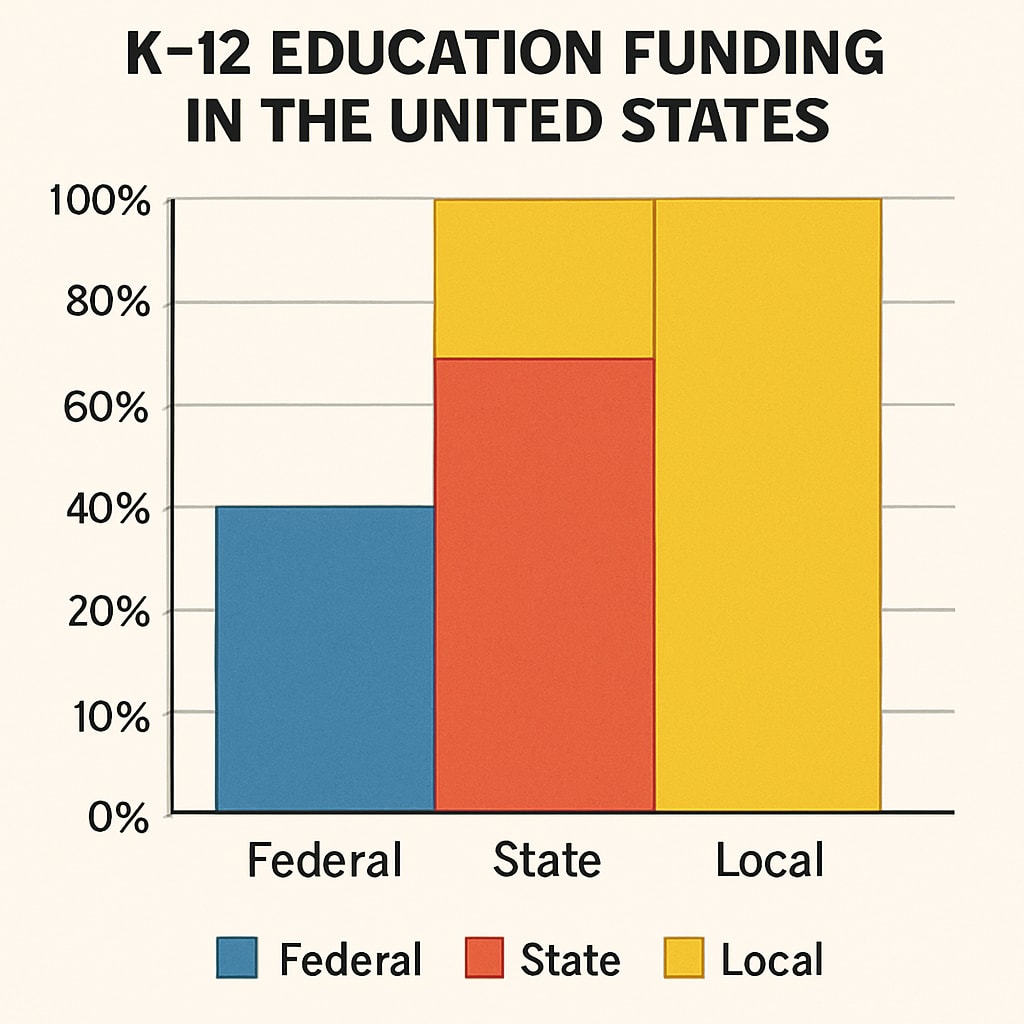
How to Access and Analyze Education Spending Data
Accessing data is just the beginning. To make the most of the available information, you’ll need to know how to analyze and interpret it effectively. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Define Your Research Question: Before diving into the data, clarify what you want to explore—for example, trends in per-student spending or disparities in funding between urban and rural districts.
- Choose the Right Dataset: Based on your research question, select the dataset that best matches your needs. For broad trends, NCES or Census Bureau data is ideal. For localized insights, state or district data may be more appropriate.
- Use Data Analysis Tools: Microsoft Excel, Google Sheets, and statistical software like SPSS or R are invaluable for organizing and analyzing large datasets. Create visualizations, such as charts and graphs, to identify trends and outliers.
- Cross-Reference Data: To ensure accuracy, compare data from multiple sources. For example, verify NCES numbers with state education department reports.
- Connect Findings to Academic Literature: Relate your analysis to existing research by citing peer-reviewed studies on education funding and its impact on student outcomes.

Tips for Incorporating Education Spending Data into Academic Papers
Once you’ve gathered and analyzed the data, the next step is to integrate it into your academic work. Here are some tips to enhance the quality of your writing:
- Use Clear Visuals: Incorporate charts, graphs, and tables to present data effectively. Ensure visuals are labeled and referenced in the text.
- Cite Sources Properly: Follow your institution’s preferred citation style (APA, MLA, Chicago, etc.) to credit your data sources.
- Provide Context: Explain the significance of the data. For example, discuss how funding disparities may affect student performance.
- Stay Objective: Use data to support your arguments without bias. Avoid cherry-picking statistics to fit a preconceived narrative.
By following these guidelines, you can create a well-researched and impactful academic paper that contributes to the broader understanding of education funding and policy.
Conclusion: Understanding and analyzing education spending data is a critical skill for researchers and students exploring policy and equity issues in U.S. K-12 education. By leveraging reliable sources like the NCES, Census Bureau, and state education departments, and applying effective research methods, you can uncover valuable insights that enhance your work. Whether you’re writing a term paper, preparing a presentation, or conducting a policy analysis, these tools and strategies will help you achieve your goals.


